Face veneer refers to the thin, decorative layer of high-quality wood applied to the surface of a product to enhance its appearance, while core veneer serves as the underlying layers that provide structural strength and stability. Understanding the difference between face veneer and core veneer helps you choose the right wood product for both aesthetic appeal and durability.
Table of Comparison
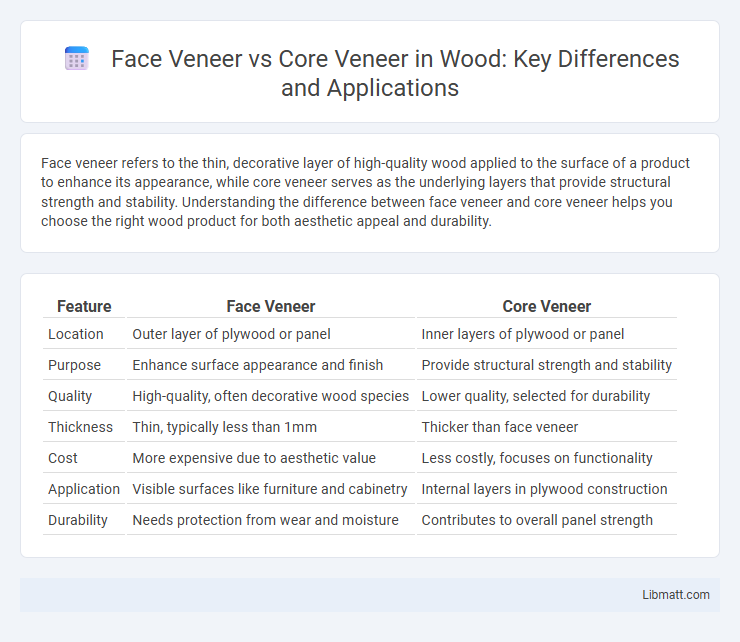
| Feature | Face Veneer | Core Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Outer layer of plywood or panel | Inner layers of plywood or panel |
| Purpose | Enhance surface appearance and finish | Provide structural strength and stability |
| Quality | High-quality, often decorative wood species | Lower quality, selected for durability |
| Thickness | Thin, typically less than 1mm | Thicker than face veneer |
| Cost | More expensive due to aesthetic value | Less costly, focuses on functionality |
| Application | Visible surfaces like furniture and cabinetry | Internal layers in plywood construction |
| Durability | Needs protection from wear and moisture | Contributes to overall panel strength |
Introduction to Face Veneer and Core Veneer
Face veneer is the outermost layer of wood applied to furniture or panels, prized for its aesthetic appeal, grain pattern, and finish quality. Core veneer forms the inner layers beneath the face veneer, providing structural stability and strength to the plywood or laminated product. High-quality face veneers are selected for appearance, while core veneers are chosen for durability and dimensional stability.
Definition and Functions of Face Veneer
Face veneer is the thin, decorative outer layer of wood applied to the surface of plywood or engineered wood products to enhance aesthetic appeal and provide a smooth finish. It primarily functions to showcase attractive grain patterns and improve the visual quality of furniture, cabinetry, or paneling. Unlike core veneer, which offers structural support and stability, face veneer is crucial for delivering your desired look and texture on wood surfaces.
Definition and Roles of Core Veneer
Core veneer refers to the inner layers of wood veneer used as the foundation in plywood manufacturing, providing structural stability and strength. Unlike face veneer, which is the outer decorative layer showcasing grain and aesthetics, core veneer primarily contributes to the panel's durability, rigidity, and resistance to warping. This essential component ensures the plywood's overall integrity, supporting applications in construction, furniture, and cabinetry.
Key Differences Between Face Veneer and Core Veneer
Face veneer consists of a thin, high-quality layer of wood applied to the visible surface of furniture or panels, emphasizing appearance with distinct grain patterns and smooth finishes. Core veneer forms the thicker, structural layer beneath the face veneer, providing stability and strength to the overall construction. Understanding the key differences between face veneer and core veneer helps you select materials that balance aesthetic appeal with durability for your woodworking projects.
Material Selection for Face vs Core Veneer
Face veneer is typically made from high-quality, visually appealing wood species chosen for their grain patterns, color, and finish potential, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of your final product. Core veneer, conversely, prioritizes structural stability and often uses lower-grade or engineered wood materials to provide strength and support without compromising durability. Optimal material selection balances the decorative qualities of face veneer with the functional properties of core veneer to ensure both beauty and performance.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Face veneer undergoes a delicate slicing or peeling process from high-quality logs to capture intricate grain patterns, while core veneer is produced by slicing thicker wood layers primarily for structural stability. The face veneer manufacturing emphasizes preserving aesthetic appeal, often involving meticulous drying and grading, whereas core veneer manufacturing focuses on uniform thickness and strength to support plywood or laminated products. Differences in processing techniques directly influence the quality and application suitability of each veneer type in wood composite manufacturing.
Impact on Plywood Quality and Appearance
Face veneer significantly influences plywood quality and appearance by providing the visible surface layer, characterized by its grain pattern, color, and smoothness, which determines the overall aesthetic appeal. Core veneer, while not visible, plays a crucial role in structural integrity, affecting plywood strength, weight, and stability. Selecting high-quality face veneer ensures an attractive finish, whereas a well-constructed core veneer contributes to the durability and resistance of Your plywood product.
Common Applications of Face and Core Veneer
Face veneers are commonly applied in high-quality furniture, cabinetry, and decorative paneling where aesthetic appeal is paramount due to their thin, fine-grained surface layer. Core veneers serve primarily structural purposes in plywood and engineered wood products, providing strength and stability without emphasis on appearance. The combination of face and core veneers enables the production of durable yet visually attractive wood products used extensively in construction and interior design.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Veneer Type
Face veneer offers high-quality aesthetics with natural wood grain visible on the surface, making it ideal for decorative furniture, but it tends to be more expensive and less durable compared to core veneer. Core veneer provides structural stability and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for engineered wood products, yet it lacks the refined appearance of face veneers. Your project choice depends on whether visual appeal or strength and budget are the primary concerns.
Tips for Choosing the Right Veneer for Your Project
Select face veneer when surface appearance and intricate wood grain patterns are the primary focus, as it provides a high-quality finish for visible surfaces. Opt for core veneer to ensure structural stability and strength in plywood or laminated panels, especially when durability is crucial. Consider the project requirements carefully, prioritizing face veneer for aesthetic appeal and core veneer for foundational support.
Face veneer vs core veneer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com