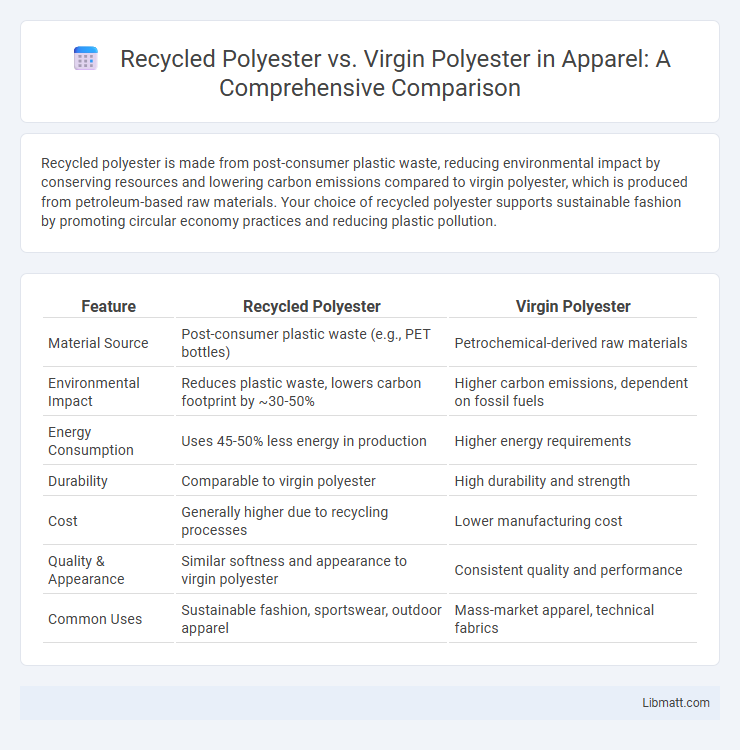
Recycled polyester is made from post-consumer plastic waste, reducing environmental impact by conserving resources and lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin polyester, which is produced from petroleum-based raw materials. Your choice of recycled polyester supports sustainable fashion by promoting circular economy practices and reducing plastic pollution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Polyester | Virgin Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer plastic waste (e.g., PET bottles) | Petrochemical-derived raw materials |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces plastic waste, lowers carbon footprint by ~30-50% | Higher carbon emissions, dependent on fossil fuels |
| Energy Consumption | Uses 45-50% less energy in production | Higher energy requirements |
| Durability | Comparable to virgin polyester | High durability and strength |
| Cost | Generally higher due to recycling processes | Lower manufacturing cost |
| Quality & Appearance | Similar softness and appearance to virgin polyester | Consistent quality and performance |
| Common Uses | Sustainable fashion, sportswear, outdoor apparel | Mass-market apparel, technical fabrics |
Introduction to Polyester: Recycled vs Virgin
Recycled polyester is made from post-consumer plastic bottles or textile waste, reducing environmental impact by lowering energy use and plastic pollution, while virgin polyester is produced from petroleum-based raw materials through an energy-intensive process. This difference results in recycled polyester contributing significantly less to carbon emissions and landfill waste compared to virgin polyester. Understanding these distinctions helps you make sustainable choices in fabric selection, balancing quality and environmental responsibility.
What Is Virgin Polyester?
Virgin polyester is a synthetic fiber made from newly produced petrochemicals, typically derived from petroleum, without any prior use or recycling. It offers consistent quality and strength, making it a preferred choice in many textiles but contributes more to environmental pollution due to higher energy consumption and carbon emissions during production. Choosing recycled polyester can reduce your carbon footprint by reusing plastic waste and lowering dependency on fossil fuels.
What Is Recycled Polyester?
Recycled polyester is a sustainable fabric made from reclaimed plastic bottles and textile waste, reducing reliance on petroleum-based virgin polyester. This eco-friendly alternative retains the durability and versatility of virgin polyester while significantly lowering environmental impact by cutting down on greenhouse gas emissions and landfill waste. Your choice of recycled polyester supports a circular economy and promotes resource conservation in the fashion and textile industries.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Recycled polyester is made by processing post-consumer plastic waste, such as PET bottles, through cleaning, shredding, and melting into new fibers, significantly reducing raw material consumption and energy use. Virgin polyester is produced from petrochemical raw materials, primarily derived from non-renewable fossil fuels, involving complex chemical synthesis and polymerization processes. The recycled process lowers greenhouse gas emissions by up to 75% compared to traditional virgin polyester manufacturing, making it a more sustainable choice in textile production.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Polyester
Recycled polyester significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions and conserving petroleum resources compared to virgin polyester, which relies on new fossil fuels and produces higher greenhouse gas emissions. The production of recycled polyester consumes less water and energy, mitigating pollution and waste generation associated with virgin polyester manufacturing. Utilizing recycled polyester supports circular economy principles by repurposing plastic waste, thereby decreasing landfill accumulation and ocean pollution linked to virgin polyester production.
Energy and Resource Consumption
Recycled polyester uses approximately 59% less energy and 32% less water compared to virgin polyester, significantly reducing environmental impact during production. It diverts plastic waste from landfills and oceans, conserving petroleum resources otherwise required for virgin polyester manufacturing. Adoption of recycled polyester supports sustainable resource management and lowers greenhouse gas emissions linked to energy-intensive virgin fiber production.
Performance and Quality Differences
Recycled polyester often matches virgin polyester in durability, moisture-wicking, and resistance to shrinking or stretching, making it a strong contender for performance-oriented applications. Some minor variations in fiber uniformity can occur, but technological advancements have minimized these differences, ensuring recycled polyester maintains high quality standards. Your choice between recycled and virgin polyester can confidently prioritize environmental benefits without compromising on fabric performance.
Cost Comparison: Which Is More Economical?
Recycled polyester generally presents higher production costs due to energy-intensive processes and quality control measures compared to virgin polyester, which benefits from established manufacturing efficiencies and lower raw material expenses. Despite the initial cost difference, recycled polyester can offer long-term economic advantages through energy savings and reduced environmental compliance costs. Market demand and scale production play critical roles in narrowing the cost gap between recycled and virgin polyester over time.
Challenges and Limitations
Recycled polyester faces challenges such as lower durability and potential contamination from mixed materials, which can affect the quality and performance compared to virgin polyester. Virgin polyester offers consistent fiber strength and purity, but its production relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to environmental concerns. Your choice between the two depends on balancing sustainability goals with specific fabric requirements and performance standards.
Future Trends in Polyester Production
Future trends in polyester production emphasize increasing the use of recycled polyester due to its lower environmental impact and reduced reliance on fossil fuels compared to virgin polyester. Innovations in chemical recycling technologies aim to enhance the quality and scalability of recycled polyester, making it more competitive with virgin polyester in performance and cost. Your choice of recycled polyester supports a growing movement toward sustainable textile manufacturing driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressures.
recycled polyester vs virgin polyester Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com