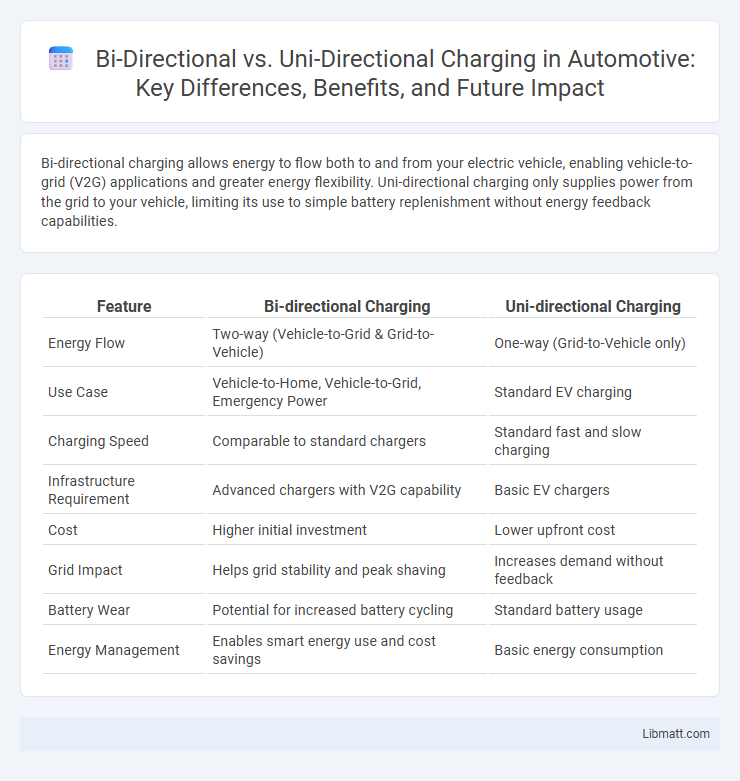
Bi-directional charging allows energy to flow both to and from your electric vehicle, enabling vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications and greater energy flexibility. Uni-directional charging only supplies power from the grid to your vehicle, limiting its use to simple battery replenishment without energy feedback capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bi-directional Charging | Uni-directional Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Flow | Two-way (Vehicle-to-Grid & Grid-to-Vehicle) | One-way (Grid-to-Vehicle only) |
| Use Case | Vehicle-to-Home, Vehicle-to-Grid, Emergency Power | Standard EV charging |
| Charging Speed | Comparable to standard chargers | Standard fast and slow charging |
| Infrastructure Requirement | Advanced chargers with V2G capability | Basic EV chargers |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Grid Impact | Helps grid stability and peak shaving | Increases demand without feedback |
| Battery Wear | Potential for increased battery cycling | Standard battery usage |
| Energy Management | Enables smart energy use and cost savings | Basic energy consumption |
Introduction to EV Charging Technologies
Bi-directional charging enables electric vehicles (EVs) to both receive energy from the grid and supply stored energy back, facilitating vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-home (V2H) applications. Uni-directional charging systems allow energy flow only from the grid to the EV battery, limiting the EV's role to a simple energy consumer. The advancement of bi-directional charging technologies enhances grid stability and maximizes renewable energy utilization, distinguishing it from traditional uni-directional EV chargers.
Defining Bi-directional and Uni-directional Charging
Bi-directional charging refers to the technology that allows electric vehicles (EVs) to not only draw power from the grid but also supply energy back to it, enabling vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-home (V2H) applications. Uni-directional charging only permits energy flow from the grid to the EV, limiting its functionality to charging without feeding energy back. Understanding these charging types is essential for optimizing your EV energy management and leveraging potential cost savings or grid support benefits.
How Bi-directional Charging Works
Bi-directional charging enables electric vehicles (EVs) to both draw power from and feed electricity back into the grid, utilizing vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. This process involves communication between the EV's battery management system and the grid operator to regulate energy flow, optimize load balancing, and support grid stability during peak demand or outages. Unlike uni-directional charging that solely charges the EV, bi-directional charging transforms the EV into a mobile energy resource, promoting renewable integration and cost savings through energy arbitrage.
How Uni-directional Charging Works
Uni-directional charging transfers electrical energy from the power grid to an electric vehicle's battery, enabling efficient energy storage without returning power to the grid. This method relies on a one-way flow of electricity managed by the vehicle's onboard charger and charging station. It ensures seamless integration with existing infrastructure while providing reliable battery replenishment for electric mobility.
Key Benefits of Bi-directional Charging
Bi-directional charging enables electric vehicles (EVs) to both charge from the grid and supply energy back to it, enhancing grid stability and supporting renewable energy integration. Your EV can act as a mobile energy storage unit, providing backup power during outages and reducing electricity costs by participating in demand response programs. This technology promotes energy flexibility and sustainability, making it a key innovation compared to traditional uni-directional charging systems.
Advantages of Uni-directional Charging
Uni-directional charging offers cost-effective and simpler infrastructure, making it ideal for widespread adoption in electric vehicle (EV) charging stations. It ensures efficient energy transfer directly from the grid to the vehicle, enhancing battery longevity by minimizing complex power flows. Its straightforward design reduces installation and maintenance expenses, providing a reliable solution for everyday EV users.
Limitations of Each Charging Method
Bi-directional charging faces limitations such as higher infrastructure costs, complex grid integration, and potential battery degradation due to frequent energy flow reversals. Uni-directional charging is limited by its inability to supply stored energy back to the grid or other devices, reducing its role in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications and energy management. Both methods require advancements in technology and standards to optimize efficiency and battery lifespan within electric vehicle ecosystems.
Use Cases: Bi-directional vs Uni-directional
Uni-directional charging is ideal for straightforward electric vehicle (EV) charging scenarios where energy flows from the grid to the vehicle, supporting daily commuting and long-distance travel needs. Bi-directional charging enables vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications, allowing your EV to supply energy back to the grid during peak demand, enhance grid stability, and provide backup power in emergencies. Use cases for bi-directional charging also include load balancing in renewable energy systems and participation in energy markets, offering greater flexibility and financial benefits compared to uni-directional setups.
Impact on Energy Grids and Sustainability
Bi-directional charging enables electric vehicles (EVs) to not only draw power from the grid but also feed stored energy back, enhancing grid stability and reducing peak load stress. This technology supports renewable integration by storing excess solar or wind energy and distributing it during high demand, thereby advancing grid sustainability. In contrast, uni-directional charging solely consumes energy, limiting its contribution to grid management and sustainable energy utilization.
Future Trends in EV Charging Solutions
Bi-directional charging technology enables electric vehicles (EVs) to both draw energy from and supply power back to the grid, enhancing grid stability and enabling vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications, while uni-directional charging only allows energy flow from the grid to the vehicle. Future trends in EV charging solutions emphasize integrating bi-directional capabilities to support renewable energy sources, reduce grid congestion, and enable energy trading. Advancements in smart grid infrastructure and increased adoption of V2G-ready vehicles will drive the proliferation of bi-directional charging, making it a cornerstone of sustainable and resilient energy systems.
Bi-directional charging vs Uni-directional charging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com