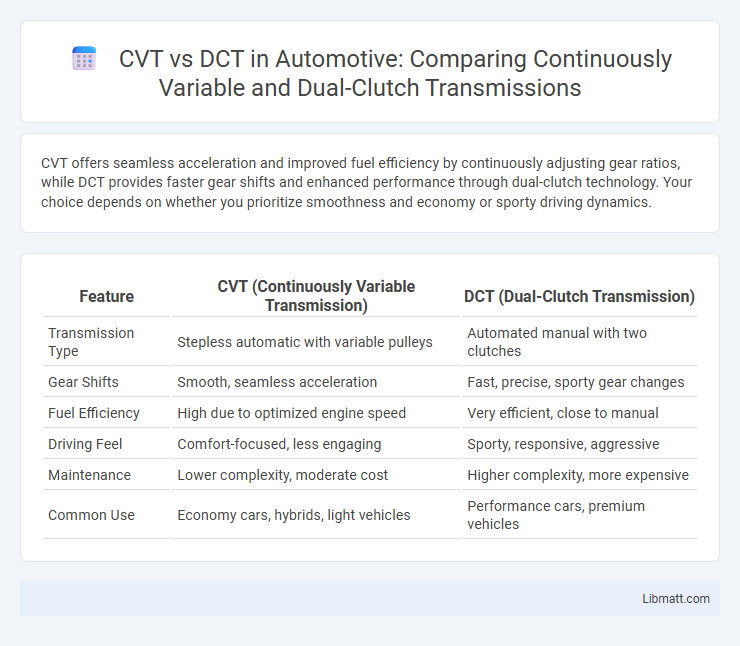
CVT offers seamless acceleration and improved fuel efficiency by continuously adjusting gear ratios, while DCT provides faster gear shifts and enhanced performance through dual-clutch technology. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize smoothness and economy or sporty driving dynamics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) | DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Type | Stepless automatic with variable pulleys | Automated manual with two clutches |
| Gear Shifts | Smooth, seamless acceleration | Fast, precise, sporty gear changes |
| Fuel Efficiency | High due to optimized engine speed | Very efficient, close to manual |
| Driving Feel | Comfort-focused, less engaging | Sporty, responsive, aggressive |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity, moderate cost | Higher complexity, more expensive |
| Common Use | Economy cars, hybrids, light vehicles | Performance cars, premium vehicles |
Introduction to CVT and DCT Transmissions
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) uses a system of belts and pulleys to provide seamless acceleration by allowing an infinite number of gear ratios, optimizing fuel efficiency and smooth driving. Dual Clutch Transmission (DCT) employs two separate clutches for odd and even gears, enabling rapid and precise gear shifts that enhance performance and acceleration. Both transmissions aim to improve driving dynamics but utilize fundamentally different mechanisms tailored for efficiency or sportiness respectively.
How CVT Works: Mechanism and Features
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) operates using a belt and pulley system that adjusts seamlessly to provide an infinite range of gear ratios, optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency. Unlike traditional transmissions, CVT eliminates gear shifts by varying the pulley diameters, creating a smooth driving experience without interruption. Key features include adaptive ratio adjustments for various driving conditions and improved torque delivery, enhancing overall vehicle efficiency and reducing mechanical complexity.
How DCT Works: Mechanism and Features
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) operate using two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling rapid and seamless gear shifts without interrupting torque delivery. The first clutch controls 1st, 3rd, and 5th gears, while the second handles 2nd, 4th, and 6th gears, allowing pre-selection of the next gear to minimize shift time. This mechanism provides quick response, enhanced fuel efficiency, and sporty driving dynamics compared to continuously variable transmissions (CVT), which use a belt-driven system for smooth but less direct power delivery.
Performance Comparison: CVT vs DCT
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) offers smooth acceleration and improved fuel efficiency due to its seamless gear ratio changes, making it ideal for urban driving and consistent power delivery. DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) excels in performance with quicker gear shifts and higher responsiveness, providing a sportier driving experience and better handling at high speeds. Your choice between CVT and DCT can impact vehicle performance significantly, depending on whether you prioritize fuel economy or dynamic driving characteristics.
Fuel Efficiency: Which Transmission Wins?
CVT transmissions generally offer superior fuel efficiency by providing seamless gear ratios that keep your engine operating at its optimal RPM. DCT systems, while delivering quicker and more responsive shifts, often result in slightly higher fuel consumption due to fixed gear steps and mechanical complexity. For drivers prioritizing fuel economy, a CVT is typically the more efficient transmission choice.
Driving Experience and Responsiveness
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) offers a smooth and seamless driving experience by eliminating gear shifts, which can feel more comfortable during city driving but may lack the sporty responsiveness you desire. DCT (Dual Clutch Transmission) provides rapid, precise gear changes that enhance driving responsiveness and deliver a sportier, more engaging feel, ideal for performance enthusiasts. Your choice between CVT and DCT will impact how directly you connect with the vehicle's power and how dynamically the car responds to acceleration.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
CVT transmissions require regular fluid changes to maintain belt and pulley integrity, with potential for belt wear leading to costly repairs if neglected. DCT systems typically involve dual clutches that may demand periodic fluid replacements and occasional clutch pack servicing, but generally offer robust performance under high-stress conditions. Your choice between CVT and DCT should account for these maintenance schedules and the reliability history associated with each transmission type.
Cost Differences: Initial and Long-term Expenses
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) typically have lower initial costs compared to Dual Clutch Transmissions (DCT) due to simpler design and fewer moving parts. However, CVTs may incur higher long-term expenses related to belt or chain replacement and specialized maintenance. In contrast, DCTs often demand more expensive initial investment but tend to offer better durability and lower maintenance costs over time.
Best Use Cases: CVT vs DCT in Different Vehicles
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) excel in fuel-efficient compact cars and hybrids due to their smooth acceleration and infinite gear ratios, optimizing city and highway driving. Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCT) deliver lightning-fast gear shifts and enhanced performance, making them ideal for sports cars and high-performance vehicles demanding precise power delivery. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize seamless efficiency or sporty responsiveness in your driving experience.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Transmission for Your Needs
Choosing between CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) and DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) depends on your driving preferences and vehicle type. CVTs provide seamless acceleration and improved fuel efficiency, ideal for city driving and comfort-focused users. DCTs offer faster gear shifts and enhanced sportiness, better suited for performance vehicles and drivers seeking a dynamic driving experience.
CVT vs DCT Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com