Belt drives offer quieter operation, lower maintenance, and smoother power transmission, making them ideal for applications requiring reduced noise and minimal lubrication. Chain drives provide higher torque capacity and durability in harsh environments, ensuring your machinery performs reliably under heavy loads and demanding conditions.
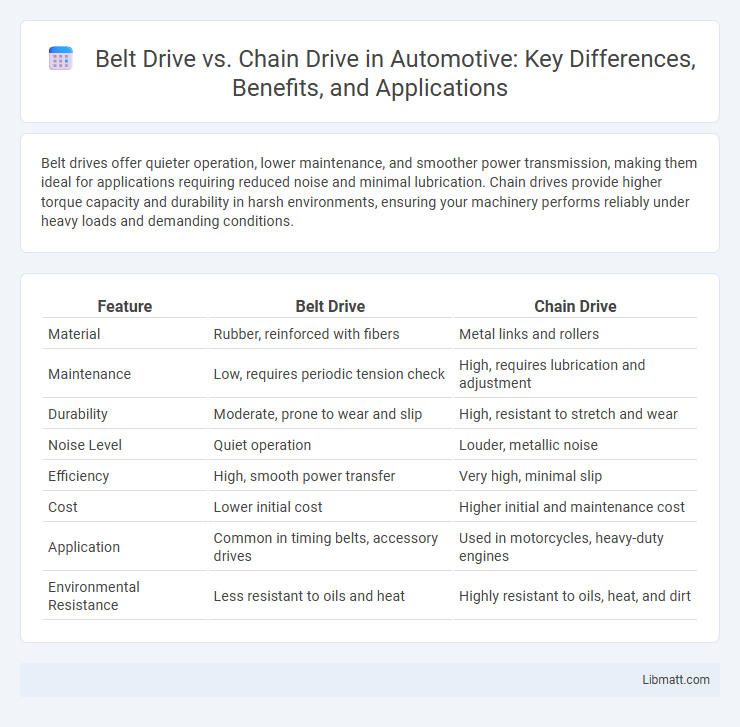
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Belt Drive | Chain Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Rubber, reinforced with fibers | Metal links and rollers |
| Maintenance | Low, requires periodic tension check | High, requires lubrication and adjustment |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear and slip | High, resistant to stretch and wear |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Louder, metallic noise |
| Efficiency | High, smooth power transfer | Very high, minimal slip |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost |
| Application | Common in timing belts, accessory drives | Used in motorcycles, heavy-duty engines |
| Environmental Resistance | Less resistant to oils and heat | Highly resistant to oils, heat, and dirt |
Introduction to Belt Drive and Chain Drive
Belt drive systems utilize flexible belts made of rubber or synthetic materials to transfer power between pulleys, offering quieter operation and lower maintenance compared to chain drives. Chain drives consist of metal links interlocked in a loop, providing precise and durable power transmission ideal for high-torque applications. Both drive types are essential in mechanical systems, with belt drives favored for smooth, low-noise performance and chain drives preferred for strength and reliability.
Key Differences Between Belt Drive and Chain Drive
Belt drives use a flexible belt made of rubber or synthetic materials to transfer power, offering quieter and smoother operation with less maintenance compared to chain drives. Chain drives rely on metal links for durability and high torque transmission, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications but requiring regular lubrication and adjustment. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right drive system for your vehicle or machinery based on performance needs and maintenance preferences.
How Belt Drive Systems Work
Belt drive systems operate by transferring rotational motion through a flexible belt that connects two or more pulleys, creating smooth and quiet power transmission. The belt's material, often reinforced rubber or polyurethane, provides durability and slip resistance, ensuring efficient energy transfer and reduced maintenance compared to chain drives. You benefit from decreased noise levels and minimal lubrication needs, making belt drives ideal for applications requiring clean and low-maintenance operation.
How Chain Drive Systems Operate
Chain drive systems operate by transferring power through a series of interlocking metal links that run over sprockets, creating a direct mechanical connection between the driving and driven components. This design offers high torque transmission efficiency and durability under heavy loads, making chain drives suitable for motorcycles, bicycles, and industrial machinery. Your choice of a chain drive system ensures consistent power delivery with minimal slip, though it requires regular maintenance such as lubrication and tension adjustment to optimize performance and longevity.
Advantages of Belt Drive
Belt drive systems offer quieter operation and require less maintenance compared to chain drives, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction is critical. They provide smoother power transmission with reduced vibration and slippage, enhancing overall efficiency and longevity. Belt drives also resist corrosion better and operate cleanly without the need for constant lubrication, which improves durability and reduces operational costs.
Advantages of Chain Drive
Chain drive systems offer superior power transmission efficiency compared to belt drives, making them ideal for high-torque applications such as motorcycles and industrial machinery. They provide precise and reliable synchronization between connected components due to minimal slip, enhancing performance consistency in timing and speed-critical operations. Chain drives also exhibit greater durability and resistance to high temperatures and harsh environments, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance frequency.
Disadvantages of Belt Drive
Belt drives can suffer from slippage, leading to reduced efficiency and inconsistent power transmission compared to chain drives. They typically have lower torque capacity, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications where high load handling is required. Your machinery may also experience belt wear and stretching over time, necessitating more frequent replacements and adjustments.
Disadvantages of Chain Drive
Chain drives require regular maintenance such as lubrication and tension adjustments to prevent wear and avoid breakage, which can be time-consuming. They tend to produce more noise and vibration compared to belt drives, impacting ride comfort and quiet operation. Your equipment may experience faster wear of sprockets and chains, leading to higher replacement costs and reduced overall efficiency.
Applications: Where to Use Each System
Belt drive systems excel in applications requiring smooth, quiet operation and low maintenance, such as HVAC units, automotive accessory drives, and treadmill motors. Chain drives are preferred in heavy-duty environments demanding high torque transmission and durability, including motorcycles, bicycles, and industrial machinery. Selecting the appropriate drive depends on factors like load capacity, speed requirements, and environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Drive for Your Needs
Belt drives offer quieter operation, lower maintenance, and smoother performance, making them ideal for applications prioritizing durability and noise reduction. Chain drives provide higher torque capacity and greater efficiency under heavy loads, suited for demanding conditions requiring maximum power transmission. Evaluating your specific load requirements, maintenance preferences, and environmental factors will help you choose the right drive system tailored to your needs.
Belt Drive vs Chain Drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com