Cylinder deactivation improves fuel efficiency by shutting off select engine cylinders under light-load conditions, reducing fuel consumption without compromising performance. Start-stop technology saves fuel by automatically turning off the engine during stops, helping Your vehicle reduce emissions and idle time in traffic.
Table of Comparison
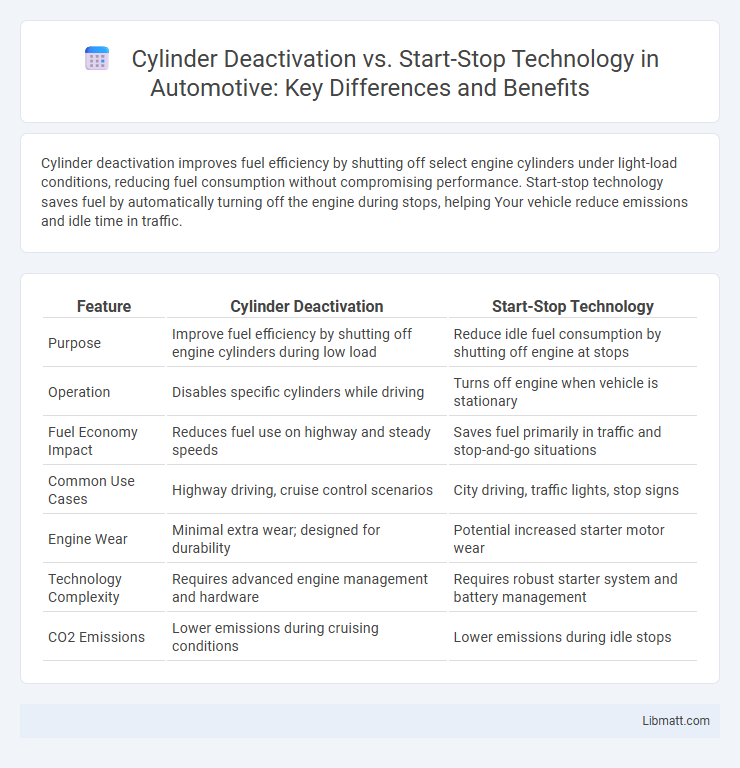
| Feature | Cylinder Deactivation | Start-Stop Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improve fuel efficiency by shutting off engine cylinders during low load | Reduce idle fuel consumption by shutting off engine at stops |
| Operation | Disables specific cylinders while driving | Turns off engine when vehicle is stationary |
| Fuel Economy Impact | Reduces fuel use on highway and steady speeds | Saves fuel primarily in traffic and stop-and-go situations |
| Common Use Cases | Highway driving, cruise control scenarios | City driving, traffic lights, stop signs |
| Engine Wear | Minimal extra wear; designed for durability | Potential increased starter motor wear |
| Technology Complexity | Requires advanced engine management and hardware | Requires robust starter system and battery management |
| CO2 Emissions | Lower emissions during cruising conditions | Lower emissions during idle stops |
Introduction to Engine Efficiency Technologies
Cylinder deactivation improves engine efficiency by shutting off selected cylinders during low-load conditions, reducing fuel consumption and emissions without compromising power. Start-stop technology enhances fuel economy by automatically turning off the engine when the vehicle is stationary and restarting it when needed, minimizing idle fuel use. Both technologies contribute significantly to reducing carbon footprint and optimizing overall vehicle performance in modern internal combustion engines.
What is Cylinder Deactivation?
Cylinder deactivation is a fuel-saving technology that shuts off some of an engine's cylinders under light-load conditions, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Unlike start-stop technology, which temporarily turns off the engine at stops, cylinder deactivation keeps the engine running but with fewer active cylinders to improve efficiency during cruising. Your vehicle can benefit from cylinder deactivation by maintaining performance while optimizing fuel economy on highways and steady-state driving.
How Start-Stop Technology Works
Start-stop technology automatically shuts off the engine when your vehicle is stationary, such as at traffic lights, and restarts it instantly when you lift your foot off the brake. This system reduces fuel consumption and emissions by minimizing idling time, enhancing overall efficiency. Unlike cylinder deactivation, which selectively disables engine cylinders during cruising, start-stop technology targets complete engine shutdown during stops for immediate fuel savings.
Key Benefits of Cylinder Deactivation
Cylinder deactivation improves fuel efficiency by shutting down select cylinders during light-load driving conditions, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. This technology enhances engine efficiency without compromising performance, allowing your vehicle to deliver power when needed while saving fuel during cruising or idle phases. Key benefits include lower fuel costs, reduced carbon footprint, and extended engine life due to decreased wear.
Advantages of Start-Stop Systems
Start-stop systems significantly improve fuel efficiency by shutting off the engine during idling, reducing unnecessary fuel consumption. This technology lowers greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to better environmental sustainability compared to cylinder deactivation. Start-stop systems also enhance urban driving economy by minimizing engine noise and wear during frequent stops.
Cylinder Deactivation vs Start-Stop: Fuel Economy Comparison
Cylinder deactivation improves fuel economy by selectively shutting off engine cylinders during low-load conditions, reducing fuel consumption without compromising power during acceleration. Start-stop technology enhances fuel efficiency by automatically turning off the engine when the vehicle is idle, such as at traffic lights, and restarting it when needed, thereby cutting fuel waste during stops. Studies show cylinder deactivation can yield fuel savings of up to 7-10% on highways, while start-stop systems typically provide 5-10% savings in urban driving cycles.
Impact on Emissions and Environmental Benefits
Cylinder deactivation reduces fuel consumption by shutting off select cylinders during light-load conditions, lowering CO2 emissions and improving overall engine efficiency. Start-stop technology minimizes idling time by automatically turning off the engine at stops, significantly cutting fuel use and tailpipe emissions in urban driving. Both technologies contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions but cylinder deactivation offers continuous efficiency gains, while start-stop technology targets emissions reduction primarily during idle periods.
Performance and Driving Experience Differences
Cylinder deactivation improves fuel efficiency by selectively shutting off cylinders under light load, maintaining smooth power delivery and preserving engine responsiveness during acceleration. Start-stop technology reduces fuel consumption and emissions by automatically turning off the engine at idle, but may introduce slight delays or vibrations when restarting, potentially affecting driving smoothness. The combination of both systems enhances overall efficiency while balancing performance and driving comfort.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Cylinder deactivation systems reduce wear on engine components by selectively shutting off cylinders during low load, potentially extending engine lifespan with proper maintenance such as regular oil changes and valve inspections. Start-stop technology decreases engine idling time, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions but may increase wear on the starter motor and battery, necessitating frequent checks and possible component replacements to maintain reliability. Both technologies require adherence to manufacturer-recommended service intervals to optimize maintenance and maximize vehicle longevity.
Which Technology is Right for Your Vehicle?
Cylinder deactivation improves fuel efficiency by reducing the number of active cylinders during low-load driving, making it ideal for larger engines and highway conditions. Start-stop technology enhances urban fuel savings by automatically shutting off the engine during idle stops, benefiting frequent city driving and stop-and-go traffic. Your choice depends on driving habits, engine type, and whether you prioritize highway fuel economy or city efficiency.
Cylinder deactivation vs Start-stop technology Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com