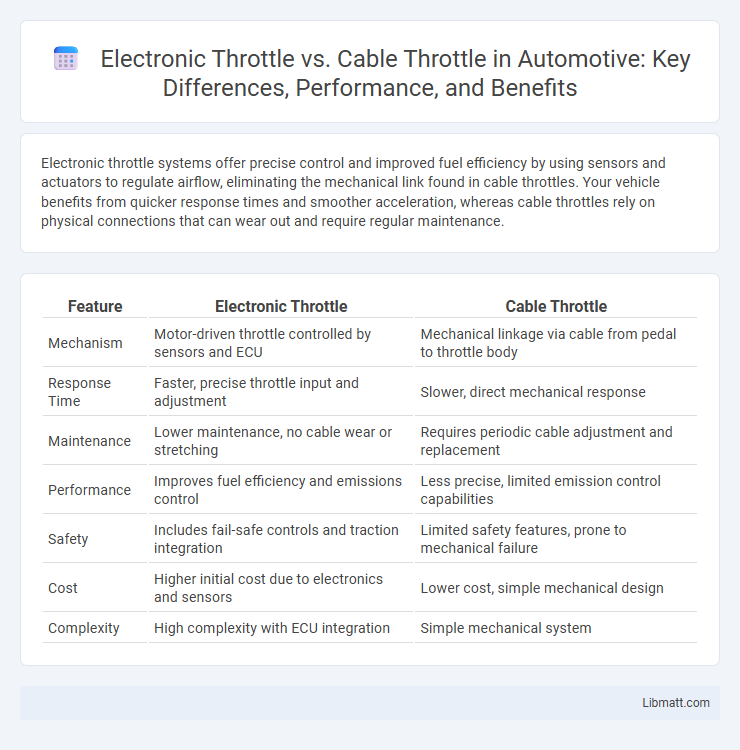
Electronic throttle systems offer precise control and improved fuel efficiency by using sensors and actuators to regulate airflow, eliminating the mechanical link found in cable throttles. Your vehicle benefits from quicker response times and smoother acceleration, whereas cable throttles rely on physical connections that can wear out and require regular maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electronic Throttle | Cable Throttle |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Motor-driven throttle controlled by sensors and ECU | Mechanical linkage via cable from pedal to throttle body |
| Response Time | Faster, precise throttle input and adjustment | Slower, direct mechanical response |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance, no cable wear or stretching | Requires periodic cable adjustment and replacement |
| Performance | Improves fuel efficiency and emissions control | Less precise, limited emission control capabilities |
| Safety | Includes fail-safe controls and traction integration | Limited safety features, prone to mechanical failure |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to electronics and sensors | Lower cost, simple mechanical design |
| Complexity | High complexity with ECU integration | Simple mechanical system |
Introduction to Throttle Systems
Electronic throttle systems replace traditional mechanical cable throttles by using sensors and actuators to control engine air intake more precisely. These systems improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by optimizing throttle response through real-time electronic adjustments. Your vehicle benefits from enhanced drivability and smoother acceleration with electronic throttle control compared to conventional cable throttles.
How Electronic Throttle Works
Electronic throttle controls engine power by using sensors and an electric motor to regulate the throttle valve based on input from the accelerator pedal. Unlike cable throttles, which mechanically connect the pedal to the throttle, electronic systems send signals to the engine control unit (ECU) for precise fuel and air mixture adjustments. Your vehicle benefits from improved responsiveness, enhanced fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions through this advanced throttle management.
How Cable Throttle Works
Cable throttle systems operate through a mechanical linkage where the accelerator pedal is connected to the throttle body via a steel cable. When the driver presses the pedal, the cable pulls the throttle plate open, regulating the amount of air entering the engine. This direct physical connection provides immediate response without the need for electronic sensors or controls.
Performance Differences
Electronic throttle systems provide more precise and instantaneous control over engine airflow compared to traditional cable throttles, enhancing throttle response and fuel efficiency. Your vehicle benefits from adaptive control algorithms that optimize performance based on driving conditions, resulting in smoother acceleration and improved emissions. Cable throttles, while mechanically straightforward, often lack the fine-tuned responsiveness and real-time adjustments available with electronic throttles.
Responsiveness and Driving Experience
Electronic throttle systems deliver precise and immediate engine response by using sensors and electronic control units, enhancing your driving experience with smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency. Cable throttles rely on mechanical linkages that can introduce lag and less accuracy, potentially leading to inconsistent throttle feel. Choosing electronic throttle technology provides superior responsiveness and a more controlled, dynamic driving experience.
Maintenance and Reliability
Electronic throttle systems generally offer lower maintenance requirements compared to cable throttles since they eliminate mechanical linkages prone to wear and stretching over time. The reliability of electronic throttles benefits from precise sensor inputs and computer control, reducing issues like throttle sticking or delayed response common in cable systems. You can expect improved longevity and consistent performance with electronic throttles, though they may require specialized diagnostic tools for troubleshooting.
Cost Comparison
Electronic throttle systems typically have higher upfront costs due to advanced sensors and control modules but can reduce long-term maintenance expenses by eliminating mechanical parts prone to wear. Cable throttle systems are generally less expensive initially, with simpler construction and easier repairs, but may incur higher upkeep costs over time because of cable stretching and adjustments. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing the initial investment of electronic throttles against the potentially increased maintenance demands of cable throttles.
Integration with Modern Technologies
Electronic throttle systems integrate seamlessly with advanced driver-assistance technologies such as adaptive cruise control, traction control, and stability management, enhancing overall vehicle performance and safety. Unlike cable throttles, electronic systems offer precise control through real-time sensor feedback and onboard computer algorithms, enabling smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency. This integration supports evolving automotive trends like autonomous driving and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, positioning electronic throttles as essential components in modern vehicles.
Pros and Cons of Electronic Throttle
Electronic throttle systems enhance vehicle performance by providing precise control of engine power, improving fuel efficiency, and enabling advanced features like traction control and cruise control. However, they may experience reliability issues due to electronic sensor failures and require more complex repairs compared to traditional cable throttles. The electronic throttle's ability to integrate with modern engine management systems outweighs its higher initial cost and potential troubleshooting challenges.
Pros and Cons of Cable Throttle
Cable throttle systems offer a direct mechanical connection between the accelerator pedal and the engine, providing immediate and predictable throttle response. However, they can suffer from cable stretch, corrosion, and require regular maintenance to ensure smooth operation, which may result in less precise control compared to electronic throttle systems. Your vehicle's performance and reliability may benefit from understanding these pros and cons when choosing between cable and electronic throttle systems.
electronic throttle vs cable throttle Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com