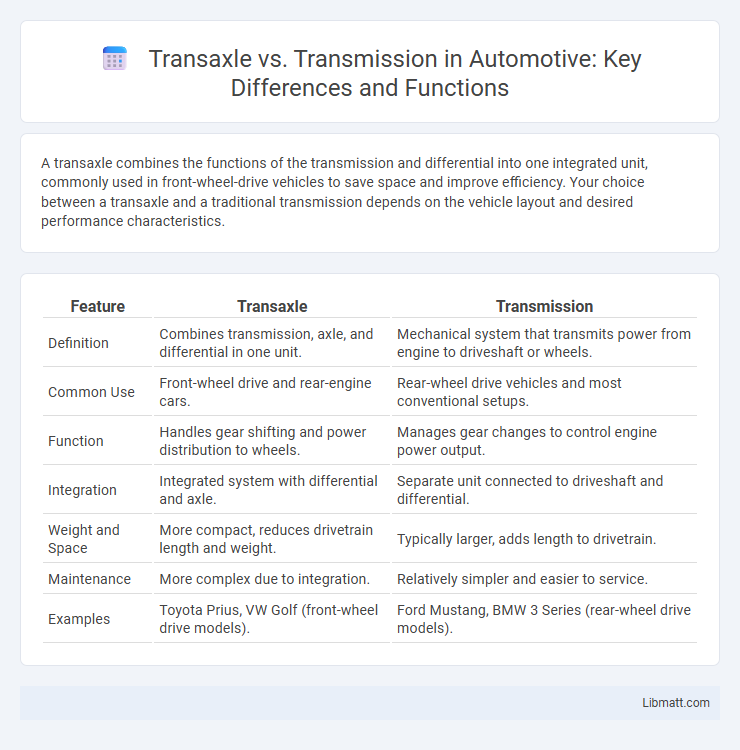
A transaxle combines the functions of the transmission and differential into one integrated unit, commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles to save space and improve efficiency. Your choice between a transaxle and a traditional transmission depends on the vehicle layout and desired performance characteristics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transaxle | Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines transmission, axle, and differential in one unit. | Mechanical system that transmits power from engine to driveshaft or wheels. |
| Common Use | Front-wheel drive and rear-engine cars. | Rear-wheel drive vehicles and most conventional setups. |
| Function | Handles gear shifting and power distribution to wheels. | Manages gear changes to control engine power output. |
| Integration | Integrated system with differential and axle. | Separate unit connected to driveshaft and differential. |
| Weight and Space | More compact, reduces drivetrain length and weight. | Typically larger, adds length to drivetrain. |
| Maintenance | More complex due to integration. | Relatively simpler and easier to service. |
| Examples | Toyota Prius, VW Golf (front-wheel drive models). | Ford Mustang, BMW 3 Series (rear-wheel drive models). |
Introduction to Transaxle and Transmission
A transaxle combines the functions of transmission, differential, and drive axle into a single integrated unit, commonly used in front-wheel-drive and some all-wheel-drive vehicles. Traditional transmission systems focus solely on transferring engine power to the drive wheels and are often paired separately with a differential. Understanding the design and application differences between transaxles and transmissions is essential for optimizing vehicle performance and drivetrain efficiency.
Core Differences Between Transaxle and Transmission
A transaxle combines the functions of the transmission, axle, and differential into a single integrated unit, commonly found in front-wheel-drive and rear-engine vehicles. In contrast, a traditional transmission transfers power from the engine to the driveshaft or axle, usually existing as a separate component from the differential and axles. The core difference lies in the design efficiency where transaxles streamline drivetrain layout and reduce weight, while transmissions allow for varied configurations and are typical in rear-wheel-drive setups.
How a Transaxle Works
A transaxle combines the functions of the transmission, differential, and axle into a single integrated unit, commonly found in front-wheel-drive and some rear-engine vehicles. It transmits power from the engine to the wheels by using a set of gears to adjust torque and speed, while simultaneously allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns. Understanding how a transaxle works can help you maintain your vehicle's drivetrain efficiency and improve overall driving performance.
How a Transmission Works
A transmission works by transferring power from the engine to the wheels through a system of gears that adjust torque and speed. Unlike a transaxle, which combines the transmission and differential in one unit, a traditional transmission functions independently and uses a clutch or torque converter to engage the gear system smoothly. Understanding how your transmission operates helps optimize gear shifting and improves vehicle performance.
Applications and Use Cases
Transaxles are primarily used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, integrating the transmission, differential, and drive axles into a single compact unit to save space and reduce weight. Traditional transmissions are common in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, separating the gearbox and differential for better handling and durability under high torque conditions. In electric and hybrid vehicles, transaxles facilitate efficient power distribution by combining multiple components, whereas conventional transmissions remain standard in internal combustion engine cars.
Pros and Cons of Transaxles
Transaxles combine the functions of transmission and differential into a single unit, saving space and reducing weight, especially beneficial in front-wheel-drive vehicles. They offer improved packaging efficiency and can enhance fuel economy but may face limitations in handling high torque compared to separate transmission and differential setups. Maintenance and repair costs for transaxles can be higher due to their integrated design, potentially increasing long-term service complexity.
Pros and Cons of Transmissions
Transmissions offer a range of benefits, including smooth gear shifts, enhanced fuel efficiency, and compatibility with various driving styles, while their complexity can lead to higher maintenance costs and potential repair challenges. Automatic transmissions provide ease of use and better performance in stop-and-go traffic, but typically come with increased initial price and possible lower durability compared to manual versions. Your choice will depend on balancing the convenience and efficiency of transmissions against their maintenance needs and upfront investment.
Performance Considerations
Transaxles integrate the transmission and differential into a single unit, optimizing weight distribution and improving handling performance, especially in front-wheel-drive and mid-engine vehicles. Transmissions provide greater flexibility with gear ratios and are often preferred in rear-wheel-drive setups for enhanced torque delivery and durability. Your choice between a transaxle and transmission should consider vehicle dynamics and performance goals to maximize efficiency and driving experience.
Maintenance and Repair Differences
Transaxles combine the transmission and differential into a single unit, often found in front-wheel-drive vehicles, making maintenance more complex due to integrated components requiring specialized tools and expertise. In contrast, traditional transmissions separate from the differential, allowing for easier access and often simpler repair or replacement processes. Understanding these differences in your vehicle's drivetrain components can help you anticipate maintenance challenges and costs more accurately.
Choosing the Right System for Your Vehicle
Selecting between a transaxle and a traditional transmission depends on vehicle design and drivetrain layout. Transaxles combine the transmission and differential in one unit, commonly used in front-wheel-drive cars for compact packaging and efficiency. Traditional transmissions separate these components, offering versatility for rear-wheel and all-wheel-drive vehicles with potential for greater power handling and customization.
transaxle vs transmission Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com