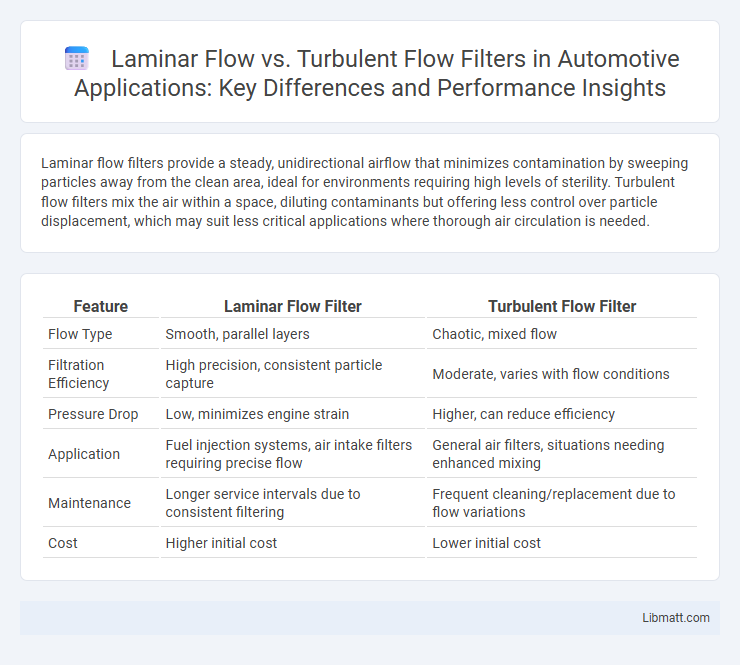
Laminar flow filters provide a steady, unidirectional airflow that minimizes contamination by sweeping particles away from the clean area, ideal for environments requiring high levels of sterility. Turbulent flow filters mix the air within a space, diluting contaminants but offering less control over particle displacement, which may suit less critical applications where thorough air circulation is needed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminar Flow Filter | Turbulent Flow Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Type | Smooth, parallel layers | Chaotic, mixed flow |
| Filtration Efficiency | High precision, consistent particle capture | Moderate, varies with flow conditions |
| Pressure Drop | Low, minimizes engine strain | Higher, can reduce efficiency |
| Application | Fuel injection systems, air intake filters requiring precise flow | General air filters, situations needing enhanced mixing |
| Maintenance | Longer service intervals due to consistent filtering | Frequent cleaning/replacement due to flow variations |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to Air Filtration Technologies
Laminar flow filters provide a uniform, unidirectional airflow that minimizes turbulence and particle disturbance, essential for cleanrooms and sensitive environments. Turbulent flow filters mix air by creating controlled turbulence, which dilutes contaminants but may cause particle resuspension, suitable for general ventilation systems. Both technologies optimize air quality by targeting specific contamination control needs depending on the application's cleanliness requirements.
Understanding Laminar Flow Filters
Laminar flow filters provide a uniform, unidirectional airflow that minimizes contamination by creating a clean air environment, ideal for sensitive laboratory or manufacturing processes. Unlike turbulent flow filters, which mix air to dilute contaminants, laminar flow filters maintain a steady, particle-free stream that protects Your workspace from airborne impurities. Understanding laminar flow filters is essential for selecting the right air filtration system to ensure maximum cleanliness and product integrity in controlled environments.
Key Features of Turbulent Flow Filters
Turbulent flow filters create chaotic fluid movement to enhance mixing and increase particle capture efficiency, making them ideal for applications requiring thorough contaminant removal. Their design typically includes irregular surfaces or baffles that disrupt the flow, improving filtration performance in environments with high particulate loads. Your choice of a turbulent flow filter ensures robust filtration in industrial and medical settings where controlling diverse contaminant sizes is critical.
Differences Between Laminar and Turbulent Flow
Laminar flow filters maintain a smooth, parallel airflow with minimal mixing, ensuring consistent filtration and reduced contamination, ideal for cleanrooms and sterile environments. Turbulent flow filters create chaotic, mixed air currents that improve dilution of contaminants but may reduce filtration efficiency in sensitive applications. The key difference lies in airflow patterns: laminar flow offers uniform velocity and direction, while turbulent flow results in irregular, swirling motion.
Efficiency Comparison: Laminar vs Turbulent Flow Filters
Laminar flow filters provide higher efficiency in contaminant removal by maintaining a uniform, parallel airflow that minimizes particle disruption and cross-contamination. Turbulent flow filters rely on mixed airflow patterns, which can lead to uneven particle capture and lower filtration precision. Your choice of filter should consider laminar flow systems for environments demanding superior air purity and consistent filtration performance.
Applications of Laminar Flow Filters
Laminar flow filters are widely used in cleanrooms, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and semiconductor fabrication due to their ability to maintain unidirectional airflow that minimizes particle contamination. These filters create a sterile environment essential for sensitive processes such as microbiological research and medical device assembly. By providing consistent, particle-free air, laminar flow filters ensure the highest level of air purity required in critical applications.
Uses of Turbulent Flow Filters
Turbulent flow filters are primarily used in industrial applications where thorough mixing and high contaminant removal efficiency are required, such as chemical processing, wastewater treatment, and HVAC systems. These filters promote chaotic fluid motion, enhancing particulate capture and filtration effectiveness for large-scale operations. Your facility benefits from turbulent flow filters when consistent contaminant removal in dynamic environments is essential.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Laminar flow filters provide a consistent, unidirectional airflow that minimizes particle disturbance, making them highly effective in cleanroom environments where contamination control is critical. Turbulent flow filters generate multidirectional airflow that promotes mixing, which can reduce localized contamination but often leads to less precise particle control and potential re-entrainment of contaminants. While laminar flow filters excel in maintaining sterile, low-particulate conditions, turbulent flow filters offer better airflow distribution in large areas but may require more frequent maintenance due to increased particle agitation.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Laminar flow filters require consistent maintenance to ensure the smooth, unidirectional airflow that prevents contamination, with frequent filter replacements and airflow calibration being critical. Turbulent flow filters, while generally more robust to airflow disruptions, demand regular cleaning to manage particulate buildup caused by chaotic airflow patterns. Operational costs for laminar filters tend to be higher due to strict environmental controls and energy consumption, whereas turbulent filters offer easier maintenance but may compromise some filtration efficiency.
Choosing the Right Filter for Your Needs
Selecting the right air filter depends on your environment's requirements for cleanliness and airflow efficiency. Laminar flow filters provide uniform, particle-free airflow ideal for sensitive applications like laboratories and medical facilities, ensuring optimal contamination control. Turbulent flow filters are better suited for general industrial use where mixing and high airflow rates are necessary, balancing filtration with operational efficiency.
Laminar Flow Filter vs Turbulent Flow Filter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com