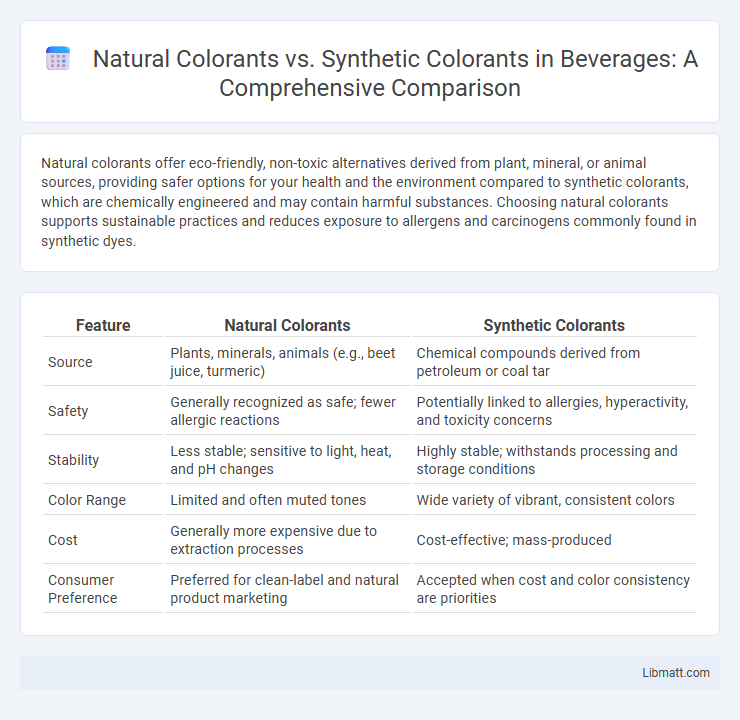
Natural colorants offer eco-friendly, non-toxic alternatives derived from plant, mineral, or animal sources, providing safer options for your health and the environment compared to synthetic colorants, which are chemically engineered and may contain harmful substances. Choosing natural colorants supports sustainable practices and reduces exposure to allergens and carcinogens commonly found in synthetic dyes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Colorants | Synthetic Colorants |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plants, minerals, animals (e.g., beet juice, turmeric) | Chemical compounds derived from petroleum or coal tar |
| Safety | Generally recognized as safe; fewer allergic reactions | Potentially linked to allergies, hyperactivity, and toxicity concerns |
| Stability | Less stable; sensitive to light, heat, and pH changes | Highly stable; withstands processing and storage conditions |
| Color Range | Limited and often muted tones | Wide variety of vibrant, consistent colors |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to extraction processes | Cost-effective; mass-produced |
| Consumer Preference | Preferred for clean-label and natural product marketing | Accepted when cost and color consistency are priorities |
Introduction to Colorants: Natural vs Synthetic
Natural colorants derive from plant, animal, or mineral sources, offering biodegradable and often non-toxic alternatives used in food, textiles, and cosmetics. Synthetic colorants, created through chemical processes, provide consistent, vibrant hues with greater stability and cost-effectiveness in large-scale production. The choice between natural and synthetic colorants influences environmental impact, health considerations, and product performance across various industries.
Sources of Natural Colorants
Natural colorants are derived from plants, minerals, and animals, including sources such as turmeric, beetroot, indigo, and cochineal insects. These sources provide vibrant pigments like curcumin, betanin, indigotin, and carminic acid, which are used in food, cosmetics, and textiles due to their biodegradability and lower toxicity. You can choose natural colorants when seeking eco-friendly and sustainable alternatives to synthetic dyes.
Common Synthetic Colorants and Their Origins
Common synthetic colorants include azo dyes like Tartrazine and Sunset Yellow, derived from petroleum-based chemicals through complex industrial processes. These man-made colorants offer vibrant, consistent hues and high stability but can pose health and environmental concerns due to their chemical composition and potential toxicity. Despite controversies, synthetic colorants remain widely used in food, cosmetics, and textiles for their cost-effectiveness and strong coloring properties.
Extraction and Production Processes
Natural colorants are derived from plant, animal, or mineral sources through processes like solvent extraction, cold-pressing, or fermentation, preserving their organic compounds. Synthetic colorants undergo chemical synthesis involving petroleum-based raw materials and complex reactions to produce consistent, long-lasting pigments. Your choice between natural and synthetic colorants impacts environmental footprint and product formulation, as natural extraction often requires more resource-intensive methods compared to industrial-scale synthetic production.
Safety and Health Impacts
Natural colorants, derived from plant, animal, or mineral sources, generally exhibit lower toxicity and reduced allergenic potential compared to synthetic colorants, promoting safer consumption and topical application. Synthetic colorants, often chemically engineered, have been linked to adverse health effects such as hyperactivity in children, skin irritation, and potential carcinogenicity due to the presence of contaminants or residual chemicals. Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EFSA enforce strict safety evaluations on synthetic dyes, but increased consumer preference for natural alternatives highlights growing concerns over long-term health impacts associated with synthetic colorant exposure.
Environmental Considerations
Natural colorants offer significant environmental benefits due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing from plants, minerals, or insects, which reduces pollution and waste accumulation. Synthetic colorants, derived from petrochemicals, often involve energy-intensive production processes and can release harmful pollutants into ecosystems during manufacturing and disposal. Choosing your products with natural colorants supports sustainability by minimizing ecological impact and promoting healthier soil and water quality.
Application in Food, Cosmetics, and Textiles
Natural colorants are widely used in food, cosmetics, and textiles due to their safety and eco-friendly properties, despite limited color range and stability issues. Synthetic colorants dominate the market with vibrant, consistent hues and greater longevity, especially in processed foods, makeup products, and fast-fashion textiles. Regulatory bodies increasingly encourage natural colorant adoption in food and cosmetic applications to reduce potential health risks associated with synthetic dyes.
Stability and Shelf Life Comparison
Natural colorants generally exhibit lower stability and a shorter shelf life compared to synthetic colorants due to their sensitivity to light, heat, and pH variations. Synthetic colorants offer enhanced durability, maintaining vibrant hues over extended periods under diverse environmental conditions. These differences impact product consistency, making synthetic dyes preferable for long-term stability in industrial applications.
Regulatory Status and Approval
Natural colorants are often recognized as safe by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EFSA, but their approval is subject to specific limits and conditions based on source and application. Synthetic colorants typically undergo rigorous safety evaluations, resulting in strict regulations and approved lists like the FDA's Color Additive Status List and the EU's Annex IV Regulation. Ongoing research and regulatory reviews ensure compliance with health standards, influencing market trends in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Future Trends in Colorant Development
Future trends in colorant development emphasize sustainable and eco-friendly solutions, driving innovation in natural colorants derived from plants, minerals, and microorganisms. Advances in biotechnology enable enhanced stability, vibrancy, and cost-effectiveness of natural dyes, making them competitive alternatives to synthetic colorants. Industry demand for non-toxic, biodegradable, and renewable colorants continues to shape research toward multifunctional pigments with improved performance across textiles, cosmetics, and food sectors.
Natural colorants vs synthetic colorants Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com