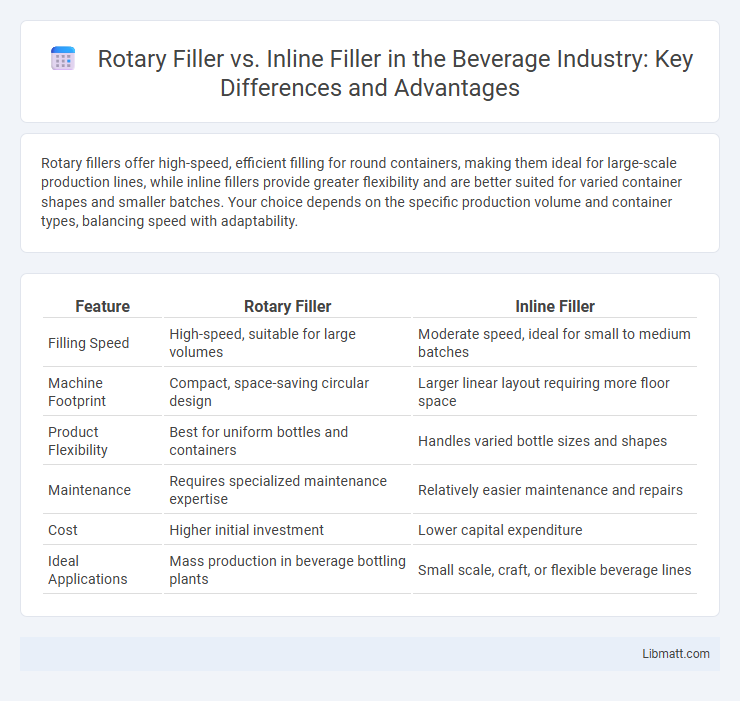
Rotary fillers offer high-speed, efficient filling for round containers, making them ideal for large-scale production lines, while inline fillers provide greater flexibility and are better suited for varied container shapes and smaller batches. Your choice depends on the specific production volume and container types, balancing speed with adaptability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rotary Filler | Inline Filler |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Speed | High-speed, suitable for large volumes | Moderate speed, ideal for small to medium batches |
| Machine Footprint | Compact, space-saving circular design | Larger linear layout requiring more floor space |
| Product Flexibility | Best for uniform bottles and containers | Handles varied bottle sizes and shapes |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized maintenance expertise | Relatively easier maintenance and repairs |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower capital expenditure |
| Ideal Applications | Mass production in beverage bottling plants | Small scale, craft, or flexible beverage lines |
Introduction to Rotary and Inline Fillers
Rotary fillers and inline fillers are essential machines in automated liquid filling processes, designed to accommodate different production speeds and container types. Rotary fillers operate with containers rotating around a central turret, enabling high-speed filling suitable for large volumes, while inline fillers move containers sequentially along a conveyor for more flexible, moderate-speed filling. Your choice depends on production scale, container shape, and desired output efficiency.
How Rotary Fillers Work
Rotary fillers operate by using multiple filling heads mounted on a rotating turret, allowing simultaneous filling of several containers as they pass through the machine. This continuous movement ensures high-speed production and precise volumetric or weight-based filling for liquids, creams, or pastes. Sensors and servo-controlled mechanisms synchronize container positioning and fill volumes, optimizing efficiency in beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic packaging lines.
How Inline Fillers Operate
Inline fillers operate by transporting containers sequentially through a linear conveyor system where filling occurs as each container pauses momentarily under the filling nozzle, ensuring precise volume control and minimal product wastage. This mechanism suits high-speed production lines with consistent container sizes, offering ease of integration and maintenance. Your production efficiency benefits from the reliability and adaptability of inline filler systems, especially in industries requiring exact dosing and flexible batch sizes.
Key Differences Between Rotary and Inline Fillers
Rotary fillers use a rotating system to fill multiple containers simultaneously, offering high-speed production ideal for large-scale operations, while inline fillers employ a linear conveyor, filling containers sequentially, providing better precision and flexibility for varied container sizes. Your choice depends on production volume, container type, and space constraints, with rotary fillers maximizing throughput in compact layouts and inline fillers excelling in customization and ease of maintenance. Key differences include speed capacity, machine footprint, and adaptability to product viscosity and container formats.
Advantages of Rotary Fillers
Rotary fillers offer high-speed filling capabilities, ideal for large-scale production lines requiring precision and consistency. Their continuous motion reduces downtime and enhances efficiency compared to intermittent inline fillers. The design supports various container shapes and sizes, providing versatile applications across industries such as beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics manufacturing.
Benefits of Inline Fillers
Inline fillers offer enhanced speed and precision for high-volume liquid packaging, reducing product waste and downtime. Their compact design allows seamless integration into existing production lines, optimizing space and operational efficiency. You benefit from consistent fill accuracy and easier maintenance, resulting in improved productivity for diverse industrial applications.
Production Capacity Comparison
Rotary fillers typically offer higher production capacity due to their ability to fill multiple containers simultaneously, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing environments. Inline fillers operate sequentially, which can limit throughput but provide greater flexibility for smaller production runs or varied container sizes. Your choice between rotary and inline fillers should consider the balance between production volume requirements and operational flexibility.
Application Suitability for Different Industries
Rotary fillers excel in high-speed applications suitable for industries like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food packaging where precise portion control is critical. Inline fillers are versatile for slower production lines, making them ideal for breweries, chemical, and small-batch food manufacturers requiring flexible and customizable filling processes. Choosing the right filler ensures Your production efficiency aligns with industry-specific demands and product characteristics.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Rotary fillers generally involve higher initial costs due to complex machinery and precise engineering, but offer greater speed and efficiency, reducing long-term operational expenses. Inline fillers typically have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance routines, making them suitable for smaller production scales or frequent product changes. Maintenance for rotary fillers demands specialized technical expertise and scheduled downtime, while inline fillers benefit from easier access and quicker repairs, minimizing production interruptions.
Choosing the Right Filler for Your Needs
Rotary fillers excel in high-speed production environments, offering efficient filling for bottles and containers with consistent accuracy, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing. Inline fillers provide greater flexibility and customization, suitable for varying bottle sizes and product viscosities, perfect for smaller batches or specialized products. Selecting the right filler depends on production volume, container type, and product characteristics to ensure optimum efficiency and product quality.
Rotary filler vs inline filler Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com