Stevia and monk fruit are natural zero-calorie sweeteners that provide a healthier alternative to sugar, with stevia often having a slightly bitter aftertaste while monk fruit is known for its mild, fruity sweetness. Your choice depends on flavor preference and how you plan to use these sweeteners in cooking or beverages.
Table of Comparison
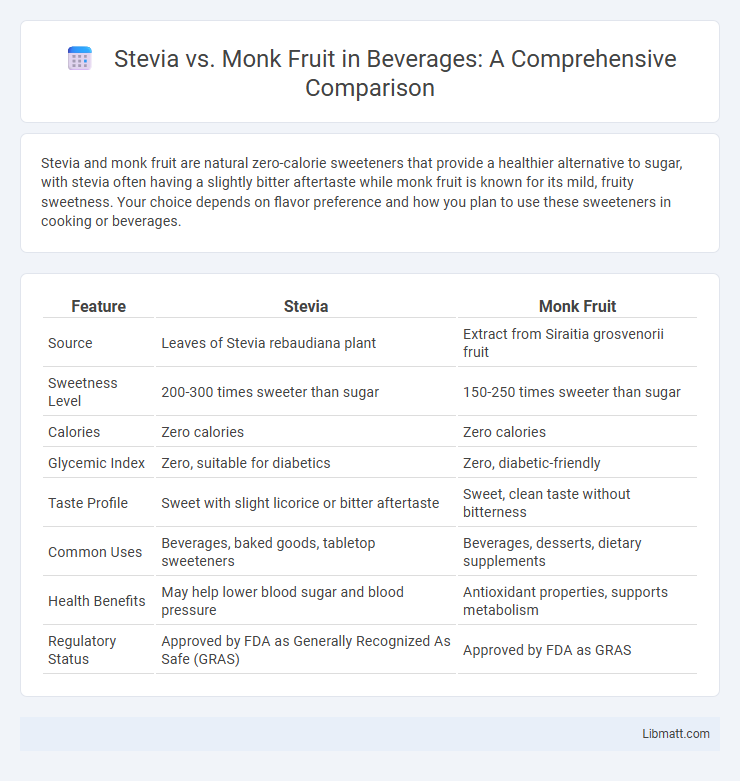
| Feature | Stevia | Monk Fruit |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Leaves of Stevia rebaudiana plant | Extract from Siraitia grosvenorii fruit |
| Sweetness Level | 200-300 times sweeter than sugar | 150-250 times sweeter than sugar |
| Calories | Zero calories | Zero calories |
| Glycemic Index | Zero, suitable for diabetics | Zero, diabetic-friendly |
| Taste Profile | Sweet with slight licorice or bitter aftertaste | Sweet, clean taste without bitterness |
| Common Uses | Beverages, baked goods, tabletop sweeteners | Beverages, desserts, dietary supplements |
| Health Benefits | May help lower blood sugar and blood pressure | Antioxidant properties, supports metabolism |
| Regulatory Status | Approved by FDA as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) | Approved by FDA as GRAS |
Introduction to Stevia and Monk Fruit
Stevia and monk fruit are natural sweeteners derived from plants, offering low-calorie alternatives to sugar for those managing blood sugar levels or reducing calorie intake. Stevia comes from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, while monk fruit is sourced from the Luo Han Guo fruit native to Southeast Asia. Your choice between these two depends on taste preference, sweetness level, and dietary needs, with monk fruit often praised for its fruity undertones and Stevia for its intense sweetness without calories.
Origins and History of Stevia
Stevia, native to Paraguay and Brazil, has been used for centuries by indigenous peoples as a natural sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant. Its history dates back to the 16th century when Spanish conquistadors first documented its use as a sugar substitute. Unlike monk fruit, which originates from Southeast Asia, Stevia's long-standing traditional use highlights its cultural and historical significance as a calorie-free sweetener.
Origins and History of Monk Fruit
Monk fruit, also known as Luo Han Guo, originates from Southern China and has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine and sweetening teas. Its natural sweetness comes from mogrosides, compounds that provide intense sweetness without calories or a glycemic impact. Your choice between monk fruit and stevia can hinge on monk fruit's long historical use as a natural sweetener with anti-inflammatory properties.
Chemical Composition and Sweetness
Stevia contains mogrosides, primarily stevioside and rebaudioside, responsible for its intense sweetness, which is around 200-300 times sweeter than sugar. Monk fruit's sweetness comes from mogrosides, particularly mogroside V, providing 150-250 times the sweetness of sugar without calories. Your choice between stevia and monk fruit depends on preferred taste profile and sensitivity to their distinct chemical compositions.
Health Benefits of Stevia
Stevia contains zero calories and has been shown to help regulate blood sugar levels, making it an ideal natural sweetener for people with diabetes and those aiming for weight management. Its active compounds, steviosides and rebaudiosides, possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that support cardiovascular health and reduce oxidative stress. Research also suggests stevia may lower blood pressure, contributing to overall heart health without raising insulin levels.
Health Benefits of Monk Fruit
Monk fruit contains mogrosides, natural antioxidants known for their anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties, which support overall health and immune function. Unlike sugar and some sweeteners, monk fruit has a negligible glycemic index, making it ideal for blood sugar management and diabetes-friendly diets. Its zero-calorie profile contributes to weight management by reducing calorie intake without sacrificing sweetness.
Safety, Side Effects, and Allergies
Stevia and monk fruit are both natural sweeteners considered safe by the FDA, with stevia derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant and monk fruit sourced from the Luo Han Guo fruit. Stevia may cause mild side effects such as bloating or nausea in some individuals, whereas monk fruit exhibits fewer reported side effects and is less likely to trigger allergic reactions. Understanding your own sensitivity is important when choosing between these sweeteners, as allergies to either are rare but possible.
Taste Profile and Culinary Uses
Stevia offers a strong sweetness with slightly bitter or licorice-like aftertones, making it ideal for beverages, desserts, and baked goods that can balance its intense flavor. Monk fruit provides a smoother, more neutral sweetness with minimal aftertaste, suitable for sweetening teas, sauces, and cold drinks without overpowering other flavors. Both natural sweeteners are popular sugar substitutes in low-calorie and keto-friendly recipes due to their high sweetening power and zero glycemic impact.
Stevia vs Monk Fruit: Nutritional Comparison
Stevia contains zero calories and has glycosides like stevioside, which are responsible for its intense sweetness while providing no impact on blood sugar levels. Monk fruit sweetener is also calorie-free and rich in mogrosides, compounds that offer potent sweetness and antioxidant properties without raising blood glucose. Both natural sweeteners provide zero glycemic index benefits, making them suitable for diabetic and low-carb diets while differing slightly in taste and antioxidant content.
Which Sweetener Should You Choose?
Stevia and monk fruit are both natural, zero-calorie sweeteners with distinct benefits; stevia has a slightly bitter aftertaste while monk fruit offers a smoother flavor profile. Monk fruit contains antioxidants called mogrosides, which may provide additional health benefits beyond sweetness. When choosing between the two, consider taste preference, dietary restrictions, and potential health impacts to determine which sweetener best suits your needs.
Stevia vs monk fruit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com