MEP encompasses the comprehensive design and integration of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within a building, while HVAC specifically focuses on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning to control indoor climate. Understanding the difference helps you ensure optimal building performance by addressing both overall infrastructure needs and specific environmental comfort requirements.
Table of Comparison
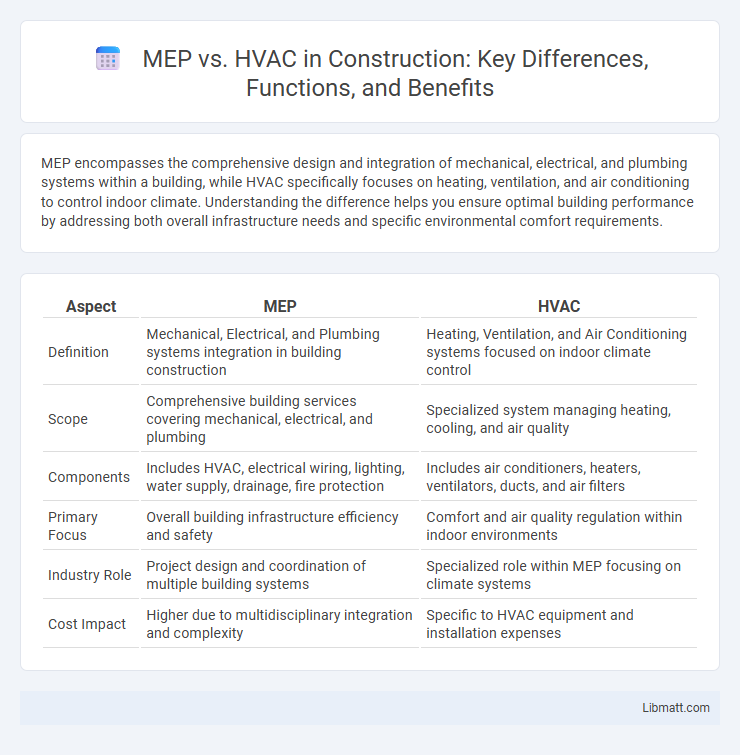
| Aspect | MEP | HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing systems integration in building construction | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems focused on indoor climate control |
| Scope | Comprehensive building services covering mechanical, electrical, and plumbing | Specialized system managing heating, cooling, and air quality |
| Components | Includes HVAC, electrical wiring, lighting, water supply, drainage, fire protection | Includes air conditioners, heaters, ventilators, ducts, and air filters |
| Primary Focus | Overall building infrastructure efficiency and safety | Comfort and air quality regulation within indoor environments |
| Industry Role | Project design and coordination of multiple building systems | Specialized role within MEP focusing on climate systems |
| Cost Impact | Higher due to multidisciplinary integration and complexity | Specific to HVAC equipment and installation expenses |
Understanding MEP and HVAC: Key Differences
MEP encompasses Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing systems in a building, while HVAC specifically refers to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. Understanding these distinctions helps you design and maintain efficient building infrastructure, ensuring each system's role is optimized. HVAC is a subset of MEP, focusing solely on climate control, whereas MEP covers a broader range of essential building services.
Components of MEP Systems
MEP systems encompass Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing components, including HVAC units, electrical wiring, lighting, fire safety, water supply, and drainage systems. HVAC specifically refers to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning equipment responsible for regulating indoor air quality and temperature. Understanding the integration of HVAC within MEP is vital for efficient building design and operation.
What Does HVAC Encompass?
HVAC encompasses heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems designed to regulate indoor climate and ensure air quality in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. It includes components such as furnaces, air conditioners, ventilation ducts, heat pumps, and control systems that maintain thermal comfort and proper airflow. HVAC systems are integral to MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) engineering, specifically addressing mechanical aspects related to climate control and air movement.
MEP vs HVAC: Scope of Services
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) includes a broad range of services encompassing HVAC systems, electrical power distribution, lighting, fire protection, and plumbing installations. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) specifically focuses on climate control systems, air quality, and thermal comfort within buildings. Understanding the distinction in scope of services helps you allocate resources effectively and ensure comprehensive building system integration.
Roles and Responsibilities: MEP Engineers vs HVAC Technicians
MEP engineers oversee the integrated design and coordination of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems in building projects, ensuring compliance with codes and efficiency standards. HVAC technicians specialize in installing, maintaining, and repairing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to optimize indoor air quality and comfort. Your project benefits when MEP engineers provide comprehensive system planning while HVAC technicians execute detailed, hands-on equipment management.
Integration of HVAC Within MEP Systems
HVAC systems are a critical component of MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems, responsible for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning within buildings. Integration of HVAC within MEP ensures seamless coordination with electrical controls and plumbing infrastructure, optimizing energy efficiency and indoor air quality. Your building's performance and occupant comfort depend on precise synchronization between HVAC components and other MEP elements.
Project Design Considerations: MEP and HVAC
MEP project design considerations encompass mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, ensuring integrated functionality and energy efficiency in building infrastructure. HVAC design specifically targets heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, focusing on indoor air quality, thermal comfort, and system zoning. Your project's success depends on aligning MEP coordination with HVAC requirements for optimal performance and code compliance.
Energy Efficiency: MEP vs HVAC Approaches
MEP systems encompass a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency by integrating mechanical, electrical, and plumbing components to optimize overall building performance. HVAC focuses specifically on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, aiming to reduce energy consumption through advanced equipment and control strategies. Your choice between MEP and HVAC approaches influences the scope and effectiveness of energy-saving measures in building design and operation.
Cost Implications: MEP Systems Compared to HVAC Installations
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems involve comprehensive building infrastructure components, often resulting in higher initial costs compared to standalone HVAC installations focused solely on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. MEP systems require integrated design and coordination among multiple trades, increasing labor and material expenses, while HVAC installation costs are typically limited to equipment and ductwork specific to climate control. Long-term maintenance and energy efficiency in MEP systems can lead to cost savings, though the upfront investment remains substantially greater than that of individual HVAC solutions.
Choosing the Right Solution: MEP or HVAC?
Choosing between MEP and HVAC solutions depends on the project's scope and complexity; MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) encompasses comprehensive building systems, while HVAC focuses exclusively on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. For large-scale commercial or industrial developments requiring integrated systems management, MEP offers a holistic approach ensuring proper coordination and energy efficiency. In contrast, smaller residential or single-purpose buildings benefit from specialized HVAC services, delivering targeted climate control and improved indoor air quality.
MEP vs HVAC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com