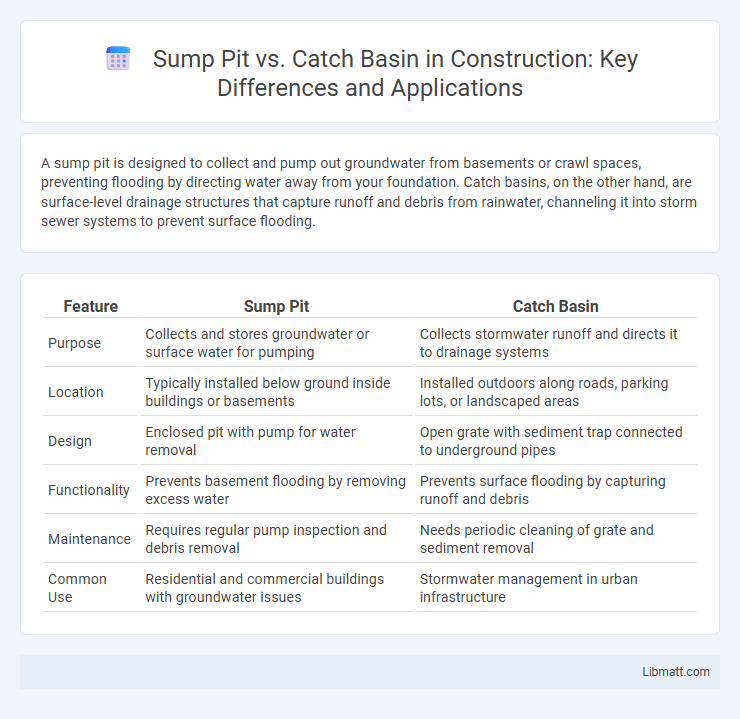
A sump pit is designed to collect and pump out groundwater from basements or crawl spaces, preventing flooding by directing water away from your foundation. Catch basins, on the other hand, are surface-level drainage structures that capture runoff and debris from rainwater, channeling it into storm sewer systems to prevent surface flooding.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sump Pit | Catch Basin |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Collects and stores groundwater or surface water for pumping | Collects stormwater runoff and directs it to drainage systems |
| Location | Typically installed below ground inside buildings or basements | Installed outdoors along roads, parking lots, or landscaped areas |
| Design | Enclosed pit with pump for water removal | Open grate with sediment trap connected to underground pipes |
| Functionality | Prevents basement flooding by removing excess water | Prevents surface flooding by capturing runoff and debris |
| Maintenance | Requires regular pump inspection and debris removal | Needs periodic cleaning of grate and sediment removal |
| Common Use | Residential and commercial buildings with groundwater issues | Stormwater management in urban infrastructure |
Introduction: Understanding Sump Pits and Catch Basins
Sump pits are underground receptacles designed to collect water from basement drainage systems, preventing flooding by directing excess water to sump pumps. Catch basins function as surface-level drainage inlets that capture rainwater runoff and debris, channeling it into storm sewer systems to reduce street flooding. Both structures play critical roles in effective water management and flood prevention in residential and urban environments.
Definition of Sump Pit
A sump pit is a recessed basin installed below floor level designed to collect water, typically found in basements or low-lying areas of a building. It serves as a central point where water accumulates before being pumped out by a sump pump to prevent flooding or water damage. Your sump pit is crucial for managing excess groundwater and protecting the foundation of your property.
Definition of Catch Basin
A catch basin is a drainage structure designed to collect surface water runoff and debris, preventing clogging in underground stormwater systems. It typically includes a grate at ground level and a sump below the outlet pipe to trap sediments and prevent them from entering the drainage system. Unlike sump pits, which are primarily used to collect groundwater or seepage, catch basins manage surface water to reduce flooding and water accumulation in urban or paved areas.
Key Differences Between Sump Pit and Catch Basin
A sump pit is an underground reservoir designed to collect and temporarily hold water, commonly used in basements to prevent flooding by channeling water to a sump pump; a catch basin, however, is a drainage structure that collects surface runoff from streets or yards and directs it into the storm sewer system. The key differences are in their primary functions and locations: sump pits manage groundwater and interior water accumulation, while catch basins handle exterior surface water. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the appropriate drainage solution for effective water management in your property.
Primary Functions and Applications
A sump pit primarily functions to collect and manage groundwater or stormwater from basement drainage systems, preventing flooding by directing water to sump pumps for removal. Catch basins serve as surface drainage structures designed to capture debris and runoff from streets or parking lots, channeling it into storm sewer systems while filtering out sediment. Your choice between a sump pit and a catch basin depends on whether you need subsurface water management or surface water drainage and sediment control.
Installation Process Comparison
The installation process for a sump pit involves excavating a deep hole in the basement or crawlspace floor, placing a sump basin, and ensuring proper connection to a sump pump system for water removal. Installing a catch basin requires grading a surface area, digging a wide pit to collect surface runoff, and connecting the basin to underground drainage pipes for efficient water flow management. Both systems demand precise placement and sealing to prevent leaks, but catch basins are typically installed outdoors in driveways or yards, while sump pits are located indoors below groundwater entry points.
Maintenance Requirements
Sump pits require regular inspection and cleaning to prevent sediment buildup, which can obstruct the sump pump and reduce its efficiency during heavy rainfall or flooding. Catch basins demand frequent debris removal to avoid blockages that can cause localized flooding and water damage in drainage systems. Your maintenance schedule should prioritize these tasks to ensure both sump pits and catch basins function effectively and protect your property from water-related issues.
Advantages and Disadvantages
A sump pit offers efficient water collection and easy maintenance, making it ideal for basement drainage but requires a sump pump to prevent flooding. A catch basin effectively manages surface runoff and prevents debris buildup in stormwater systems but can become clogged and requires regular cleaning. Your choice depends on the specific drainage needs and site conditions of your property.
Cost Considerations
Sump pits generally cost less to install because they are smaller and simpler, designed primarily to collect and pump groundwater from basements or crawl spaces. Catch basins involve higher expenses due to their larger size, complex drainage systems, and frequent connection to municipal stormwater infrastructure. Evaluating your property's drainage needs will help determine which option fits your budget and provides effective water management.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Property
Sump pits are ideal for residential properties prone to basement flooding by collecting and pumping out groundwater, while catch basins are suited for surface water drainage in areas with heavy rainfall or paved surfaces. Selecting the right solution depends on your property's topography, drainage needs, and whether the concern is groundwater seepage or stormwater runoff. Properly evaluating these factors ensures effective water management and prevents structural damage or erosion.
Sump pit vs catch basin Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com