Diesel-electric submarines are quieter during battery-powered operations and ideal for coastal missions, while nuclear submarines offer unmatched endurance and speed for extended deep-sea deployments. Your choice depends on mission requirements, with diesel-electric subs favoring stealth and short-range tactics, and nuclear subs excelling in sustained, global naval presence.
Table of Comparison
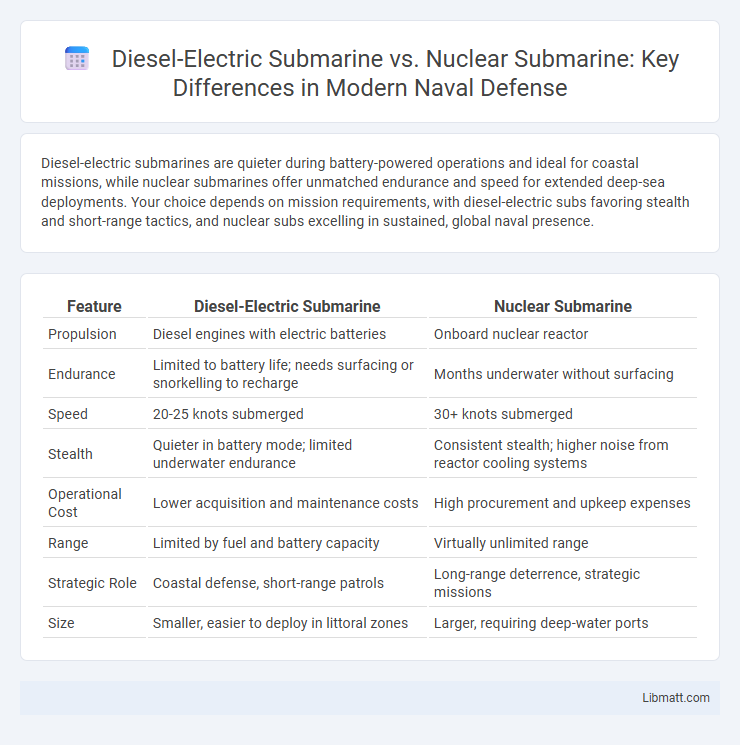
| Feature | Diesel-Electric Submarine | Nuclear Submarine |
|---|---|---|
| Propulsion | Diesel engines with electric batteries | Onboard nuclear reactor |
| Endurance | Limited to battery life; needs surfacing or snorkelling to recharge | Months underwater without surfacing |
| Speed | 20-25 knots submerged | 30+ knots submerged |
| Stealth | Quieter in battery mode; limited underwater endurance | Consistent stealth; higher noise from reactor cooling systems |
| Operational Cost | Lower acquisition and maintenance costs | High procurement and upkeep expenses |
| Range | Limited by fuel and battery capacity | Virtually unlimited range |
| Strategic Role | Coastal defense, short-range patrols | Long-range deterrence, strategic missions |
| Size | Smaller, easier to deploy in littoral zones | Larger, requiring deep-water ports |
Introduction: Diesel-Electric vs Nuclear Submarines
Diesel-electric submarines rely on battery power and diesel engines, providing stealth advantages in shallow coastal waters by minimizing noise emissions. Nuclear submarines use nuclear reactors for propulsion, enabling them to operate submerged for extended periods with greater speed and endurance. The choice between diesel-electric and nuclear submarines depends on mission requirements, operational range, and strategic deployment needs.
Propulsion Systems: How Each Submarine Operates
Diesel-electric submarines operate using diesel engines to charge batteries that power electric motors for underwater propulsion, requiring periodic surfacing to recharge. Nuclear submarines utilize nuclear reactors to generate continuous power, allowing them to remain submerged for extended periods without surfacing. Understanding these propulsion differences helps you assess operational endurance and stealth capabilities critical for mission requirements.
Stealth and Acoustic Signature
Diesel-electric submarines produce significantly lower acoustic signatures compared to nuclear submarines due to their reliance on battery-powered propulsion when submerged, making them quieter and harder to detect in shallow coastal waters. Nuclear submarines generate continuous noise from their reactor coolant pumps and propulsion systems, which can be detected by advanced sonar arrays despite their endurance and speed advantages. Your choice between the two should consider the operational environment, with diesel-electric subs excelling in stealth during short missions and nuclear subs offering sustained deployment but at a higher acoustic risk.
Operational Range and Endurance
Diesel-electric submarines typically have a limited operational range and endurance compared to nuclear submarines due to their reliance on battery power and the need to surface or snorkel for air to recharge. Nuclear submarines can operate underwater for months at a time, powered by a nuclear reactor that provides virtually unlimited range and endurance without the need to surface. Your mission's duration and range requirements are critical factors in choosing between these two types, with nuclear subs favored for extended underwater deployments and diesel-electric subs preferred for shorter, covert operations.
Speed and Maneuverability
Diesel-electric submarines offer superior maneuverability and quieter operation at low speeds due to their electric propulsion systems, making them ideal for stealth missions in shallow waters. Nuclear submarines achieve much higher speeds, often exceeding 30 knots submerged, powered by their nuclear reactors, enabling rapid transit and long-range deployments without refueling. Your choice depends on mission requirements, prioritizing either the stealthy agility of diesel-electric subs or the sustained high-speed capabilities of nuclear-powered vessels.
Armament and Combat Capability
Diesel-electric submarines typically carry torpedoes, and some are equipped with anti-ship missiles, offering stealth advantages in littoral waters but limited endurance and weapon payload compared to nuclear submarines. Nuclear submarines boast superior armament versatility, including long-range cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, and advanced torpedo systems, enabling extended global deployment and strategic strike capabilities. Your choice depends on mission requirements, with nuclear submarines excelling in sustained power projection and diesel-electrics providing stealth in coastal defense scenarios.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs
Diesel-electric submarines generally have lower initial acquisition costs but require more frequent and intensive maintenance, leading to higher operational expenses over their lifespan. Nuclear submarines incur significantly higher upfront costs and complex maintenance procedures due to their nuclear reactors, but their longer service life and greater endurance can result in lower cost per operational hour. Your choice between the two should account for the total lifecycle costs, balancing upfront investment with long-term maintenance and operational demands.
Strategic Roles and Mission Profiles
Diesel-electric submarines excel in coastal defense, anti-submarine warfare, and intelligence gathering due to their stealth in shallow waters and limited endurance. Nuclear submarines support strategic deterrence and power projection with global reach and extended submerged endurance, enabling continuous patrols and ballistic missile deployment. Your choice depends on mission requirements, balancing stealth, range, and strategic impact.
Environmental Impact and Risks
Diesel-electric submarines produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions during operation, relying on battery power and air-independent propulsion systems, which contribute to a lower environmental footprint. Nuclear submarines rely on uranium-powered reactors, posing risks of radioactive contamination and long-term nuclear waste management challenges. Your choice between these submarine types involves weighing cleaner operational emissions against potential hazards from radioactive materials.
Future Trends in Submarine Technology
Future trends in submarine technology emphasize enhanced stealth, extended underwater endurance, and advanced propulsion systems, with diesel-electric submarines incorporating air-independent propulsion (AIP) to reduce acoustic signatures while nuclear submarines develop compact, more efficient reactors for longer deployments. Advances in AI-driven autonomous navigation and improved sonar capabilities will further elevate operational effectiveness and survivability. Your strategic advantage depends on adopting these innovations to maintain underwater dominance and mission flexibility.
diesel-electric submarine vs nuclear submarine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com