EO/IR guidance relies on electro-optical and infrared sensors to detect and track targets based on heat signatures and visual imagery, offering high precision in various weather conditions. Radar guidance uses radio waves to identify and follow objects, providing longer detection ranges and better performance in poor visibility, making Your choice dependent on specific mission requirements and environmental factors.
Table of Comparison
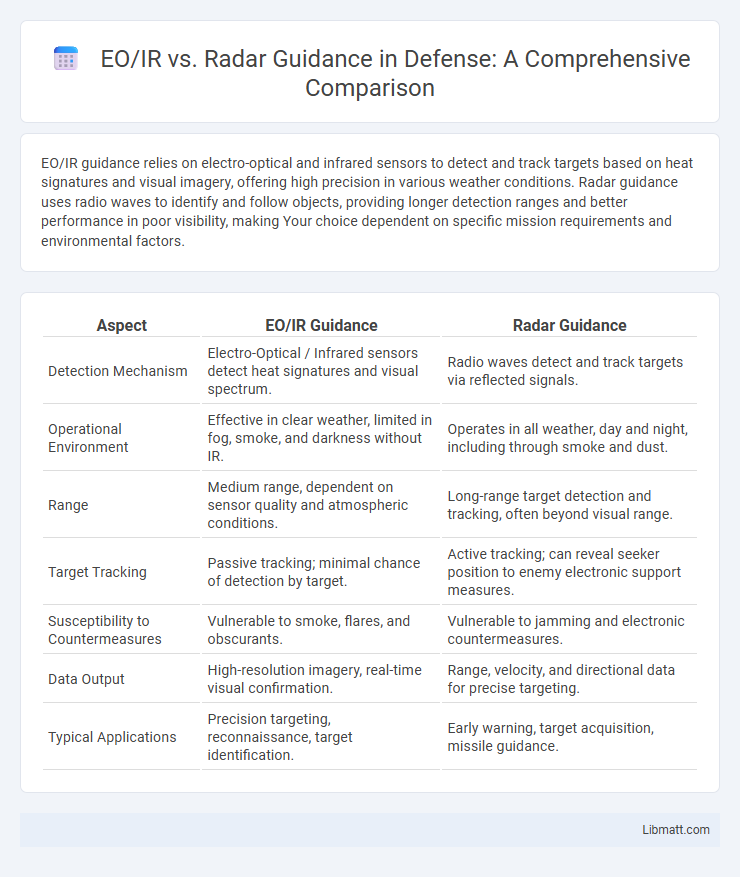
| Aspect | EO/IR Guidance | Radar Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Mechanism | Electro-Optical / Infrared sensors detect heat signatures and visual spectrum. | Radio waves detect and track targets via reflected signals. |
| Operational Environment | Effective in clear weather, limited in fog, smoke, and darkness without IR. | Operates in all weather, day and night, including through smoke and dust. |
| Range | Medium range, dependent on sensor quality and atmospheric conditions. | Long-range target detection and tracking, often beyond visual range. |
| Target Tracking | Passive tracking; minimal chance of detection by target. | Active tracking; can reveal seeker position to enemy electronic support measures. |
| Susceptibility to Countermeasures | Vulnerable to smoke, flares, and obscurants. | Vulnerable to jamming and electronic countermeasures. |
| Data Output | High-resolution imagery, real-time visual confirmation. | Range, velocity, and directional data for precise targeting. |
| Typical Applications | Precision targeting, reconnaissance, target identification. | Early warning, target acquisition, missile guidance. |
Introduction to EO/IR and Radar Guidance
EO/IR (Electro-Optical/Infrared) guidance systems utilize sensors detecting visible light and infrared radiation to track targets based on heat signatures and visual contrast, offering high-resolution imaging in various environmental conditions. Radar guidance relies on radio waves to detect and track objects by measuring the reflection and Doppler shifts, providing reliable performance in adverse weather and through obscurants such as smoke or fog. Both systems are integral to modern targeting and surveillance, with EO/IR excelling in detailed target identification and radar excelling in all-weather detection and range accuracy.
Fundamental Principles of EO/IR Systems
EO/IR systems operate by detecting electromagnetic radiation in the visible and infrared spectrums, converting this energy into electronic signals to create detailed images for target identification. Unlike radar guidance, which relies on radio wave reflection, EO/IR systems provide high-resolution, passive tracking capabilities that reduce detectability. Understanding these fundamental principles helps optimize your choice between EO/IR and radar systems based on mission requirements such as stealth and image clarity.
Core Concepts of Radar Guidance
Radar guidance uses radio waves to detect and track targets by emitting electromagnetic signals and analyzing their reflections, enabling precise target location regardless of weather or lighting conditions. This system offers long-range detection and can track multiple moving targets simultaneously, making it highly effective for missile and defense applications. Your strategic advantage lies in radar's ability to provide continuous, all-weather tracking compared to EO/IR's reliance on optical and infrared signatures.
Key Differences Between EO/IR and Radar Guidance
EO/IR (Electro-Optical/Infrared) guidance relies on visual and thermal imaging to detect and track targets, providing high-resolution imagery ideal for precision targeting in clear weather conditions. Radar guidance uses radio waves to identify and follow targets, offering superior performance in adverse weather and through smoke, fog, or camouflage. Your choice depends on operational environment demands, with EO/IR excelling in detailed target discrimination and radar guidance offering enhanced all-weather, long-range detection.
Detection Range: EO/IR vs Radar
EO/IR systems offer high-resolution imaging capable of detecting targets at shorter ranges, typically effective up to several kilometers depending on atmospheric conditions. Radar guidance systems provide longer detection ranges, often exceeding tens of kilometers, by using radio waves that penetrate weather and obscurants. Your choice between EO/IR and radar guidance will depend on mission requirements for detection distance and environmental factors influencing sensor performance.
Performance in Challenging Weather Conditions
Electro-Optical/Infrared (EO/IR) guidance systems face limitations in challenging weather conditions such as fog, heavy rain, or snow, which degrade sensor visibility and target acquisition. Radar guidance excels in these adverse environments by using radio waves that penetrate weather obscurants, maintaining reliable tracking and target detection. This capability makes radar guidance more effective for all-weather operations, especially in low-visibility scenarios critical for military and surveillance applications.
Countermeasure Resistance and Vulnerabilities
EO/IR guidance systems rely on infrared and electro-optical sensors, making them vulnerable to countermeasures like flares, smoke screens, and laser jamming that can obscure or distort the target's thermal or visual signature. Radar guidance offers greater countermeasure resistance by using radio waves less affected by visual obstructions, but it remains susceptible to electronic countermeasures such as radar jamming, deception techniques, and stealth technology that reduce radar cross-section. Effective missile guidance often integrates EO/IR and radar to balance vulnerabilities and enhance resistance against diverse countermeasures.
Applications in Modern Military Systems
EO/IR (Electro-Optical/Infrared) guidance systems excel in precision targeting and identification through high-resolution imagery and thermal detection, making them ideal for close-range and urban combat scenarios. Radar guidance provides long-range detection and tracking capabilities, penetrating adverse weather conditions and electronic countermeasures, essential for missile defense and surveillance in expansive battlefields. Modern military systems integrate EO/IR and radar guidance to leverage the complementary strengths of both technologies for enhanced situational awareness and target acquisition.
Cost, Integration, and Operational Considerations
EO/IR systems generally offer lower cost and easier integration with existing platforms compared to radar guidance, which requires more complex hardware and signal processing. EO/IR sensors provide high-resolution imagery ideal for target identification but are limited by weather and lighting conditions, whereas radar operates effectively in all environments but at a higher operational expense. Operational considerations favor EO/IR for covert missions and precision targeting, while radar guidance excels in long-range detection and tracking of multiple targets simultaneously.
Future Trends in Sensor Guidance Technologies
EO/IR (Electro-Optical/Infrared) and radar guidance technologies are advancing with enhanced sensor fusion capabilities, improving target detection accuracy in complex environments. Future trends emphasize integrating AI-driven data processing and adaptive algorithms to optimize real-time threat assessment and tracking. Emerging developments in quantum sensors and high-resolution multi-spectral imaging will further elevate the precision and reliability of EO/IR and radar guidance systems in next-generation defense applications.
EO/IR vs radar guidance Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com