Man-portable air defense systems offer enhanced mobility and rapid deployment for Your infantry units, enabling effective engagement of low-flying aircraft and drones in diverse terrains. Vehicle-mounted air defense provides greater firepower, extended range, and armor protection, making it ideal for integrated, mobile battlefield operations requiring sustained air defense coverage.
Table of Comparison
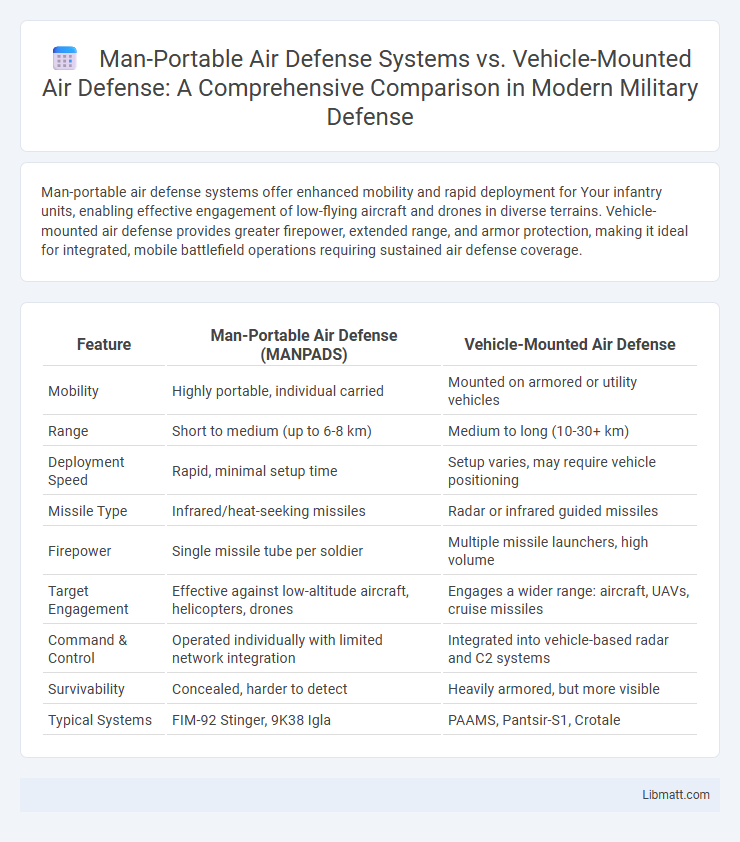
| Feature | Man-Portable Air Defense (MANPADS) | Vehicle-Mounted Air Defense |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Highly portable, individual carried | Mounted on armored or utility vehicles |
| Range | Short to medium (up to 6-8 km) | Medium to long (10-30+ km) |
| Deployment Speed | Rapid, minimal setup time | Setup varies, may require vehicle positioning |
| Missile Type | Infrared/heat-seeking missiles | Radar or infrared guided missiles |
| Firepower | Single missile tube per soldier | Multiple missile launchers, high volume |
| Target Engagement | Effective against low-altitude aircraft, helicopters, drones | Engages a wider range: aircraft, UAVs, cruise missiles |
| Command & Control | Operated individually with limited network integration | Integrated into vehicle-based radar and C2 systems |
| Survivability | Concealed, harder to detect | Heavily armored, but more visible |
| Typical Systems | FIM-92 Stinger, 9K38 Igla | PAAMS, Pantsir-S1, Crotale |
Introduction to Modern Air Defense Systems
Modern air defense systems differ significantly between man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) and vehicle-mounted counterparts, each offering unique tactical advantages and operational limitations. MANPADS provide infantry units with highly mobile, short-range surface-to-air missile capabilities, ideal for rapid deployment and engagement of low-flying aircraft. Vehicle-mounted air defense systems enhance protection with higher missile capacity, improved targeting radar, and greater range, adapting better to counter sophisticated aerial threats in diverse combat scenarios.
Defining Man-Portable Air Defense Systems (MANPADS)
Man-Portable Air Defense Systems (MANPADS) are lightweight, shoulder-fired surface-to-air missiles designed for rapid deployment by individual soldiers, providing effective short-range defense against low-flying aircraft and helicopters. These systems use infrared homing or other guidance technologies to track and engage aerial targets within a few kilometers, making them highly portable and ideal for infantry units. Your tactical advantage lies in MANPADS' agility and minimal logistical footprint compared to heavier vehicle-mounted air defense platforms.
Overview of Vehicle-Mounted Air Defense Systems
Vehicle-mounted air defense systems offer enhanced mobility and rapid deployment capabilities, equipped with advanced radar and missile technologies to intercept diverse aerial threats. These systems provide superior range and firepower compared to man-portable air defense, enabling protection of larger areas and ground forces from aircraft, drones, and missiles. Your defense strategy benefits from vehicle-mounted systems due to their integration with command networks and ability to operate in coordinated air defense layers.
Key Technical Differences Between MANPADS and Vehicle-Mounted Systems
MANPADS (Man-Portable Air Defense Systems) are lightweight, shoulder-fired missile systems designed for short-range targeting with infrared homing guidance, offering high mobility and quick deployment by individual soldiers. Vehicle-mounted air defense systems integrate larger missile launchers with radar and electro-optical tracking, enabling longer ranges, faster reaction times, and the ability to engage multiple targets simultaneously. The key technical differences lie in their range, targeting capabilities, sensor integration, and operational flexibility, with MANPADS favoring portability and vehicle-mounted systems prioritizing firepower and detection.
Deployment and Mobility Advantages
Man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) offer superior deployment flexibility due to their lightweight design, enabling rapid transport and concealment by individual soldiers in diverse terrains. Vehicle-mounted air defense systems provide enhanced mobility over larger distances and rough terrains, supporting sustained operations with integrated power supplies and advanced radar tracking. Both systems complement each other by balancing quick, agile response with extended operational range and firepower in integrated air defense strategies.
Range and Target Engagement Capabilities
Man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) typically offer shorter engagement ranges, generally up to 6 kilometers, suitable for targeting low-altitude threats such as helicopters and drones. Vehicle-mounted air defense systems extend this range significantly, often exceeding 20 kilometers, enabling engagement of high-speed aircraft, cruise missiles, and multiple simultaneous targets at varying altitudes. Your choice between these systems depends on operational needs for mobility, target versatility, and engagement distance.
Operational Scenarios: Urban vs. Battlefield Applications
Man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) excel in urban environments due to their lightweight design and ability to be rapidly deployed by infantry within confined spaces, providing targeted air defense against low-flying threats such as helicopters and drones. Vehicle-mounted air defense systems offer enhanced firepower, mobility, and radar integration suitable for expansive battlefield scenarios, effectively covering larger operational areas and engaging multiple targets simultaneously. Urban operations benefit from MANPADS' concealment and agility, while battlefield deployments prioritize vehicle-mounted systems for sustained area defense and power projection.
Cost-Effectiveness and Maintenance Considerations
Man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) offer superior cost-effectiveness due to their lower acquisition and operational expenses compared to vehicle-mounted air defense units, which require significant investment in platforms and infrastructure. Maintenance of MANPADS is generally simpler and less resource-intensive, relying on periodic checks and minimal technical support, whereas vehicle-mounted systems demand comprehensive upkeep, including engine servicing, electronic system diagnostics, and armored vehicle maintenance. The reduced logistical footprint of MANPADS enhances their suitability for rapid deployment and sustained operations in diverse environments, making them a strategic choice for budget-conscious military forces.
Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures
Man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) are vulnerable to detection and targeting due to their need for close proximity to threats, making operators susceptible to counter-fire and limiting their effective range. Vehicle-mounted air defense systems offer enhanced protection through armored platforms and integrated sensor suites, allowing rapid threat identification and target engagement while reducing operator exposure. Your choice between MANPADS and vehicle-mounted options should consider the trade-offs between mobility, stealth, and survivability in countermeasure deployment.
Future Trends in Air Defense Technology
Future trends in air defense technology highlight advancements in both man-portable air defense systems (MANPADS) and vehicle-mounted air defense platforms, emphasizing enhanced mobility, networked targeting, and integration with AI-driven threat detection. MANPADS are evolving to incorporate infrared counter-countermeasures and extended range missiles, providing individuals like you with greater flexibility in diverse combat scenarios. Meanwhile, vehicle-mounted systems are increasingly equipped with multi-sensor arrays and automated response capabilities, ensuring rapid and precise defense against emerging aerial threats such as drones and stealth aircraft.
man-portable air defense vs vehicle-mounted air defense Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com