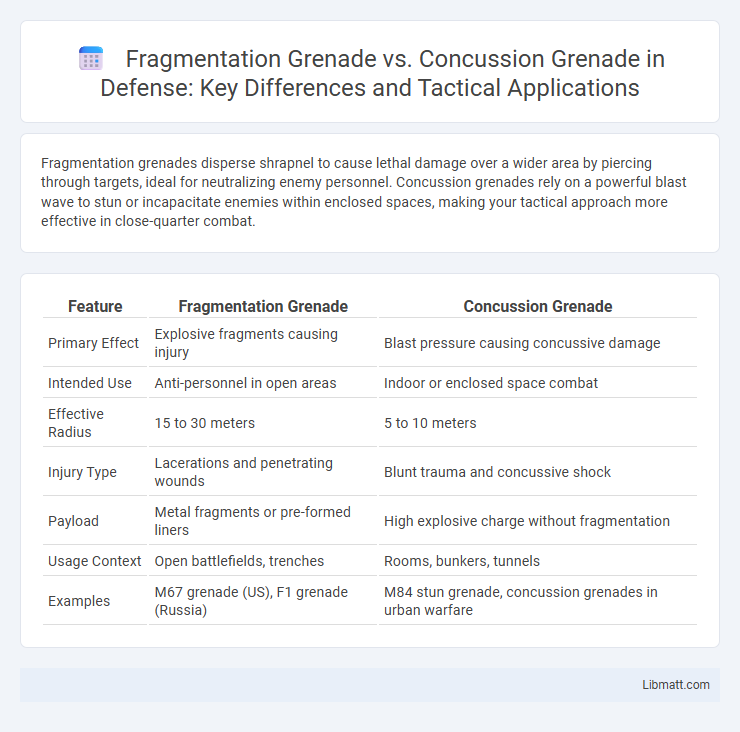
Fragmentation grenades disperse shrapnel to cause lethal damage over a wider area by piercing through targets, ideal for neutralizing enemy personnel. Concussion grenades rely on a powerful blast wave to stun or incapacitate enemies within enclosed spaces, making your tactical approach more effective in close-quarter combat.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fragmentation Grenade | Concussion Grenade |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Effect | Explosive fragments causing injury | Blast pressure causing concussive damage |
| Intended Use | Anti-personnel in open areas | Indoor or enclosed space combat |
| Effective Radius | 15 to 30 meters | 5 to 10 meters |
| Injury Type | Lacerations and penetrating wounds | Blunt trauma and concussive shock |
| Payload | Metal fragments or pre-formed liners | High explosive charge without fragmentation |
| Usage Context | Open battlefields, trenches | Rooms, bunkers, tunnels |
| Examples | M67 grenade (US), F1 grenade (Russia) | M84 stun grenade, concussion grenades in urban warfare |
Introduction to Grenade Types
Fragmentation grenades are designed to disperse metal fragments upon detonation, causing lethal damage over a wide radius, making them effective for neutralizing enemy personnel in open areas. Concussion grenades primarily rely on blast pressure and shockwaves to incapacitate targets through concussive force, ideal for enclosed spaces where shrapnel risk is minimized. Your choice between these grenade types depends on the tactical environment and intended effect on targets.
Fragmentation Grenades: Key Features
Fragmentation grenades are designed to disperse high-velocity metal shards upon detonation, maximizing damage over a wide radius and effectively targeting personnel in open areas. Their casing is engineered to fragment explosively, creating lethal shrapnel that can penetrate body armor and cause extensive injuries. These grenades are commonly used in military operations for clearing rooms, trenches, or outdoor environments where enemy forces are exposed.
Concussion Grenades: Core Characteristics
Concussion grenades deliver a powerful blast that primarily causes damage through overpressure and shockwaves rather than shrapnel, making them effective in enclosed spaces like bunkers or rooms. Their core characteristics include a heavy metal or plastic casing designed to maximize the blast effect, a relatively short delay fuse, and minimal fragmentation to reduce collateral injuries. Understanding these features can help you choose the right grenade type for close-quarters combat or situations where reducing shrapnel risk is critical.
Mechanisms of Action
Fragmentation grenades detonate and disperse metal shards to inflict injuries through high-velocity shrapnel, making them effective against personnel in open areas. Concussion grenades produce a powerful blast wave designed to incapacitate targets primarily through overpressure, making them more suitable for enclosed spaces. The differing mechanisms rely on fragmentation for physical piercing damage versus blast-induced trauma for disorientation and internal injury.
Lethality and Damage Profiles
Fragmentation grenades deliver lethal damage through shrapnel dispersion, causing widespread injury over a larger radius, making them highly effective against personnel in open areas. Concussion grenades inflict damage primarily through a powerful blast wave, producing devastating internal injuries and concussions within a more confined radius, ideal for enclosed spaces. The fragmentation grenade excels in area denial and casualty increase, while the concussion grenade is optimized for close-quarters combat and structural clearing.
Tactical Uses and Deployment
Fragmentation grenades are designed to disperse lethal shrapnel over a wide radius, making them ideal for targeting enemy personnel in open or covered positions during offensive and defensive combat operations. Concussion grenades rely on blast overpressure to incapacitate or disorient enemies within enclosed spaces such as bunkers, rooms, or trenches, making them effective for close-quarters combat and clearing confined areas. Your choice of grenade depends on the tactical context, where fragmentation grenades maximize lethal effect in open environments while concussion grenades prioritize shock and concussive force in tight, enclosed combat zones.
Safety Concerns and Handling
Fragmentation grenades pose higher safety risks due to their metal casing designed to disperse shrapnel upon detonation, necessitating strict handling protocols to avoid unintended injury. Concussion grenades create blast pressure with minimal fragmentation, making them safer to handle in close quarters but still requiring cautious use to prevent blast-related harm. Your training should emphasize proper grip, throw technique, and adherence to safety guidelines to mitigate risks with both grenade types.
Military and Law Enforcement Applications
Fragmentation grenades are primarily used in military and law enforcement operations for their ability to disperse lethal shrapnel over a wide radius, effectively neutralizing enemy personnel in open or confined spaces. Concussion grenades, also known as stun or blast grenades, generate powerful overpressure waves that incapacitate targets through shock without extensive fragmentation, making them suitable for urban combat, hostage rescue, and riot control where minimizing collateral damage is crucial. Tactical deployment decisions depend on mission objectives, with fragmentation grenades favored for offensive assaults and concussion grenades preferred for breaching and crowd management scenarios.
Historical Development and Evolution
Fragmentation grenades originated during World War I as anti-personnel weapons designed to disperse shrapnel upon detonation, evolving with improved casing materials to enhance lethality and reliability. Concussion grenades, developed later, primarily rely on blast overpressure rather than fragmentation, gaining prominence during World War II for use in enclosed spaces and against fortifications. Your understanding of these grenades benefits from their distinct tactical roles shaped by historical advancements in munitions technology.
Choosing the Right Grenade for the Mission
Selecting the appropriate grenade depends on the tactical mission's requirements; fragmentation grenades are ideal for dispersing shrapnel to neutralize enemy personnel over a wide area. Concussion grenades rely on blast overpressure to stun or disorient targets in enclosed spaces without causing extensive fragmentation damage. Your decision should consider the environment and the desired impact to maximize effectiveness and minimize unintended harm.
fragmentation grenade vs concussion grenade Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com