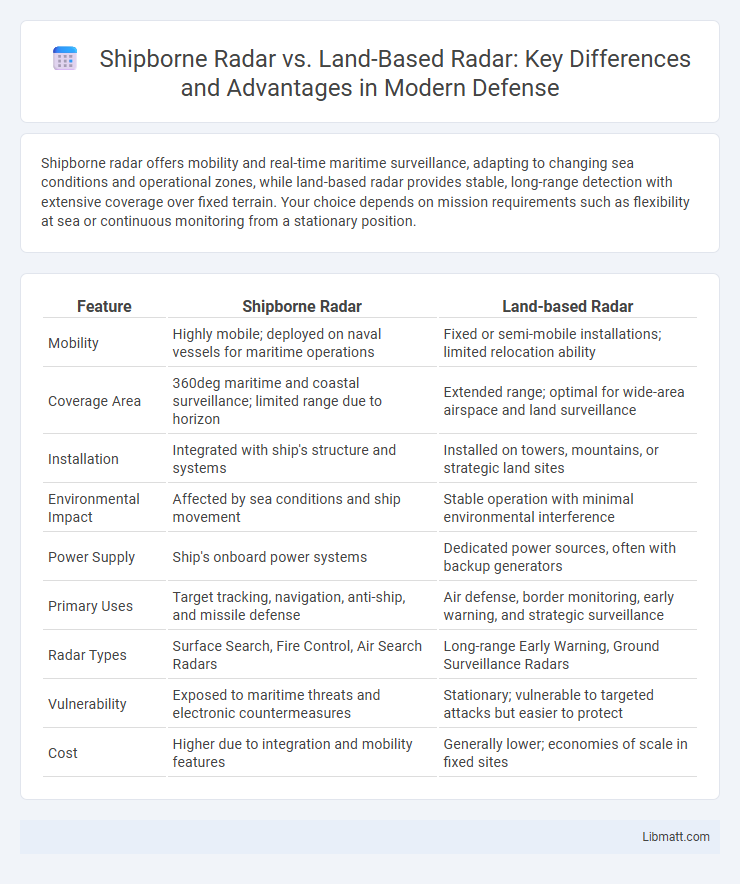
Shipborne radar offers mobility and real-time maritime surveillance, adapting to changing sea conditions and operational zones, while land-based radar provides stable, long-range detection with extensive coverage over fixed terrain. Your choice depends on mission requirements such as flexibility at sea or continuous monitoring from a stationary position.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shipborne Radar | Land-based Radar |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Highly mobile; deployed on naval vessels for maritime operations | Fixed or semi-mobile installations; limited relocation ability |
| Coverage Area | 360deg maritime and coastal surveillance; limited range due to horizon | Extended range; optimal for wide-area airspace and land surveillance |
| Installation | Integrated with ship's structure and systems | Installed on towers, mountains, or strategic land sites |
| Environmental Impact | Affected by sea conditions and ship movement | Stable operation with minimal environmental interference |
| Power Supply | Ship's onboard power systems | Dedicated power sources, often with backup generators |
| Primary Uses | Target tracking, navigation, anti-ship, and missile defense | Air defense, border monitoring, early warning, and strategic surveillance |
| Radar Types | Surface Search, Fire Control, Air Search Radars | Long-range Early Warning, Ground Surveillance Radars |
| Vulnerability | Exposed to maritime threats and electronic countermeasures | Stationary; vulnerable to targeted attacks but easier to protect |
| Cost | Higher due to integration and mobility features | Generally lower; economies of scale in fixed sites |
Introduction to Radar Systems
Shipborne radar systems are specially designed for maritime navigation and surveillance, incorporating features to withstand harsh sea conditions and detect objects over water surfaces with high precision. Land-based radar systems focus on terrestrial applications such as air traffic control, weather monitoring, and ground surveillance, offering wider range coverage and stable installation environments. Both systems utilize radio wave reflection principles but differ in antenna design, signal processing, and environmental adaptations to optimize performance in their respective domains.
Overview of Shipborne Radar
Shipborne radar systems are specifically designed to operate on moving vessels, providing real-time navigation, target detection, and weather monitoring capabilities essential for maritime safety. These radars often feature specialized stabilization technology to compensate for the ship's movement and sea conditions, ensuring accurate tracking and situational awareness. Your vessel's operational safety and mission effectiveness depend heavily on the precision and reliability of shipborne radar compared to static land-based radar installations.
Overview of Land-based Radar
Land-based radar systems are fixed installations that provide continuous, long-range surveillance and tracking capabilities critical for airspace monitoring and missile defense. These radars typically operate with higher power and larger antenna arrays, enabling precise detection of aircraft, weather formations, and ballistic projectiles over vast terrestrial areas. Their strategic placement on elevated terrain enhances signal coverage and reduces interference, making them essential components of national defense and air traffic control infrastructures.
Key Differences in Deployment
Shipborne radar systems are deployed directly on vessels, providing real-time maritime navigation and threat detection capabilities with mobility across oceans and seas. Land-based radar installations are fixed on terrestrial locations, offering broad, stationary coverage ideal for long-range surveillance, air traffic control, and early warning systems. The mobility of shipborne radar enables dynamic positioning and operational flexibility, while land-based radar benefits from stable infrastructure and higher power output for extended range and accuracy.
Range and Coverage Capabilities
Shipborne radar systems typically have shorter range capabilities compared to land-based radar due to power limitations and platform size but excel in providing 360-degree coverage essential for maritime navigation and threat detection. Land-based radars benefit from higher power outputs and elevated installation points, enabling greater range detection and broader horizon coverage over fixed terrestrial environments. The mobility of shipborne radar allows dynamic deployment in diverse oceanic regions, contrasting with the static, high-resolution long-range surveillance optimized by land-based radar installations.
Mobility and Flexibility Comparison
Shipborne radar offers superior mobility and flexibility compared to land-based radar systems, as it can be redeployed across vast oceanic regions to support dynamic maritime missions. Land-based radar installations, while often more powerful and stable, are fixed in location and limited by geographic constraints, restricting their coverage scope. Your operational strategy benefits from shipborne radar's ability to adapt quickly to changing mission parameters and emerging threats in diverse maritime environments.
Environmental and Operational Challenges
Shipborne radar faces unique environmental challenges such as saltwater corrosion, constant motion from waves, and limited space for installation, which impact its operational stability and maintenance. Land-based radar benefits from a stable, controlled environment with easier access for repairs but must contend with terrain obstacles and electromagnetic interference from urban infrastructure. Your radar system choice should consider these factors to ensure optimal performance in the intended operational setting.
Technological Advancements
Shipborne radar systems have integrated advanced phased-array antennas and adaptive signal processing to enhance target detection in harsh marine environments, outperforming many traditional land-based radars in real-time situational awareness. Land-based radar technologies emphasize high-resolution imaging and long-range surveillance capabilities, benefiting from stable platforms and extensive power supplies for continuous operation. Your choice between shipborne and land-based radar should consider these technological advancements based on mission requirements and environmental conditions.
Tactical Advantages and Limitations
Shipborne radar offers tactical advantages such as mobility, enabling real-time tracking of maritime targets and rapid repositioning for optimal coverage across vast ocean areas. Land-based radar systems benefit from stable, elevated installations providing prolonged surveillance with higher resolution and better clutter discrimination, though they lack flexibility in deployment. Your operational strategy must weigh shipborne radar's adaptability against land-based radar's superior range and fixed-site advantages to maximize situational awareness in diverse environments.
Applications and Future Trends
Shipborne radar excels in maritime navigation, targeting, and defense, enabling real-time threat detection and situational awareness in dynamic marine environments. Land-based radar applications include air traffic control, weather forecasting, and missile defense, providing extensive coverage and high-resolution data over fixed territories. Future trends emphasize integrating AI-driven analytics, enhanced sensor fusion, and increased automation to improve accuracy, adaptability, and operational efficiency across both platforms.
Shipborne radar vs Land-based radar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com