Hydraulic actuation offers high force density and precise control, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring strong and smooth power transmission. Electric actuation provides energy efficiency, easier maintenance, and greater responsiveness, enhancing Your system's flexibility in lighter or more compact designs.
Table of Comparison
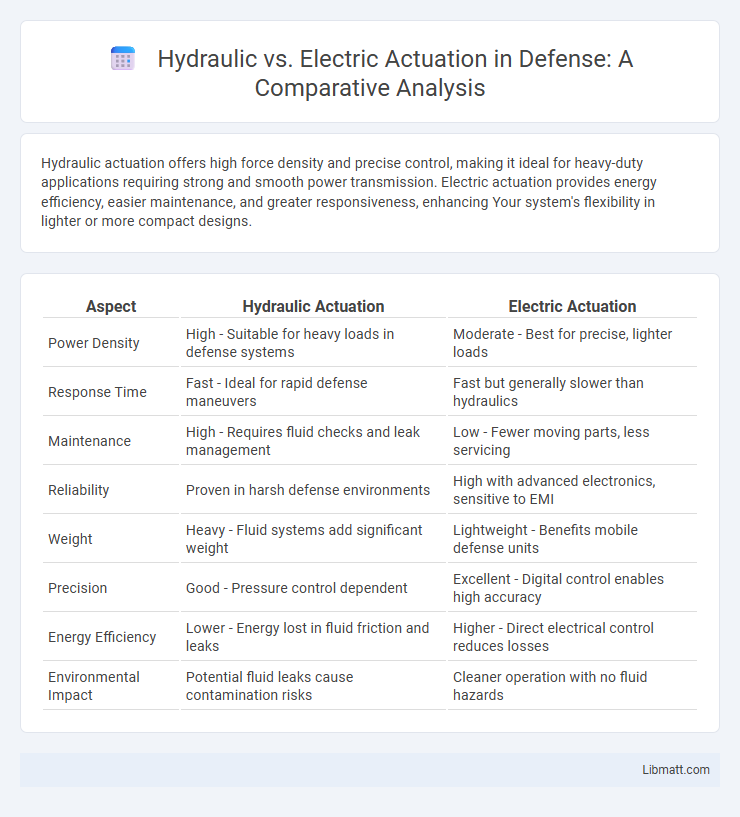
| Aspect | Hydraulic Actuation | Electric Actuation |
|---|---|---|
| Power Density | High - Suitable for heavy loads in defense systems | Moderate - Best for precise, lighter loads |
| Response Time | Fast - Ideal for rapid defense maneuvers | Fast but generally slower than hydraulics |
| Maintenance | High - Requires fluid checks and leak management | Low - Fewer moving parts, less servicing |
| Reliability | Proven in harsh defense environments | High with advanced electronics, sensitive to EMI |
| Weight | Heavy - Fluid systems add significant weight | Lightweight - Benefits mobile defense units |
| Precision | Good - Pressure control dependent | Excellent - Digital control enables high accuracy |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower - Energy lost in fluid friction and leaks | Higher - Direct electrical control reduces losses |
| Environmental Impact | Potential fluid leaks cause contamination risks | Cleaner operation with no fluid hazards |
Introduction to Actuation Systems
Hydraulic actuation systems utilize fluid pressure to generate powerful mechanical movement, offering high force density ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications and mobile machinery. Electric actuation relies on electric motors converting electrical energy into precise, controllable motion, favored in automation and robotics for energy efficiency and ease of integration. Both systems serve critical roles in modern engineering, with hydraulic actuation excelling in force-intensive tasks and electric actuation providing superior accuracy and responsiveness.
Overview of Hydraulic Actuation
Hydraulic actuation relies on pressurized fluid to generate powerful and precise motion, commonly used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment. This system offers high force density and excellent controllability under varying loads, making it ideal for applications requiring robust performance and durability. Hydraulic actuators excel in environments where compact size and consistent force output are critical factors.
Overview of Electric Actuation
Electric actuation uses electric motors to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, offering precise control and rapid response times ideal for automation systems. This technology provides high efficiency, reduced maintenance needs, and cleaner operation compared to hydraulic actuation, which relies on fluid pressure. Your choice of electric actuation supports energy savings and integration with digital control systems, enhancing overall performance in industrial applications.
Key Components and Operation Principles
Hydraulic actuation relies on key components such as pumps, valves, actuators, and hydraulic fluid to generate force and motion through fluid pressure, providing high power density and precise control in heavy-duty applications. Electric actuation uses electric motors, control circuits, and sensors to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, offering fast response times, efficiency, and ease of integration with digital control systems. Understanding your system requirements drives the choice between hydraulic systems' robust force capabilities and electric actuators' precision and energy efficiency.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Force, and Precision
Hydraulic actuation delivers superior force and high-speed response, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring powerful, rapid movements. Electric actuation excels in precision and control, providing finer positional accuracy with smoother operation and lower maintenance needs. Your choice depends on whether maximum force and speed or precise, energy-efficient performance is the priority.
Energy Efficiency and Power Consumption
Hydraulic actuation typically consumes more energy due to continuous fluid pressure maintenance and pump operation, resulting in higher power consumption and heat loss. Electric actuation offers superior energy efficiency through precise control of motor torque and speed, minimizing energy waste during idle or low-load conditions. Advanced electric actuators often integrate energy recovery technologies, further reducing overall power consumption compared to hydraulic systems.
Maintenance Requirements and Reliability
Hydraulic actuation systems typically demand regular maintenance due to fluid leaks, seal wear, and filter replacements, which can impact long-term reliability if neglected. Electric actuation offers lower maintenance needs with fewer moving parts and no fluid handling, enhancing overall system dependability and reducing downtime. Optimizing your machinery with electric actuators can lead to improved reliability and decreased maintenance costs.
Application Areas and Industry Preferences
Hydraulic actuation dominates heavy industries such as construction, mining, and aerospace due to its superior force output and durability under extreme conditions. Electric actuation is preferred in automotive, robotics, and consumer electronics where precision, energy efficiency, and low maintenance are critical. Industry trends show a growing shift toward electric actuation driven by advancements in motor technology and environmental regulations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydraulic actuation systems typically consume more energy and rely on fluid-based mechanisms that can cause leaks and environmental contamination, making them less sustainable compared to electric actuation. Electric actuators offer higher energy efficiency, reduced emissions, and easier integration with renewable energy sources, enhancing their environmental friendliness. Your choice of actuation technology directly influences operational sustainability and ecological responsibility in various applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Hydraulic actuation systems typically incur higher initial costs due to complex components and maintenance requirements, while electric actuation offers lower upfront expenses and reduced operational costs. Your choice impacts long-term economic efficiency, as electric actuators benefit from energy savings and simpler installation, whereas hydraulic systems may demand more frequent repairs and fluid management. Cost analysis should weigh lifecycle expenses, including energy consumption, maintenance, and downtime, ensuring optimized investment based on application needs.
hydraulic actuation vs electric actuation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com