RF seekers detect targets by emitting and receiving radio frequency signals, allowing for long-range tracking and resistance to adverse weather conditions, while IR seekers rely on detecting infrared radiation or heat emitted by targets, making them highly effective for identifying heat signatures in close to medium ranges. Your choice between RF seeker and IR seeker depends on the mission's environmental conditions and target characteristics.
Table of Comparison
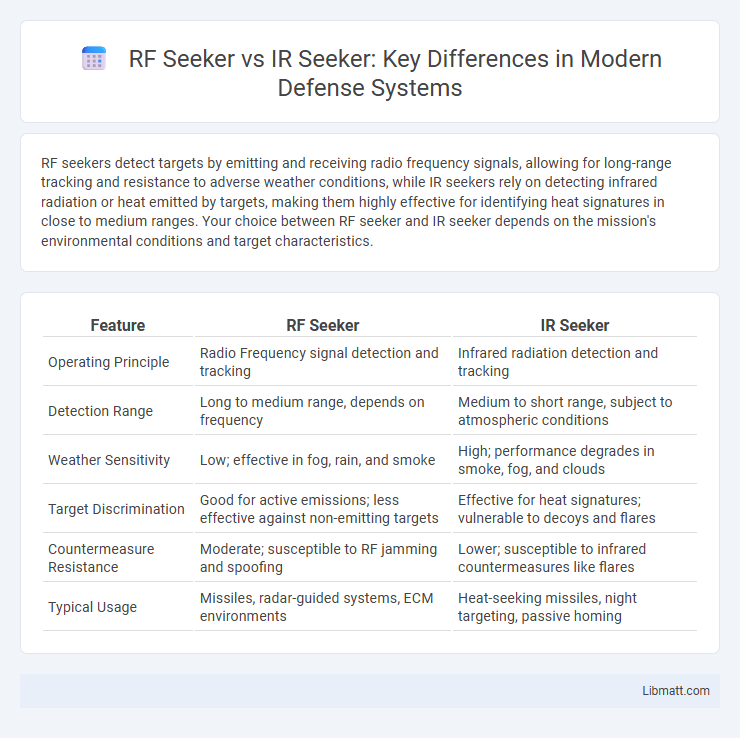
| Feature | RF Seeker | IR Seeker |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Radio Frequency signal detection and tracking | Infrared radiation detection and tracking |
| Detection Range | Long to medium range, depends on frequency | Medium to short range, subject to atmospheric conditions |
| Weather Sensitivity | Low; effective in fog, rain, and smoke | High; performance degrades in smoke, fog, and clouds |
| Target Discrimination | Good for active emissions; less effective against non-emitting targets | Effective for heat signatures; vulnerable to decoys and flares |
| Countermeasure Resistance | Moderate; susceptible to RF jamming and spoofing | Lower; susceptible to infrared countermeasures like flares |
| Typical Usage | Missiles, radar-guided systems, ECM environments | Heat-seeking missiles, night targeting, passive homing |
Introduction to RF and IR Seekers
RF seekers utilize radio frequency signals to detect and track targets by emitting and receiving electromagnetic waves, offering long-range capabilities and resistance to environmental obscurants. IR seekers rely on detecting infrared radiation emitted by a target's heat signature, enabling precise tracking in various weather conditions and providing high accuracy in close-range engagements. Both technologies are critical in modern missile guidance systems, with RF seekers excelling in beyond-visual-range scenarios and IR seekers being preferred for stealthy, heat-sensitive target acquisition.
Basic Principles of RF Seekers
RF seekers operate by detecting and homing in on radio frequency signals emitted or reflected by targets, allowing effective tracking even in adverse weather or low-visibility conditions. They analyze the amplitude, frequency, and phase of incoming RF signals to determine the target's location and movement. Your missile guidance benefits from RF seekers' ability to engage targets beyond line-of-sight and resist infrared countermeasures common in IR seekers.
Core Functionality of IR Seekers
IR seekers operate by detecting infrared radiation emitted from heat sources, allowing them to accurately track targets based on their thermal signatures. These seekers excel in environments with low visibility, such as smoke or darkness, by focusing on temperature differentials rather than relying on reflected signals. Their core functionality enables precise target acquisition and guidance in missile systems, especially against moving or heat-emitting objects.
Key Differences Between RF and IR Seekers
RF seekers operate by detecting radio frequency signals emitted or reflected by targets, offering superior long-range detection and all-weather capability. IR seekers track the infrared radiation or heat signatures from targets, providing higher resolution and better accuracy in close-range engagements but are more susceptible to environmental conditions. The fundamental difference lies in RF seekers' reliance on electromagnetic waves within the radio spectrum versus IR seekers' detection of thermal energy in the infrared spectrum.
Applications in Modern Missile Systems
RF seeker technology enhances modern missile systems by providing all-weather targeting capabilities and long-range detection, making it ideal for anti-radiation and air-to-air missiles. IR seeker systems excel in accurately detecting and tracking heat signatures from aircraft or vehicles, offering high precision in close-range engagements and countermeasures against stealth threats. Your choice between RF and IR seekers depends on mission-specific requirements such as range, environmental conditions, and target characteristics.
Advantages of RF Seekers
RF seekers offer superior target detection capabilities under adverse weather conditions such as fog, smoke, or dust, where IR seekers may struggle due to limited infrared signal availability. They provide extended range tracking and are less susceptible to countermeasures like flares that commonly deceive IR seekers. Enhanced signal processing in RF seekers improves target discrimination and resilience against electronic jamming, making them highly effective for modern missile guidance systems.
Strengths of IR Seekers
IR seekers excel in detecting and tracking heat signatures emitted by targets, providing high sensitivity in low-visibility conditions such as smoke, fog, or darkness. Their passive operation reduces the risk of detection, as they do not emit signals that could reveal the missile's presence. These seekers offer precise targeting against aircraft and vehicles by distinguishing thermal contrasts, enhancing accuracy against maneuvering or decoy-equipped adversaries.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Seeker Type
RF seekers face limitations such as susceptibility to electronic countermeasures and difficulty in detecting low radar cross-section targets at close range. IR seekers struggle with performance degradation in adverse weather conditions, such as fog or rain, and can be misled by thermal background clutter or decoys. Both seeker types require advanced signal processing algorithms to overcome targeting inaccuracies and environmental interferences.
Countermeasure Resistance: RF vs IR
RF seekers exhibit superior countermeasure resistance compared to IR seekers by operating across a broad frequency spectrum, enabling better discrimination of electronic warfare signals and reducing susceptibility to false targets. IR seekers, while effective in detecting heat signatures, are more vulnerable to flares and thermal decoys that can degrade their tracking accuracy. Advanced RF seekers integrate adaptive filtering and electronic counter-countermeasure (ECCM) techniques, enhancing resilience against jamming and spoofing attempts in complex combat environments.
Future Trends in Seeker Technology
Future trends in seeker technology emphasize enhanced sensor fusion, combining RF seeker and IR seeker capabilities to improve target detection and tracking in complex environments. Advances in artificial intelligence enable your systems to distinguish threats with greater accuracy, reducing false alarms and enhancing response times. Continued miniaturization and increased sensitivity of both RF and IR seekers will drive the development of more adaptive and versatile missile guidance systems.
RF seeker vs IR seeker Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com