Satellite jamming disrupts communication by overpowering signals with interference, rendering them unusable, while satellite spoofing tricks receivers by sending false signals to manipulate or deceive your navigation and communication systems. Understanding these threats is crucial for protecting satellite-based technologies from signal loss and data breaches.
Table of Comparison
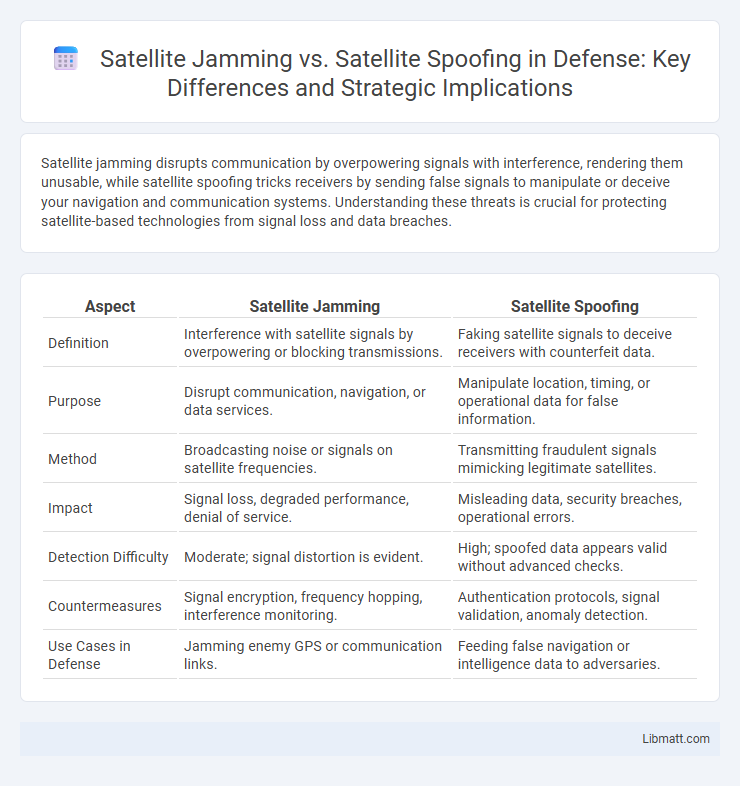
| Aspect | Satellite Jamming | Satellite Spoofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interference with satellite signals by overpowering or blocking transmissions. | Faking satellite signals to deceive receivers with counterfeit data. |
| Purpose | Disrupt communication, navigation, or data services. | Manipulate location, timing, or operational data for false information. |
| Method | Broadcasting noise or signals on satellite frequencies. | Transmitting fraudulent signals mimicking legitimate satellites. |
| Impact | Signal loss, degraded performance, denial of service. | Misleading data, security breaches, operational errors. |
| Detection Difficulty | Moderate; signal distortion is evident. | High; spoofed data appears valid without advanced checks. |
| Countermeasures | Signal encryption, frequency hopping, interference monitoring. | Authentication protocols, signal validation, anomaly detection. |
| Use Cases in Defense | Jamming enemy GPS or communication links. | Feeding false navigation or intelligence data to adversaries. |
Introduction to Satellite Jamming and Spoofing
Satellite jamming disrupts communication by overwhelming satellite signals with interference, rendering the targeted satellite's transmissions ineffective. In contrast, satellite spoofing involves sending counterfeit signals to deceive receivers, causing them to accept false data or manipulate positioning information. Both techniques pose significant threats to satellite navigation, communication, and surveillance systems, necessitating robust countermeasures in space security.
Understanding Satellite Jamming: Definition and Methods
Satellite jamming involves deliberately transmitting radio signals to interfere with the communication signals between a satellite and its receiver, effectively disrupting services such as GPS, telecommunications, and broadcasting. Common methods include barrage jamming, which floods the target frequency with noise, and spot jamming, which targets specific signals to cause localized disruption. Understanding these techniques helps in recognizing threats to satellite integrity and safeguarding Your critical satellite-dependent operations.
What Is Satellite Spoofing? Techniques and Tactics
Satellite spoofing involves the transmission of false signals to deceive satellite receivers, causing them to misinterpret their location or timing information. Techniques include signal replication with altered data, signal delay, or generation of counterfeit signals mimicking authentic satellite broadcasts, which confuse GPS or communication systems. Common tactics exploit vulnerabilities in signal authentication and weak encryption to manipulate navigation, timing, or communication functions critical for civilian and military applications.
Key Differences Between Jamming and Spoofing
Satellite jamming disrupts communication by overwhelming signals with noise, effectively blocking legitimate transmissions, whereas satellite spoofing deceives receivers by sending false signals that mimic authentic ones. Jamming attacks focus on signal interference and denial of service, while spoofing manipulates location data or command inputs, leading to potential misguidance. Understanding these key differences is crucial for protecting your satellite systems against distinct types of cyber threats.
Impacts on Communication and Navigation Systems
Satellite jamming disrupts communication and navigation systems by overwhelming signals with interference, causing loss of data transmission and degraded GPS accuracy. Satellite spoofing manipulates these systems by sending false signals, leading to incorrect positioning information and compromised decision-making. Your reliance on precise satellite data for operations can be severely impacted by both threats, resulting in reduced reliability and potential safety hazards.
Detection Methods for Jamming and Spoofing
Detection methods for satellite jamming primarily rely on signal quality monitoring through metrics such as signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and bit error rate (BER) to identify anomalous interference patterns. Satellite spoofing detection employs advanced cryptographic authentication and cross-referencing signals with known satellite ephemeris data to ensure signal integrity and origin verification. You can enhance protection by integrating real-time spectrum analysis and machine learning algorithms to differentiate between legitimate satellite signals and malicious disruptions.
Notable Incidents: Real-World Examples
Notable incidents of satellite jamming include the 2017 GPS disruption in the Black Sea region, which impacted commercial and military navigation systems, highlighting vulnerabilities in satellite communication. Satellite spoofing incidents such as the 2019 Iran Strait event involved false GPS signals redirecting ships, demonstrating risks to maritime security and navigation accuracy. Understanding these real-world examples emphasizes the importance of protecting your satellite-dependent infrastructure from cyber and electronic interference.
Mitigation Strategies and Countermeasures
Mitigation strategies for satellite jamming focus on enhancing signal resilience through techniques such as frequency hopping, beamforming, and power control to reduce interference impact. Countermeasures against satellite spoofing include robust cryptographic authentication, encryption of signal transmissions, and real-time anomaly detection algorithms to identify and prevent forged signals. Implementing multi-layered defense systems combining these approaches significantly strengthens satellite communication security and reliability.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Satellite jamming involves intentionally disrupting satellite signals, often violating international laws such as the ITU Radio Regulations that prohibit harmful interference with authorized transmissions. Satellite spoofing, which deceives receivers by mimicking legitimate satellite signals, raises severe ethical concerns as it can compromise navigation safety, data integrity, and national security, often falling under cybersecurity and telecommunications regulations. Both practices challenge global governance frameworks, require stringent enforcement mechanisms, and prompt ongoing debates about accountability, sovereignty, and the protection of critical space infrastructure.
Future Challenges and Evolving Threats
Future challenges in satellite security include increasingly sophisticated jamming techniques that disrupt signal integrity and evolving spoofing methods designed to deceive navigation and communication systems. Adversaries leverage advanced signal processing and AI to create more convincing fake signals, complicating detection and mitigation efforts. Protecting Your satellite operations will require adaptive technologies and robust encryption to counter these persistent threats in an evolving threat landscape.
satellite jamming vs satellite spoofing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com