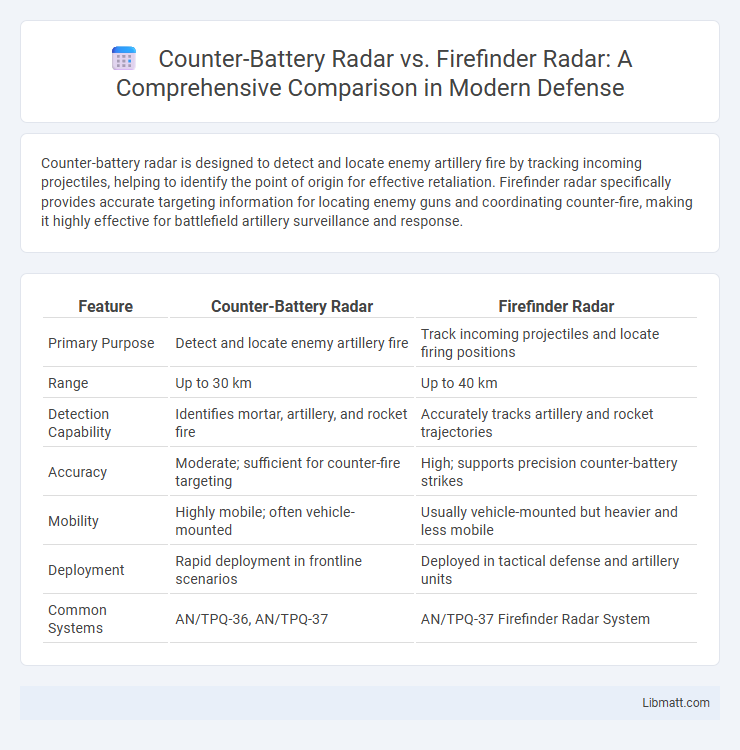
Counter-battery radar is designed to detect and locate enemy artillery fire by tracking incoming projectiles, helping to identify the point of origin for effective retaliation. Firefinder radar specifically provides accurate targeting information for locating enemy guns and coordinating counter-fire, making it highly effective for battlefield artillery surveillance and response.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Counter-Battery Radar | Firefinder Radar |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Detect and locate enemy artillery fire | Track incoming projectiles and locate firing positions |
| Range | Up to 30 km | Up to 40 km |
| Detection Capability | Identifies mortar, artillery, and rocket fire | Accurately tracks artillery and rocket trajectories |
| Accuracy | Moderate; sufficient for counter-fire targeting | High; supports precision counter-battery strikes |
| Mobility | Highly mobile; often vehicle-mounted | Usually vehicle-mounted but heavier and less mobile |
| Deployment | Rapid deployment in frontline scenarios | Deployed in tactical defense and artillery units |
| Common Systems | AN/TPQ-36, AN/TPQ-37 | AN/TPQ-37 Firefinder Radar System |
Introduction to Counter-Battery and Firefinder Radars
Counter-battery radars detect and track incoming artillery, mortar, and rocket fire to quickly locate the source and enable rapid counter-fire. Firefinder radar systems, a specialized subset of counter-battery radars, provide precise target acquisition and tracking with enhanced detection range and accuracy for artillery and missile threats. Both systems are integral to modern battlefield surveillance and force protection, using radar signal processing to identify and neutralize hostile fire sources effectively.
Defining Counter-Battery Radar: Key Functions
Counter-battery radar detects and locates enemy artillery fire to enable rapid counter-attacks and improve battlefield survivability. Firefinder radar is a specialized type of counter-battery radar designed to track and pinpoint incoming artillery shells and rockets with high precision. Your ability to neutralize threats quickly depends on the accuracy and responsiveness of these radar systems in detecting hostile fire origins.
Firefinder Radar: Features and Capabilities
Firefinder radar, developed by the U.S. Army, specializes in detecting and tracking incoming artillery, mortars, and rockets with high precision and rapid response time. Its advanced electronic scanning technology provides real-time location data for counter-battery fire, enhancing battlefield situational awareness and target engagement accuracy. The system integrates seamlessly with command and control networks, supporting both ground and air defense operations through automated target acquisition and tracking capabilities.
Historical Evolution: Counter-Battery vs Firefinder Technologies
Counter-battery radar technology originated during World War II, evolving from basic artillery detection methods to advanced radar systems capable of locating enemy fire through trajectory analysis. Firefinder radar, developed by the U.S. Army in the Cold War era, introduced precise electronic counter-battery capabilities with real-time tracking and target acquisition, significantly enhancing battlefield responsiveness. The evolution from early counter-battery radar to Firefinder systems marks a transition from rudimentary detection to sophisticated digital processing and integration with modern command and control networks.
Detection Range and Accuracy Comparison
Counter-battery radar typically offers a broader detection range, often exceeding 30 kilometers, allowing for early identification of enemy artillery positions. Firefinder radar, specialized for precise artillery tracking, provides superior accuracy with targeting errors usually within a few meters, enhancing your ability to coordinate counter-fire effectively. While Counter-battery radar prioritizes wide-area surveillance, Firefinder radar focuses on pinpoint precision, making each system suitable for different tactical needs based on range and accuracy requirements.
Mobility and Deployment in Battlefield Scenarios
Counter-battery radar systems prioritize rapid mobility and quick deployment to track enemy artillery fire in dynamic battlefield scenarios, often featuring lightweight designs and vehicle-mounted platforms for enhanced tactical flexibility. Firefinder radar systems, such as the AN/TPQ-36 and AN/TPQ-37, offer robust mobility with integrated transport and can be rapidly set up to provide continuous surveillance and targeting data across wide areas. Your choice between these radars should consider the specific mobility requirements and deployment speed necessary to maintain battlefield superiority and effective counter-artillery operations.
Technological Innovations: Radar Systems and Sensor Integration
Counter-battery radar systems utilize advanced phased-array antennas and Doppler processing technologies to detect and track incoming artillery projectiles with high precision. Firefinder radar integrates cutting-edge sensor fusion techniques combining radar signals with electro-optical and infrared sensors, enhancing target classification and situational awareness. Innovations in these radar systems focus on improving detection range, tracking accuracy, and rapid response capabilities through real-time data processing and networked sensor integration.
Operational Efficiency and Response Times
Counter-battery radar systems utilize advanced Doppler and phase array technologies to detect and track incoming artillery projectiles with high precision, enabling rapid counter-fire targeting. Firefinder radar, a specific type of counter-battery radar developed by AN/TPQ series, offers enhanced operational efficiency through its automated tracking algorithms and real-time threat analysis, significantly reducing response times. Both systems improve battlefield survivability by accelerating detection-to-engagement cycles, but Firefinder radars are often preferred for their integration capabilities with command and control networks, maximizing operational responsiveness.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Radar Type
Counter-battery radar faces challenges in detecting low-velocity rockets and mortars due to their limited radar cross-section and short flight times, which can hinder timely tracking and identification. Firefinder radar, while highly effective at long-range target acquisition, has limitations in cluttered urban environments where interference and signal reflections can degrade accuracy. Both radar types also contend with adverse weather conditions and electronic countermeasures that can reduce operational effectiveness and target discrimination capabilities.
Future Trends in Artillery Countermeasures Radar Systems
Future trends in artillery countermeasure radar systems emphasize enhanced detection accuracy and faster response times with advancements like artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms integrated into both Counter-battery radar and Firefinder radar platforms. These systems will increasingly feature multi-function capabilities, combining surveillance, target acquisition, and electronic warfare to improve battlefield situational awareness. Your investment in next-generation radar technology ensures superior counter-artillery capabilities by leveraging real-time data fusion and advanced signal processing.
Counter-battery radar vs Firefinder radar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com