Surface warfare focuses on combat operations involving naval vessels on the ocean's surface, utilizing ships, aircraft, and missiles to control sea lanes and engage enemy forces. Subsurface warfare targets underwater threats such as submarines and mines, requiring stealth tactics, sonar technology, and specialized weapons to protect Your fleet below the waves.
Table of Comparison
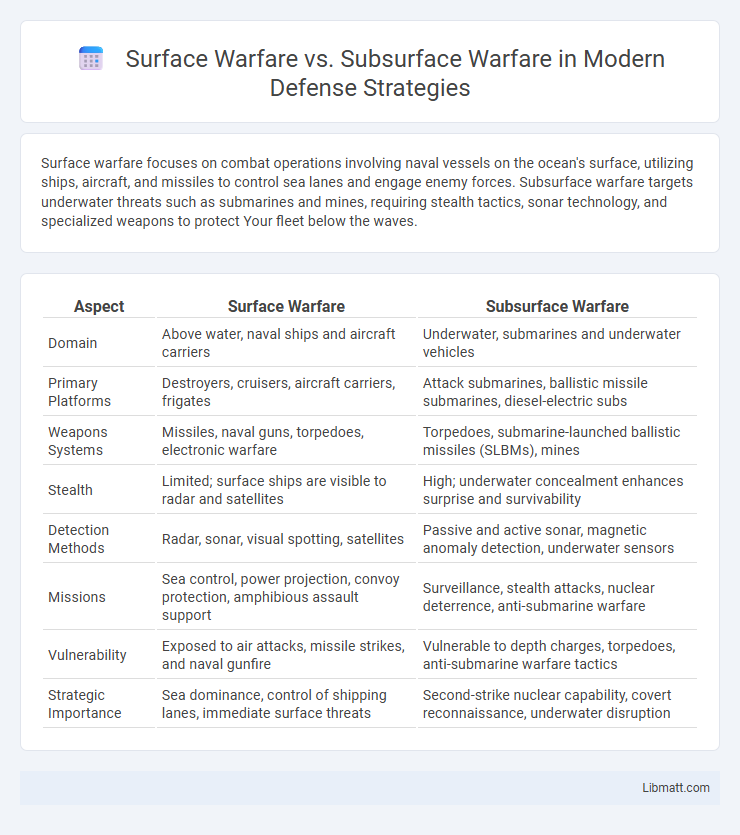
| Aspect | Surface Warfare | Subsurface Warfare |
|---|---|---|
| Domain | Above water, naval ships and aircraft carriers | Underwater, submarines and underwater vehicles |
| Primary Platforms | Destroyers, cruisers, aircraft carriers, frigates | Attack submarines, ballistic missile submarines, diesel-electric subs |
| Weapons Systems | Missiles, naval guns, torpedoes, electronic warfare | Torpedoes, submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), mines |
| Stealth | Limited; surface ships are visible to radar and satellites | High; underwater concealment enhances surprise and survivability |
| Detection Methods | Radar, sonar, visual spotting, satellites | Passive and active sonar, magnetic anomaly detection, underwater sensors |
| Missions | Sea control, power projection, convoy protection, amphibious assault support | Surveillance, stealth attacks, nuclear deterrence, anti-submarine warfare |
| Vulnerability | Exposed to air attacks, missile strikes, and naval gunfire | Vulnerable to depth charges, torpedoes, anti-submarine warfare tactics |
| Strategic Importance | Sea dominance, control of shipping lanes, immediate surface threats | Second-strike nuclear capability, covert reconnaissance, underwater disruption |
Introduction to Surface and Subsurface Warfare
Surface warfare involves naval operations conducted on the ocean's surface using ships, aircraft, and missiles to control sea lanes and engage enemy vessels. Subsurface warfare focuses on underwater combat primarily with submarines, deploying torpedoes and stealth tactics to detect and neutralize threats below the waterline. Your understanding of these distinct domains is crucial for appreciating the strategic complexities and technological advancements that define modern naval engagements.
Historical Evolution of Naval Combat
Surface warfare has evolved from wooden sailing ships armed with cannon broadsides to modern guided missile destroyers featuring advanced radar and missile systems, shaping naval dominance through direct ship-to-ship engagements. Subsurface warfare emerged in the early 20th century with the introduction of the submarine, revolutionizing naval combat by enabling stealth attacks on surface vessels and disrupting maritime logistics. The historical evolution of naval combat reflects a strategic shift from visible surface engagements to underwater stealth operations, fundamentally changing maritime tactics and defense technologies.
Key Technologies in Surface Warfare
Key technologies in surface warfare include advanced radar systems, electronic warfare capabilities, and missile defense mechanisms that enhance situational awareness and target engagement. Integrated combat systems like Aegis provide real-time data fusion and precision strike coordination, while stealth technologies reduce ship detectability against enemy sensors. Additionally, automated weapon platforms, such as vertical launch systems and close-in weapon systems (CIWS), enable rapid response to air, surface, and missile threats.
Innovations Driving Subsurface Warfare
Innovations in subsurface warfare have revolutionized underwater combat capabilities with advancements in stealth technology, autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), and enhanced sonar systems. These cutting-edge developments improve detection accuracy, reduce vulnerability to enemy sensors, and enable extended mission durations without surface support. Your strategic advantage in modern naval operations increasingly depends on leveraging these technological breakthroughs to dominate beneath the waves.
Tactical Approaches: Surface vs Subsurface Forces
Surface warfare relies on rapid maneuvering, overwhelming firepower, and electronic warfare systems to dominate vast maritime areas and establish control over sea lanes. Subsurface warfare emphasizes stealth, surprise attacks, and advanced sonar technology to detect and engage enemy vessels while remaining undetected beneath the ocean surface. Your tactical approach must balance the visibility and firepower advantages of surface forces with the covert, precision capabilities of subsurface units to achieve comprehensive maritime dominance.
Threat Detection and Countermeasures
Surface warfare relies heavily on radar and optical sensors for threat detection, enabling rapid identification of enemy vessels and missiles above the water. Subsurface warfare prioritizes sonar systems, both passive and active, to detect underwater threats such as submarines and mines. Countermeasures include electronic warfare and decoys for surface threats, while deploying acoustic countermeasures and torpedoes targets underwater opponents effectively.
Advantages and Limitations of Surface Vessels
Surface vessels offer superior speed, maneuverability, and ease of communication compared to subsurface warfare platforms, making them highly effective for rapid response and area control. Their advanced radar and missile systems enhance offensive and defensive capabilities, but limitations include higher visibility to enemy detection and vulnerability to air and missile attacks. You benefit from the ability to project power over vast ocean areas, though surface ships require robust defense strategies to mitigate exposure risks.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Submarines
Submarines excel in stealth and surprise, enabling covert reconnaissance and undetected attacks in subsurface warfare, but their limited speed and vulnerability when surfaced are notable weaknesses. Their ability to operate silently and launch torpedoes or missiles makes them formidable against surface ships, yet restricted space and lengthy missions can affect crew endurance. Your strategic advantage lies in leveraging submarines' concealment to avoid detection, maximizing strike potential while mitigating exposure risks.
Modern Naval Conflicts: Case Studies
Modern naval conflicts highlight distinct strategies and technologies between surface warfare and subsurface warfare. Surface warfare leverages advanced missile systems, radar, and electronic warfare on destroyers and frigates, as demonstrated in the 2020 Strait of Hormuz tensions, where surface ships maintained control of key maritime chokepoints. Subsurface warfare, critical in stealth and surprise attacks, uses nuclear-powered submarines equipped with torpedoes and ballistic missiles, as seen in the 2022 South China Sea confrontations where subsurface forces ensured underwater dominance and strategic deterrence. Your understanding of these dynamics is essential for grasping the evolving scope of modern naval power projection.
Future Trends in Maritime Warfare
Future trends in maritime warfare emphasize advanced autonomous surface vessels equipped with AI-driven sensors and weapons systems, enhancing real-time threat detection and response in surface warfare. In subsurface warfare, developments include next-generation stealth submarines employing enhanced acoustic cloaking and underwater drones capable of extended reconnaissance and targeted strikes. Integration of network-centric warfare technologies aims to create a seamless maritime battlespace, combining surface and subsurface assets for coordinated dominance.
Surface warfare vs Subsurface warfare Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com