String inverters efficiently manage power conversion for multiple solar panels connected in series, offering a cost-effective solution for uniform sun exposure conditions. Microinverters optimize energy harvest from each individual panel, enhancing overall system performance and reliability in areas with shading or varied panel orientation, making them ideal for maximizing your solar energy output.
Table of Comparison
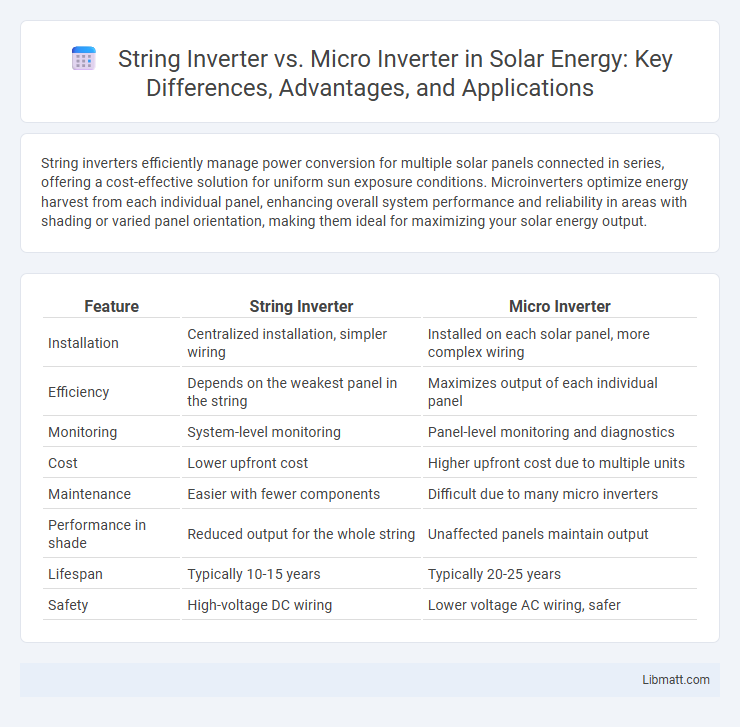
| Feature | String Inverter | Micro Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Centralized installation, simpler wiring | Installed on each solar panel, more complex wiring |
| Efficiency | Depends on the weakest panel in the string | Maximizes output of each individual panel |
| Monitoring | System-level monitoring | Panel-level monitoring and diagnostics |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost due to multiple units |
| Maintenance | Easier with fewer components | Difficult due to many micro inverters |
| Performance in shade | Reduced output for the whole string | Unaffected panels maintain output |
| Lifespan | Typically 10-15 years | Typically 20-25 years |
| Safety | High-voltage DC wiring | Lower voltage AC wiring, safer |
Introduction to Solar Inverter Technologies
String inverters convert direct current (DC) from a series of solar panels into alternating current (AC) for home or grid use, offering centralized system management and cost efficiency. Microinverters attach to individual solar panels, optimizing power output per panel and improving energy harvest in shaded or complex roof configurations. Both technologies play crucial roles in solar energy systems, influencing performance, installation complexity, and maintenance.
What is a String Inverter?
A string inverter is a centralized device that converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by multiple solar panels connected in series into alternating current (AC) for use in your home or grid. It manages the power output of the entire solar panel string as one unit, optimizing efficiency based on the weakest panel's performance. String inverters are cost-effective and commonly used in residential and commercial solar power systems, especially where panels receive uniform sunlight exposure.
What is a Micro Inverter?
A micro inverter is a small solar power inverter that converts the direct current (DC) output of a single solar panel into alternating current (AC) individually, allowing for optimized energy production at the panel level. Unlike string inverters, which manage multiple panels collectively, micro inverters enhance performance in shaded or complex roof installations by reducing the impact of one panel's shading or malfunction on the entire system. Understanding the role of micro inverters can help you maximize the efficiency and reliability of your solar energy setup.
How String Inverters Work
String inverters convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels connected in series into alternating current (AC) for household or grid use. These inverters manage power from multiple panels as a single string, optimizing overall output but potentially limiting efficiency if one panel underperforms. Their centralized design simplifies maintenance but may reduce energy harvest compared to panel-level optimization found in microinverters.
How Micro Inverters Operate
Micro inverters operate by converting direct current (DC) generated from individual solar panels into alternating current (AC) at the module level, maximizing energy harvest from each panel independently. Unlike string inverters which handle the DC to AC conversion for an entire array, micro inverters optimize performance under varying shading or orientation conditions by isolating panel output. This module-level conversion enhances system efficiency, improves monitoring, and reduces the impact of panel-level failures on overall energy production.
Efficiency Comparison: String Inverter vs Micro Inverter
String inverters generally provide higher efficiency rates, often around 97-98%, due to centralized energy conversion and reduced power loss. Micro inverters optimize each solar panel individually, enhancing overall system performance in shaded or complex roof layouts but typically have slightly lower peak efficiency, averaging 95-96%. Your choice between the two affects energy yield, with string inverters excelling in uniform sunlight conditions and micro inverters maximizing output under variable shading.
Installation and Scalability Differences
String inverters feature centralized installation, connecting multiple solar panels in series to one inverter, which simplifies initial setup but limits expansion flexibility. Microinverters are installed on each solar panel individually, allowing easy scalability by adding panels without redesigning the system. Your choice impacts future upgrades, with microinverters offering greater modularity and simplified installation for expanding solar arrays.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Microinverters offer enhanced reliability by isolating individual panels, reducing the impact of single-point failures and simplifying maintenance since issues can be pinpointed and addressed at the module level. String inverters, while typically easier to service due to centralized components, may experience downtime if the entire string is affected by a single panel failure, potentially increasing maintenance complexity. The decentralized design of microinverters often results in lower maintenance costs and improved system uptime compared to traditional string inverter setups.
Cost Analysis: String Inverter vs Micro Inverter
String inverters generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to micro inverters, making them a budget-friendly choice for larger solar installations. Micro inverters, while pricier initially, provide higher efficiency and better shading tolerance, potentially increasing your overall energy yield and long-term savings. Evaluating your system size and shading conditions will help determine whether the upfront cost of micro inverters justifies the potential gains over string inverters.
Which Inverter Is Best for Your Solar Project?
String inverters are cost-effective and ideal for large-scale solar projects with uniform shading, offering centralized monitoring and simpler maintenance. Microinverters provide optimum energy harvest for complex roofs with multiple orientations by maximizing output from each panel independently. Choosing the best inverter depends on your solar array layout, budget, and shading conditions to ensure maximum efficiency and return on investment.
String inverter vs Micro inverter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com