Smart meters provide real-time energy usage data, enabling you to monitor and manage consumption more efficiently compared to analog meters, which only record cumulative usage manually. With smart meters, energy providers can offer more accurate billing and faster outage detection, improving overall service reliability.
Table of Comparison
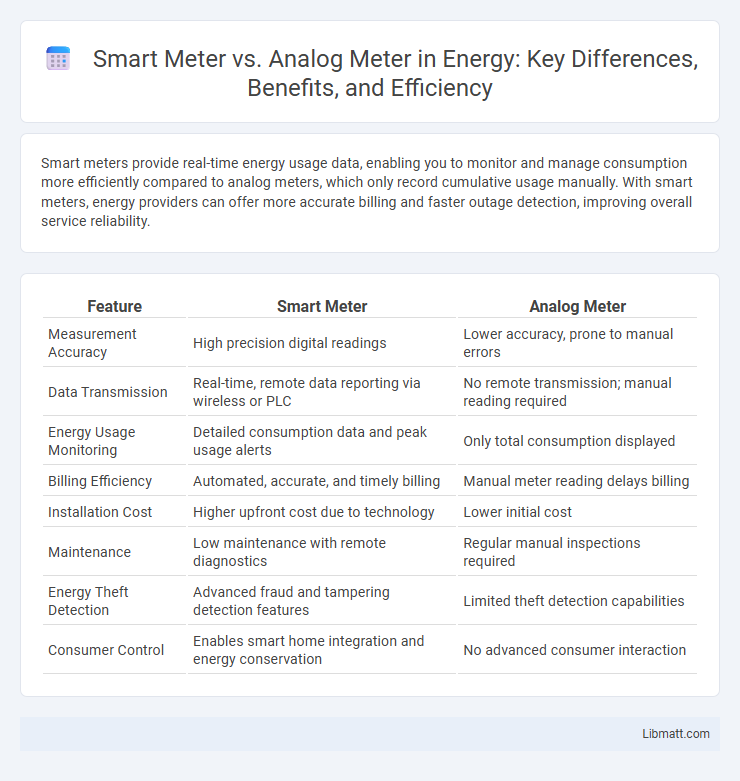
| Feature | Smart Meter | Analog Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Accuracy | High precision digital readings | Lower accuracy, prone to manual errors |
| Data Transmission | Real-time, remote data reporting via wireless or PLC | No remote transmission; manual reading required |
| Energy Usage Monitoring | Detailed consumption data and peak usage alerts | Only total consumption displayed |
| Billing Efficiency | Automated, accurate, and timely billing | Manual meter reading delays billing |
| Installation Cost | Higher upfront cost due to technology | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with remote diagnostics | Regular manual inspections required |
| Energy Theft Detection | Advanced fraud and tampering detection features | Limited theft detection capabilities |
| Consumer Control | Enables smart home integration and energy conservation | No advanced consumer interaction |
Introduction to Smart Meters and Analog Meters
Smart meters are digital devices that provide real-time energy usage data, enabling remote monitoring and automatic billing, while analog meters use mechanical dials to record electricity consumption manually. Unlike analog meters, smart meters offer enhanced accuracy, instant data transmission, and support for dynamic pricing models. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions about upgrading to more efficient energy monitoring technology.
How Smart Meters Work
Smart meters use digital technology to record electricity consumption in real time and transmit this data wirelessly to utility companies, enabling accurate and timely billing. Unlike analog meters, which require manual readings and display usage through mechanical dials, smart meters automatically track electricity usage with high precision. Your energy consumption patterns can be monitored remotely, allowing for better energy management and potential cost savings.
How Analog Meters Function
Analog meters function by using a spinning disk mechanism driven by the flow of electric current through coils, which generates a magnetic field proportional to energy consumption. The rotating disk moves a series of gears connected to a numerical display, recording cumulative electricity usage in kilowatt-hours. Unlike smart meters, analog meters provide only cumulative readings without real-time data transmission or consumption analysis.
Key Differences Between Smart and Analog Meters
Smart meters provide real-time data on electricity usage, enabling better energy management and accurate billing, while analog meters rely on mechanical dials and manual readings, which can lead to estimation errors. Smart meters support remote monitoring and automated data transmission, whereas analog meters require onsite visits for meter reading. Your energy consumption insights improve significantly with smart meters, allowing for more efficient usage and cost savings compared to traditional analog meters.
Advantages of Smart Meters
Smart meters provide real-time energy consumption data, allowing you to monitor usage more accurately and manage your electricity costs effectively. They enable automated meter readings, eliminating the need for manual readings and reducing errors associated with analog meters. Enhanced features like remote disconnects, outage detection, and integration with smart home systems make smart meters a superior choice for modern energy management.
Limitations of Smart Meters
Smart meters face limitations such as data security concerns and potential privacy issues due to continuous data transmission. Connectivity problems may disrupt real-time data reporting, impacting accuracy and timely energy usage tracking. High initial installation costs and compatibility challenges with older infrastructure can also hinder smart meter deployment.
Benefits of Analog Meters
Analog meters provide reliable, low-cost energy measurement with minimal maintenance and no dependency on external power sources or complex digital systems. Their simple mechanical design offers durability and long-term accuracy in varied environmental conditions. Analog meters are less susceptible to cybersecurity risks compared to smart meters, ensuring data privacy without the need for network connectivity.
Drawbacks of Analog Meters
Analog meters suffer from limited accuracy and manual reading errors, leading to billing discrepancies and inefficient energy management. These meters lack real-time data transmission, preventing timely detection of outages or abnormal consumption patterns. Your energy usage insights remain minimal, hindering optimization and cost savings.
Impact on Energy Efficiency and Consumption
Smart meters enable real-time monitoring of energy usage, allowing consumers to identify high consumption periods and adjust behavior to reduce waste, significantly enhancing energy efficiency. Unlike analog meters, which provide only monthly consumption totals, smart meters facilitate detailed data analysis, promoting informed energy management and lowering overall consumption. This advanced monitoring capability helps reduce peak demand and supports utility providers in optimizing grid performance and integrating renewable energy sources.
Choosing the Right Meter for Your Needs
Smart meters offer real-time energy usage data and remote monitoring capabilities, ideal for households seeking precise consumption tracking and automated billing. Analog meters, though less advanced, provide basic energy measurement without the need for digital infrastructure, making them suitable for areas with limited connectivity or lower tech requirements. Evaluating your access to smart grid technology, budget constraints, and desire for detailed usage analytics helps determine whether a smart or analog meter best fits your energy management needs.
Smart Meter vs Analog Meter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com