Smart meters provide real-time energy usage data, enabling you to monitor and manage your consumption more efficiently than traditional meters, which only record cumulative usage. This enhanced visibility helps reduce energy costs and supports more sustainable living practices.
Table of Comparison
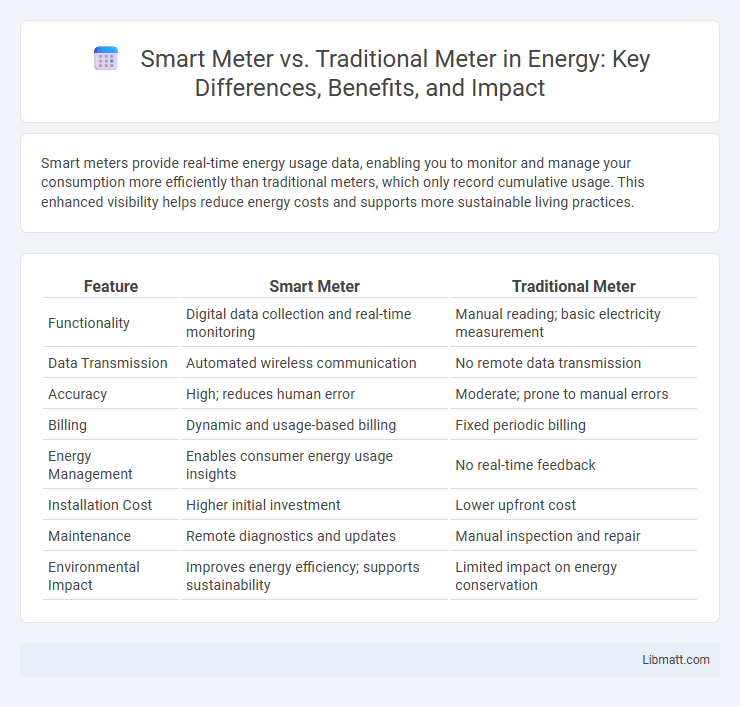
| Feature | Smart Meter | Traditional Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Digital data collection and real-time monitoring | Manual reading; basic electricity measurement |
| Data Transmission | Automated wireless communication | No remote data transmission |
| Accuracy | High; reduces human error | Moderate; prone to manual errors |
| Billing | Dynamic and usage-based billing | Fixed periodic billing |
| Energy Management | Enables consumer energy usage insights | No real-time feedback |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Maintenance | Remote diagnostics and updates | Manual inspection and repair |
| Environmental Impact | Improves energy efficiency; supports sustainability | Limited impact on energy conservation |
Introduction to Smart Meters and Traditional Meters
Smart meters provide real-time energy usage data through digital technology, enabling accurate monitoring and remote communication with utility providers. Traditional meters record energy consumption using mechanical or electromechanical methods, requiring manual readings and offering no immediate data access. The transition to smart meters supports efficient energy management and faster response times for both consumers and utilities.
How Traditional Meters Work
Traditional meters operate by mechanically measuring electricity consumption through a spinning disc that moves in proportion to the amount of electrical current used. These meters record cumulative usage and require manual readings to monitor your energy consumption. The lack of remote data transmission means updates are often delayed compared to smart meters.
How Smart Meters Work
Smart meters function by using digital technology to record electricity consumption in real-time and communicate data wirelessly to utility providers. These advanced devices measure energy usage at frequent intervals, enabling precise tracking and remote monitoring without manual readings. The integration of smart meters facilitates dynamic pricing, improves grid management, and enhances customer energy awareness.
Key Differences Between Smart and Traditional Meters
Smart meters provide real-time energy consumption data, enabling consumers and utility providers to monitor usage more accurately and optimize energy efficiency, while traditional meters record cumulative usage and require manual reading. Unlike traditional meters, smart meters support automated data transmission, reducing labor costs and allowing for quicker detection of faults or power outages. Additionally, smart meters facilitate dynamic pricing models and demand response programs, features absent in traditional metering systems.
Benefits of Smart Meters
Smart meters provide real-time energy consumption data, enabling more accurate billing and better energy management compared to traditional meters. They help detect outages faster and facilitate remote monitoring and control, reducing the need for manual meter readings. You can optimize your energy use and lower utility costs by leveraging the detailed insights smart meters offer.
Limitations of Traditional Meters
Traditional meters have limitations such as requiring manual readings, which can lead to human errors and delayed billing cycles. They often lack real-time data transmission, preventing timely energy consumption monitoring and efficient demand management. Your energy management can be significantly improved by switching to smart meters, which offer automated readings and instant data access.
Energy Monitoring and Data Accuracy
Smart meters provide real-time energy monitoring with high data accuracy, enabling you to track consumption patterns instantly and make informed energy-saving decisions. Unlike traditional meters, which require manual readings and may have delays or errors, smart meters automatically transmit precise usage data to utility companies. This enhanced accuracy and continuous monitoring contribute to optimized energy management and more accurate billing.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Maintenance
Smart meters typically have higher initial installation costs compared to traditional meters due to advanced technology and integration with digital systems. Maintenance expenses for smart meters are generally lower over time because they enable remote diagnostics and reduce the need for manual inspections. Traditional meters involve lower upfront costs but incur higher long-term maintenance expenses due to manual reading and potential service visits.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Smart meters collect real-time energy usage data, raising concerns about potential unauthorized access and data breaches compared to traditional meters, which record usage less frequently and store minimal information. Advanced encryption and secure communication protocols are essential for protecting smart meter data from cyberattacks and ensuring user privacy. Your security depends on utility providers implementing robust privacy policies and regularly updating smart meter software to mitigate risks associated with data interception and misuse.
Future Trends in Metering Technology
Smart meters are rapidly transforming metering technology by enabling real-time energy consumption monitoring, remote data transmission, and enhanced grid management, unlike traditional meters that rely on manual readings. Future trends emphasize the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, advanced analytics, and artificial intelligence to optimize energy efficiency and support dynamic pricing models. Your energy usage will become more transparent and controllable as smart meters pave the way for sustainable and interconnected energy systems.
Smart Meter vs Traditional Meter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com