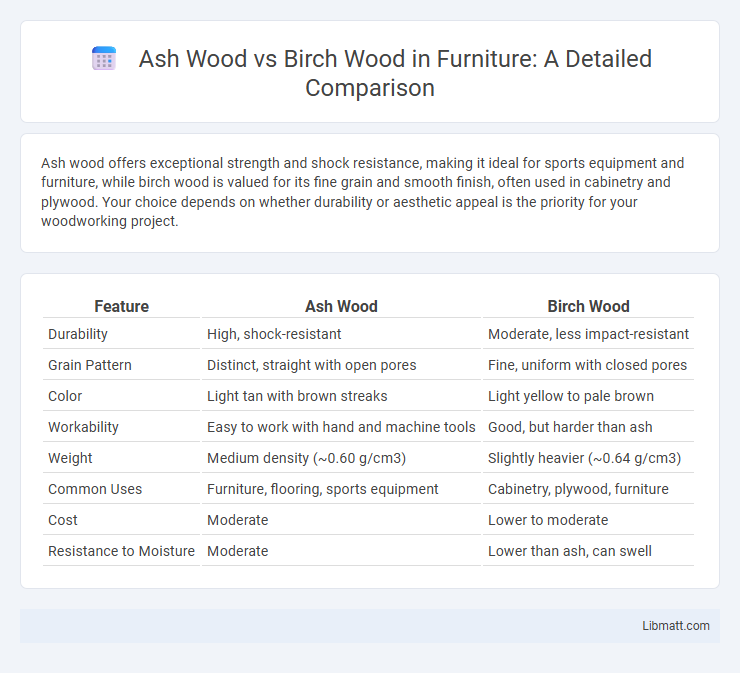
Ash wood offers exceptional strength and shock resistance, making it ideal for sports equipment and furniture, while birch wood is valued for its fine grain and smooth finish, often used in cabinetry and plywood. Your choice depends on whether durability or aesthetic appeal is the priority for your woodworking project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ash Wood | Birch Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, shock-resistant | Moderate, less impact-resistant |
| Grain Pattern | Distinct, straight with open pores | Fine, uniform with closed pores |
| Color | Light tan with brown streaks | Light yellow to pale brown |
| Workability | Easy to work with hand and machine tools | Good, but harder than ash |
| Weight | Medium density (~0.60 g/cm3) | Slightly heavier (~0.64 g/cm3) |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, sports equipment | Cabinetry, plywood, furniture |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower to moderate |
| Resistance to Moisture | Moderate | Lower than ash, can swell |
Introduction to Ash Wood and Birch Wood
Ash wood, known for its durability and light color, is commonly used in furniture, flooring, and sports equipment due to its strong yet flexible grain structure. Birch wood features a fine, even texture with a pale color, making it popular for cabinetry, plywood, and decorative veneers. Both woods offer excellent workability and strength but differ in grain patterns and finish versatility.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Ash wood derives from the genus Fraxinus, predominantly found in temperate regions of North America, Europe, and Asia, thriving in moist, well-drained soils. Birch wood originates from the Betula genus, commonly distributed across northern temperate zones, especially in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, favoring cooler climates and well-drained sandy soils. Both woods are integral to diverse ecosystems but differ in botanical classification and habitat preferences, influencing their physical characteristics and usage.
Physical Appearance and Grain Patterns
Ash wood features a light beige to pale brown color with a straight, pronounced grain pattern that often displays prominent growth rings and a coarse texture. Birch wood, in contrast, has a pale yellow to creamy white hue with a fine, even grain and a smoother surface, sometimes exhibiting occasional curls or waves. Your choice between ash and birch wood will depend on whether you prefer a bold, rustic look or a subtle, uniform appearance in your woodworking projects.
Hardness and Durability Comparison
Ash wood has a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1,320, making it moderately hard and highly durable, ideal for flooring and furniture requiring strength. Birch wood, with a Janka hardness of around 1,260, is slightly softer but still offers good durability for various woodworking projects. Both woods provide solid hardness and durability, with ash generally preferred for heavy-use applications due to its greater resilience.
Workability and Machining Properties
Ash wood offers excellent workability with smooth cutting, sanding, and nailing, making it ideal for intricate woodworking projects. Birch wood, while also workable, tends to be harder and denser, requiring sharper tools and more effort during machining. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize ease of shaping with ash or the strong, fine grain finish achievable with birch.
Common Uses in Furniture and Flooring
Ash wood is prized in furniture making for its strength, light color, and attractive grain, commonly used in chairs, tables, and cabinetry. Birch wood, valued for its fine grain and smooth finish, is frequently utilized in flooring, plywood, and delicate furniture pieces. Your choice between ash and birch depends on durability needs and the desired aesthetic for interior design projects.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Ash wood typically commands a higher price than birch due to its durability and popularity in furniture and flooring, making it less accessible for budget-conscious projects. Birch wood is more readily available and affordable, often preferred for cost-effective woodworking without sacrificing aesthetic appeal. Your choice between ash and birch should consider these factors to balance quality and budget effectively.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ash wood is prized for its renewability, as ash trees grow relatively quickly and can be sustainably harvested with proper forest management practices. Birch wood, while generally abundant, requires careful sourcing to prevent deforestation and maintain biodiversity, especially in regions with high logging activity. Your choice between ash and birch wood should consider certified sustainability standards like FSC to minimize environmental impact and support responsible forestry.
Maintenance and Longevity Tips
Ash wood requires regular sealing and occasional sanding to maintain its durability against moisture and wear, ensuring a lifespan of up to 50 years with proper care. Birch wood benefits from consistent cleaning and protective finishes to prevent staining and warping, typically lasting around 20 to 40 years depending on environmental conditions. You can extend the longevity of both woods by avoiding excessive humidity and using appropriate wood oils or sealants tailored for each species.
Choosing Between Ash Wood and Birch Wood
Ash wood offers exceptional durability and a distinct grain pattern ideal for furniture requiring strength, while birch wood provides a fine, even texture that excels in cabinetry and decorative projects. Birch is typically lighter in color with a smooth finish, making it easier to paint or stain uniformly, whereas ash boasts greater shock resistance and flexibility, suitable for flooring and sports equipment. When choosing between ash wood and birch wood, consider your project's needs for hardness, appearance, and finishing options to ensure your final result meets both functional and aesthetic goals.
Ash wood vs birch wood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com