Blockboard consists of a core made from wooden strips sandwiched between veneer sheets, providing stability and resistance to warping, while plywood is made by gluing multiple thin layers of wood veneers with grains oriented at right angles, offering superior strength and flexibility. Choosing between blockboard and plywood depends on Your project's need for lightweight panels or structural durability, with plywood often preferred for heavy-duty applications and blockboard for furniture and interior partitions.
Table of Comparison
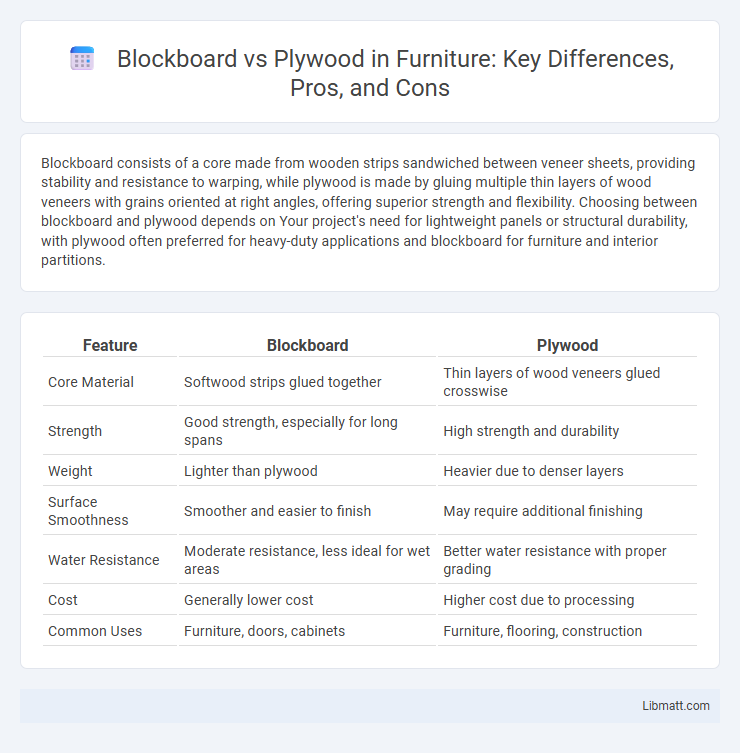
| Feature | Blockboard | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Core Material | Softwood strips glued together | Thin layers of wood veneers glued crosswise |
| Strength | Good strength, especially for long spans | High strength and durability |
| Weight | Lighter than plywood | Heavier due to denser layers |
| Surface Smoothness | Smoother and easier to finish | May require additional finishing |
| Water Resistance | Moderate resistance, less ideal for wet areas | Better water resistance with proper grading |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
| Common Uses | Furniture, doors, cabinets | Furniture, flooring, construction |
Introduction to Blockboard and Plywood
Blockboard consists of a core made from softwood strips glued between two hardwood veneers, offering a lightweight yet strong alternative to solid wood. Plywood is manufactured by laminating multiple thin layers of wood veneers with grains oriented perpendicular to each other, providing enhanced strength and resistance to warping. Both materials serve as versatile options in furniture and construction, with blockboard favored for flat surfaces and plywood for applications requiring greater stability and durability.
Composition and Material Differences
Blockboard consists of a core made from wooden strips glued together, sandwiched between layers of veneer, offering strength and stability ideal for furniture. Plywood is composed of thin layers of wood veneer bonded with adhesive, with each layer's grain running perpendicular to the next, enhancing its resistance to warping and twisting. Understanding these material differences helps you choose the right panel based on your specific structural and aesthetic requirements.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Blockboard is manufactured by gluing solid wood strips edgewise between two veneers, creating a lightweight yet strong panel ideal for furniture and interior applications. Plywood consists of multiple thin layers of wood veneers laminated together with adjacent layers having their grain at right angles, enhancing strength and resistance to warping. The cross-grain layering in plywood results in superior dimensional stability compared to the solid-strip core of blockboard, influencing their respective uses in construction and cabinetry.
Key Physical Properties
Blockboard features a core of wooden strips glued together, providing superior rigidity and resistance to warping compared to plywood, which consists of multiple thin veneer layers bonded with adhesives. Plywood offers better flexibility and is generally lighter in weight, making it suitable for applications requiring bending or curved shapes. Both materials exhibit comparable strength, but blockboard typically has a smoother surface ideal for laminates and veneers.
Strength and Durability: Side-by-Side
Blockboard offers excellent strength and durability due to its core of wooden strips glued together in layers, providing resistance to warping and bending under pressure. Plywood, made from thin layers of veneer glued with grains perpendicular to each other, delivers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced resistance to cracking and shrinkage. Both materials excel in structural stability, but plywood generally provides higher tensile strength, while blockboard is favored for load-bearing applications in furniture making.
Common Applications and Uses
Blockboard is commonly used for furniture, doors, and interior paneling due to its strength and smooth surface, making it ideal for applications requiring sturdy yet lightweight materials. Plywood is favored in construction, flooring, roofing, and cabinetry because of its high durability, resistance to warping, and ability to withstand heavy load and moisture. Both materials offer versatility, but blockboard suits fine woodworking, while plywood excels in structural and exterior applications.
Cost Analysis: Blockboard vs Plywood
Blockboard generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to plywood, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious projects. The core of blockboard consists of softwood strips, which reduces material expenses, while plywood uses multiple thin layers of hardwood or softwood veneers, increasing production costs. Your selection between blockboard and plywood should balance cost with application needs, as plywood typically provides superior strength and durability despite the higher price.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Blockboard offers superior workability due to its lightweight core made of softwood strips, making it easy to cut, drill, and shape without splintering. Plywood, composed of multiple thin veneers glued together, provides excellent dimensional stability and strength but can be harder to work with because of its density and layered structure. Your choice depends on whether ease of installation or structural strength is the priority for your project.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Blockboard and plywood differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with plywood generally considered more eco-friendly due to its efficient use of thin veneer layers from fast-growing trees, reducing deforestation. Blockboard uses solid wood strips as its core, requiring larger timber pieces, which may contribute to higher resource consumption and environmental degradation. When choosing materials, your decision can directly influence sustainability efforts, favoring plywood for its lower carbon footprint and better resource utilization.
Which One Should You Choose?
Blockboard offers greater strength and resistance to warping due to its solid core of wooden strips, making it ideal for furniture and building applications requiring durability. Plywood, constructed from thin layers of wood veneer glued together, provides excellent flexibility and water resistance, suitable for surfaces exposed to moisture. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize structural stability with blockboard or the versatility and moisture resistance provided by plywood.
blockboard vs plywood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com