Cane is derived from the outer bark of the rattan vine, offering a smoother and more flexible material ideal for weaving furniture surfaces, while rattan refers to the sturdy, solid core used for constructing frames and structural components. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize lightweight durability or intricate, flexible design in home furnishings.
Table of Comparison
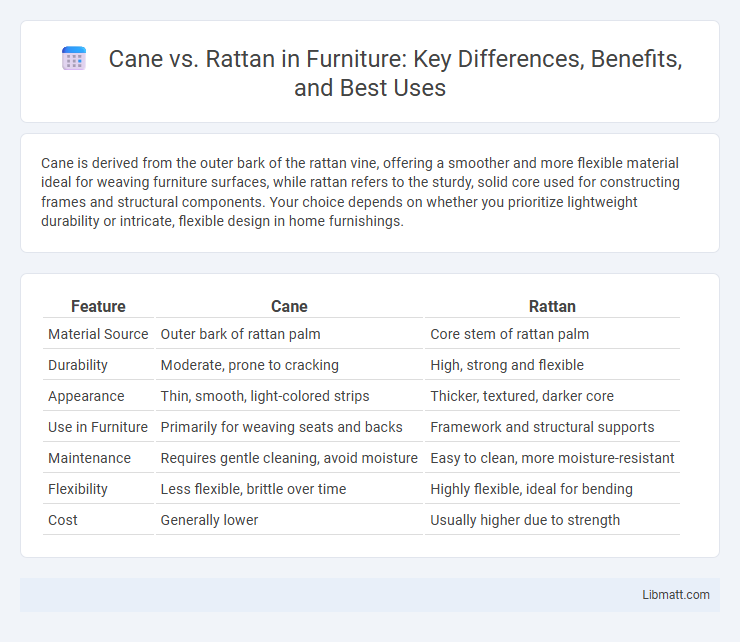
| Feature | Cane | Rattan |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Outer bark of rattan palm | Core stem of rattan palm |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, strong and flexible |
| Appearance | Thin, smooth, light-colored strips | Thicker, textured, darker core |
| Use in Furniture | Primarily for weaving seats and backs | Framework and structural supports |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle cleaning, avoid moisture | Easy to clean, more moisture-resistant |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, brittle over time | Highly flexible, ideal for bending |
| Cost | Generally lower | Usually higher due to strength |
Understanding Cane and Rattan: Key Differences
Cane originates from the outer bark of the rattan palm, offering a flexible and lightweight material commonly used in furniture weaving. Rattan refers to the entire plant, a woody vine known for its strength and durability in crafting furniture frames and decor. Understanding that cane is derived from the rattan plant helps clarify their distinct roles in manufacturing and design applications.
Origin and Sources of Cane and Rattan
Cane primarily originates from the outer bark of rattan palms, harvested mostly in Southeast Asia, particularly in Indonesia, the Philippines, and Malaysia. Rattan itself is a type of climbing palm native to tropical regions of Africa, Asia, and Australia, valued for its long, flexible stems used in furniture and handicrafts. Understanding the geographic and botanical sources of cane and rattan helps you choose sustainable materials for your decor or craft projects.
Physical Characteristics: Strength and Flexibility
Cane is derived from the outer bark of rattan vines, featuring a smooth, hollow structure that offers moderate flexibility and strength, making it ideal for weaving lightweight furniture. Rattan consists of solid, woody stems with greater thickness and density, delivering superior durability and resistance to bending under heavy loads. Both materials exhibit natural flexibility, but rattan's solid core provides enhanced strength for robust construction and long-lasting applications.
Popular Uses in Furniture and Decor
Cane is widely used for seating surfaces and backs in chairs due to its lightweight, flexible, and breathable properties, making it ideal for creating intricate woven patterns in traditional and contemporary furniture. Rattan, known for its sturdy core and durability, is favored for constructing entire furniture frames, including sofas, loungers, and tables, often featured in outdoor and tropical-themed decor. Both materials complement rustic, bohemian, and coastal interior styles, with cane adding delicate texture and rattan providing robust structural support.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Cane furniture, made from the outer bark of rattan vines, offers moderate durability but requires regular maintenance such as cleaning and occasional re-varnishing to prevent wear and cracking. Rattan, a core material within the same plant species, is more robust and resilient, often treated with protective finishes that enhance resistance to moisture and pests, reducing overall upkeep. Choosing rattan can extend your furniture's lifespan with less frequent maintenance compared to cane, making it a practical option for high-traffic areas or outdoor settings.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cane and rattan are both renewable resources harvested from climbing palms, but rattan grows faster, making it more sustainable for furniture production. Cane harvesting often involves stripping older stems, which can impact plant regeneration, whereas rattan's flexibility allows for selective harvesting with less environmental damage. Both materials contribute to reducing deforestation when sourced responsibly, supporting eco-friendly practices in the furniture industry.
Cost Comparison: Cane vs Rattan
Cane furniture typically costs less than rattan due to its simpler harvesting and processing methods. Rattan, being a vine with a denser core, requires more labor-intensive treatment, which increases its price. When choosing between cane and rattan, your budget will largely determine which material offers better value for your furniture needs.
Design Versatility and Aesthetics
Cane offers a delicate, open-weave pattern that enhances lightness and intricate design, making it ideal for creating airy, vintage-inspired furniture. Rattan's solid core allows for robust, sculptural forms and a polished, natural finish that suits tropical and modern aesthetics. Both materials provide exceptional adaptability in crafting stylish, durable pieces tailored to diverse interior design themes.
Indoor and Outdoor Suitability
Cane, derived from the outer skin of rattan vines, is more suitable for indoor furniture due to its delicate texture and lower resistance to moisture and sunlight. Rattan, consisting of the entire vine including the inner core, offers greater durability and weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor use. Both materials provide natural aesthetics but require different maintenance levels based on their exposure to environmental conditions.
Choosing Between Cane and Rattan: Factors to Consider
Choosing between cane and rattan involves evaluating durability, flexibility, and design aesthetics for your furniture or decor. Cane offers a lightweight, natural finish ideal for intricate weaving, while rattan provides greater strength and robustness suitable for outdoor use. Consider your environment, maintenance preferences, and desired style to select the material that best complements your space and lifestyle.
Cane vs Rattan Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com