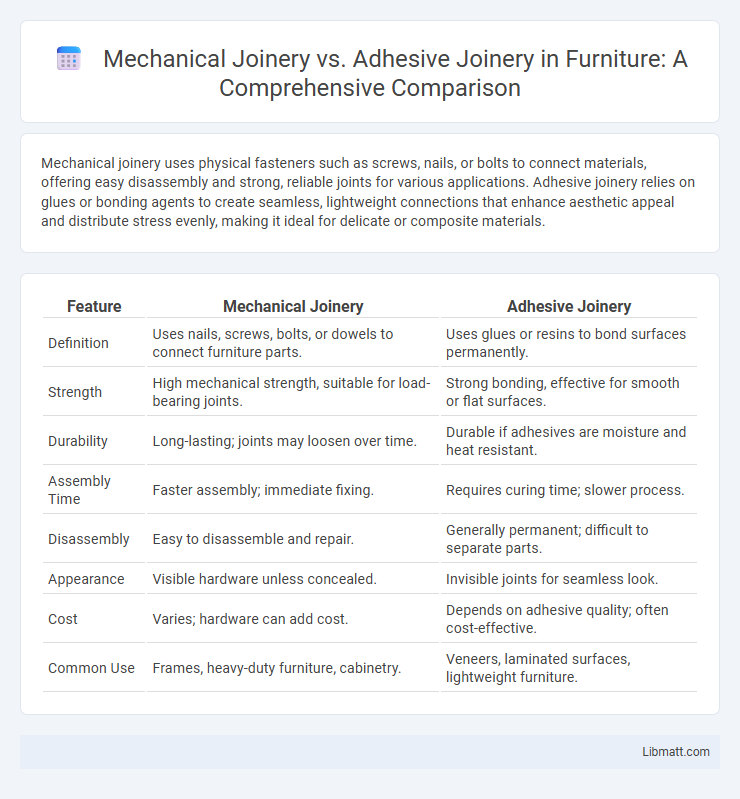
Mechanical joinery uses physical fasteners such as screws, nails, or bolts to connect materials, offering easy disassembly and strong, reliable joints for various applications. Adhesive joinery relies on glues or bonding agents to create seamless, lightweight connections that enhance aesthetic appeal and distribute stress evenly, making it ideal for delicate or composite materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mechanical Joinery | Adhesive Joinery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses nails, screws, bolts, or dowels to connect furniture parts. | Uses glues or resins to bond surfaces permanently. |
| Strength | High mechanical strength, suitable for load-bearing joints. | Strong bonding, effective for smooth or flat surfaces. |
| Durability | Long-lasting; joints may loosen over time. | Durable if adhesives are moisture and heat resistant. |
| Assembly Time | Faster assembly; immediate fixing. | Requires curing time; slower process. |
| Disassembly | Easy to disassemble and repair. | Generally permanent; difficult to separate parts. |
| Appearance | Visible hardware unless concealed. | Invisible joints for seamless look. |
| Cost | Varies; hardware can add cost. | Depends on adhesive quality; often cost-effective. |
| Common Use | Frames, heavy-duty furniture, cabinetry. | Veneers, laminated surfaces, lightweight furniture. |
Introduction to Mechanical and Adhesive Joinery
Mechanical joinery uses physical fasteners like screws, bolts, or nails to securely connect materials, providing strong, easily disassembled joints ideal for heavy loads and structural applications. Adhesive joinery relies on bonding agents such as epoxy, polyurethane, or cyanoacrylates to create seamless connections that distribute stress evenly and resist moisture or chemicals. Your choice between mechanical and adhesive joinery depends on factors like material type, load requirements, and environmental conditions for optimal durability and performance.
Overview of Mechanical Joinery Methods
Mechanical joinery methods involve techniques such as screws, nails, bolts, dowels, and brackets that physically connect materials by penetration or clamping. These methods offer strong, reliable joints ideal for load-bearing applications and allow for disassembly or adjustments when needed. Understanding these options enables you to select the best mechanical fastener to ensure durability and ease of maintenance in your woodworking or construction projects.
Overview of Adhesive Joinery Techniques
Adhesive joinery techniques utilize chemical bonding agents like epoxy, polyurethane, and cyanoacrylate to fuse materials, offering benefits such as uniform stress distribution and minimal material distortion. Common methods include surface bonding, where adhesives are applied to cleaned surfaces; film adhesives that provide a consistent bonding layer; and structural adhesives designed for high-strength applications. These techniques excel in joining dissimilar materials and provide enhanced durability compared to traditional mechanical fasteners like screws or nails.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Mechanical joinery, such as screws and bolts, offers high strength by physically holding materials together, making it ideal for applications requiring easy disassembly and load-bearing support. Adhesive joinery provides excellent durability by distributing stress evenly across the bonded surface, reducing the risk of localized failures and enhancing resistance to vibrations and environmental factors. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize mechanical strength for structural integrity or adhesive durability for seamless, long-lasting bonds.
Application Suitability in Various Industries
Mechanical joinery excels in heavy-duty applications across automotive, aerospace, and construction industries due to its high strength and reusability. Adhesive joinery is preferred in electronics, furniture, and packaging sectors, offering flexibility, corrosion resistance, and enhanced aesthetic appeal. Selecting between mechanical and adhesive joinery depends on factors like load requirements, material compatibility, and environmental conditions specific to the industry.
Speed and Ease of Assembly
Mechanical joinery offers faster assembly due to simple, repeatable fastening methods like screws, nails, and bolts that require minimal curing time. Adhesive joinery, while providing strong and seamless bonds, demands longer curing periods and precise surface preparation, slowing down the overall assembly process. In high-volume production, mechanical joinery enhances speed and ease, whereas adhesive methods excel in applications needing clean aesthetics and flexibility.
Cost Factors and Material Considerations
Mechanical joinery typically incurs higher initial costs due to the need for specialized fasteners and precise machining, but offers easier disassembly and repair, impacting long-term expenses. Adhesive joinery can reduce material stress and allows bonding of dissimilar materials, lowering overall production costs with fewer mechanical parts required. Your choice depends on factors like load requirements, material types, and budget constraints, balancing upfront investment with maintenance considerations.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Mechanical joinery offers distinct visual elements like exposed screws, bolts, and brackets that contribute to an industrial or rustic aesthetic, allowing designers to highlight craftsmanship and structural integrity. Adhesive joinery provides seamless joints with no visible fasteners, enabling smooth surfaces and continuous lines that suit modern, minimalist, or intricate designs. This design flexibility makes adhesive joinery ideal for applications requiring clean aesthetics and complex shapes that mechanical fasteners might disrupt.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mechanical joinery often involves metal fasteners or screws, which can be recycled, but the extraction and processing of these materials contribute to environmental degradation and energy consumption. Adhesive joinery, depending on the type of adhesive used, may introduce challenges in recyclability and potential release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), impacting indoor air quality and landfill waste. Sustainable practices favor mechanical joinery when using recyclable metals and wood, while eco-friendly adhesives made from bio-based materials are emerging to reduce environmental footprints in adhesive joinery.
Choosing the Right Joinery Method for Your Project
Mechanical joinery offers strong, removable connections ideal for structural projects requiring disassembly, while adhesive joinery provides seamless bonds suited for materials needing uniform stress distribution and aesthetic appeal. Your choice depends on factors like load requirements, material compatibility, and project longevity, with mechanical joinery excelling in high-strength and repairable joints, and adhesive joinery enhancing continuous surface integrity. Evaluating these criteria ensures the selected joinery method aligns with your project's functional and design demands.
mechanical joinery vs adhesive joinery Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com