Vertical grain wood features lines running straight along the board, offering greater stability, strength, and resistance to warping or shrinking compared to flat grain wood, which has a more varied, wavy pattern that can be more prone to movement. Choosing vertical grain for your projects ensures enhanced durability and a cleaner, more uniform appearance.
Table of Comparison
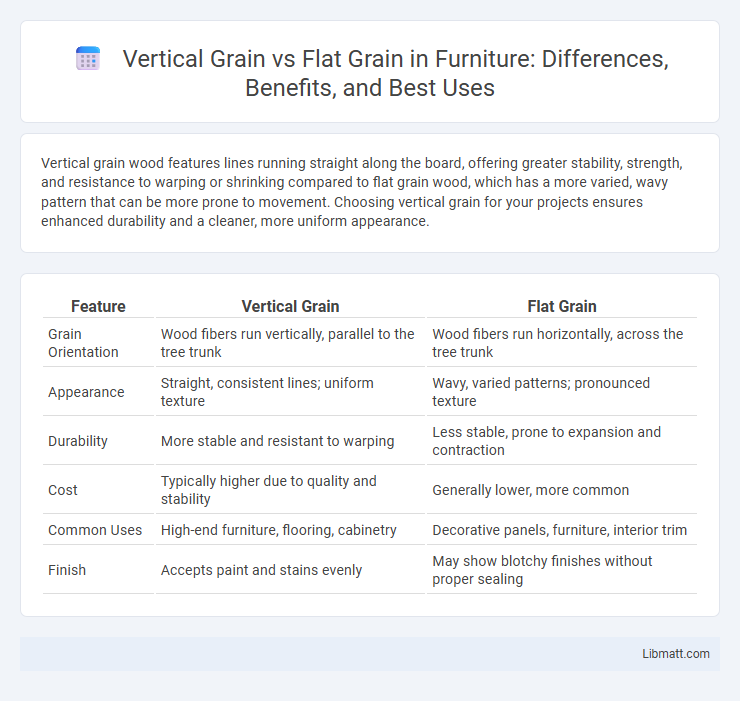
| Feature | Vertical Grain | Flat Grain |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Orientation | Wood fibers run vertically, parallel to the tree trunk | Wood fibers run horizontally, across the tree trunk |
| Appearance | Straight, consistent lines; uniform texture | Wavy, varied patterns; pronounced texture |
| Durability | More stable and resistant to warping | Less stable, prone to expansion and contraction |
| Cost | Typically higher due to quality and stability | Generally lower, more common |
| Common Uses | High-end furniture, flooring, cabinetry | Decorative panels, furniture, interior trim |
| Finish | Accepts paint and stains evenly | May show blotchy finishes without proper sealing |
Understanding Vertical Grain and Flat Grain
Vertical grain wood, also known as quarter-sawn, features growth rings that run perpendicular to the board's surface, offering superior stability, reduced warping, and a straighter grain pattern. Flat grain wood, or plain-sawn, displays growth rings that are more parallel to the surface, resulting in a wider grain pattern with increased potential for expansion and contraction. Understanding the differences between vertical grain and flat grain helps in selecting wood with desired aesthetic and structural properties for flooring, cabinetry, and woodworking projects.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Flat Grain
Vertical grain wood displays a straight and uniform grain pattern, offering enhanced stability and resistance to warping, making it ideal for flooring and fine woodworking projects. Flat grain wood shows broader, wavy grain patterns with more pronounced growth rings, which can create visually appealing surfaces but tends to be more prone to expansion and contraction. Understanding these key differences allows you to select the best grain orientation that balances durability and aesthetics for your woodworking needs.
Visual Characteristics of Each Grain Type
Vertical grain lumber displays straight, uniform lines running parallel to the board's length, offering a sleek and consistent appearance favored for fine woodworking and furniture. Flat grain, characterized by its wider, more varied growth rings visible on the board's face, presents a more pronounced, wavy pattern that highlights natural wood figuring and texture. These distinct visual characteristics influence aesthetic choices in cabinetry, flooring, and decorative woodwork depending on design preference and grain prominence.
Strength and Durability: Vertical vs Flat Grain
Vertical grain wood, characterized by its straight, tightly packed growth rings, offers superior strength and durability compared to flat grain, which has wider, more irregular growth rings prone to warping and splitting. The dense alignment of fibers in vertical grain enhances resistance to moisture and mechanical stress, making it ideal for structural applications and surfaces subject to heavy wear. Flat grain wood, while visually appealing with its varied patterns, is less stable and more susceptible to shrinkage and deformation over time.
Applications: When to Choose Vertical or Flat Grain
Vertical grain wood is ideal for applications requiring enhanced stability and durability, such as cabinetry, flooring, and fine furniture, due to its resistance to warping and shrinking. Flat grain wood is preferred for projects where aesthetic grain patterns and cost-effectiveness are prioritized, commonly used in paneling, decorative trim, and rustic-style furniture. Selecting between vertical and flat grain depends on the balance of structural performance and visual appeal needed for the specific woodworking application.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Vertical grain lumber typically costs more due to its slower growth rate and tighter grain pattern, making it rarer and often preferred for high-quality woodworking. Flat grain lumber is more abundant and less expensive, widely available from most suppliers, which makes it a budget-friendly option for large projects. When considering your project, weigh the cost difference and availability to choose the grain type that best matches your budget and desired aesthetics.
Finishing and Maintenance Considerations
Vertical grain wood features tighter growth rings that create a smoother surface, making it easier to sand and finish with fewer imperfections compared to flat grain wood. Flat grain wood, displaying a wider grain pattern, requires more extensive sealing to prevent moisture absorption and potential warping during maintenance. Proper finishing products, such as penetrating oils or varnishes, enhance durability for both grains, but vertical grain generally demands less frequent upkeep due to its natural resistance to wear and smoother texture.
Aesthetic Impact in Interior Design
Vertical grain wood showcases pronounced, straight grain lines that create a sleek and modern aesthetic, often enhancing the perception of height and elegance in interior spaces. Flat grain wood features wider, wavy patterns that produce a warm, rustic, and natural look, adding depth and texture to your interior design scheme. Choosing between vertical and flat grain significantly influences the visual rhythm and atmosphere of wooden surfaces like flooring, cabinetry, and paneling.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Vertical grain wood, cut along the tree's growth rings, tends to have a tighter grain structure that enhances durability and reduces the need for frequent replacements, contributing to sustainability by lowering resource consumption. Flat grain wood, cut tangentially, often exhibits faster wear but is typically sourced from more readily available parts of the tree, which can minimize waste and optimize material use. Choosing vertical grain wood for long-term projects can support your environmental goals by ensuring extended lifecycle performance and reducing the demand for harvesting additional timber.
Expert Tips for Selecting the Right Grain Orientation
Selecting the right grain orientation depends on the intended use and aesthetic preferences; vertical grain offers superior stability and less movement, making it ideal for structural applications and outdoor projects. Flat grain provides a more pronounced wood pattern and warmth, favored in furniture and decorative surfaces where visual appeal is paramount. Experts recommend considering environmental exposure, expected wear, and finish type to ensure durability and optimal performance of the wood product.
Vertical grain vs flat grain Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com