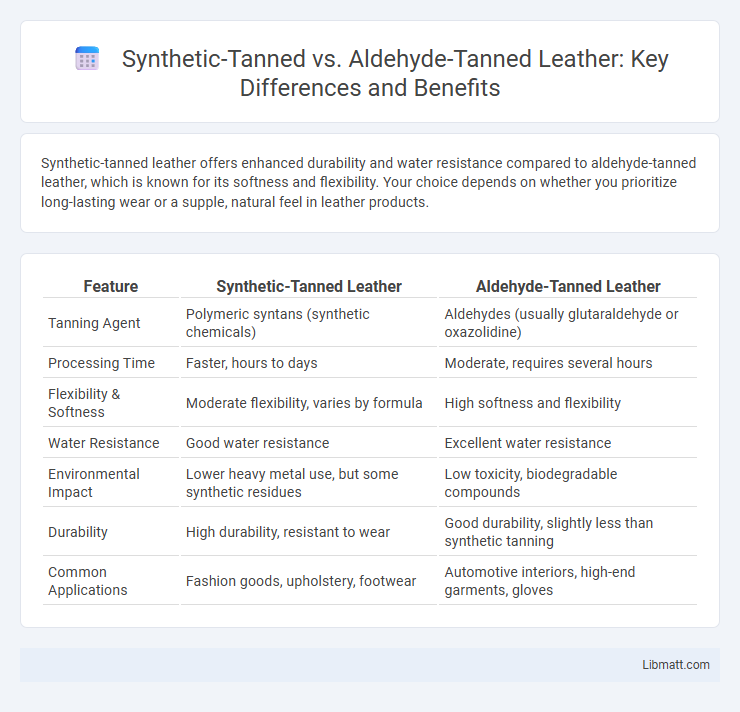
Synthetic-tanned leather offers enhanced durability and water resistance compared to aldehyde-tanned leather, which is known for its softness and flexibility. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize long-lasting wear or a supple, natural feel in leather products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic-Tanned Leather | Aldehyde-Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Tanning Agent | Polymeric syntans (synthetic chemicals) | Aldehydes (usually glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine) |
| Processing Time | Faster, hours to days | Moderate, requires several hours |
| Flexibility & Softness | Moderate flexibility, varies by formula | High softness and flexibility |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance | Excellent water resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Lower heavy metal use, but some synthetic residues | Low toxicity, biodegradable compounds |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to wear | Good durability, slightly less than synthetic tanning |
| Common Applications | Fashion goods, upholstery, footwear | Automotive interiors, high-end garments, gloves |
Introduction to Leather Tanning Methods
Synthetic-tanned leather utilizes chemical agents such as chromium salts to produce durable, flexible hides with enhanced water resistance and uniform coloration. Aldehyde-tanned leather employs organic compounds like glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine to create softer, hypoallergenic leather ideal for automotive and upholstery applications. Both tanning methods significantly influence leather's texture, durability, and environmental impact, shaping its suitability for various industrial uses.
What Is Synthetic Tanning?
Synthetic tanning utilizes chemical agents such as synthetic tanning agents or aldehyde compounds to convert rawhide into durable leather with enhanced resistance to heat and moisture. Unlike traditional vegetable tanning, synthetic tanning accelerates the process, producing leather with consistent texture and color, ideal for industrial applications. Your choice between synthetic-tanned and aldehyde-tanned leather depends on the desired durability, flexibility, and end-use requirements.
Understanding Aldehyde Tanning
Aldehyde tanning utilizes glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine, producing leather that is more flexible, water-repellent, and hypoallergenic compared to synthetic-tanned leather. This process results in leather with excellent heat resistance and lower environmental impact due to fewer toxic chemicals than synthetic tanning methods. Understanding aldehyde tanning highlights its advantages in producing eco-friendly, durable leather ideal for automotive and medical applications.
Chemical Processes: Synthetic vs Aldehyde Tanning
Synthetic tanning utilizes chromium salts, primarily chromium(III) sulfate, to stabilize collagen fibers through coordination bonds, resulting in durable and water-resistant leather. Aldehyde tanning employs glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine compounds, which form covalent cross-links with lysine residues in collagen, producing softer and more flexible leather with reduced environmental impact. The distinct chemical mechanisms influence leather properties, with synthetic tanning emphasizing metal complexation and aldehyde tanning relying on aldehyde-amine condensation reactions.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Synthetic-tanned leather relies on chemical compounds such as chromium salts, which pose significant environmental challenges due to toxic waste and water pollution during manufacturing, while aldehyde-tanned leather uses formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde, resulting in lower toxicity but still generating hazardous chemical runoff. Waste management in synthetic tanning requires advanced treatment facilities to mitigate chromium contamination, whereas aldehyde tanning offers better biodegradability but can release harmful aldehydes into ecosystems if not properly handled. Your choice between these tanning methods affects the sustainability footprint, with aldehyde tanning generally presenting a reduced environmental impact compared to traditional synthetic tanning processes.
Durability and Performance Differences
Synthetic-tanned leather offers superior durability due to enhanced resistance to water, heat, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for heavy-use products such as footwear and automotive interiors. Aldehyde-tanned leather, known for its softness and flexibility, provides moderate durability but tends to be less resistant to moisture and abrasion. The performance gap lies in synthetic tanning's enhanced structural stability, resulting in longer-lasting leather under harsh conditions compared to the more natural but less robust aldehyde tanning process.
Applications in the Leather Industry
Synthetic-tanned leather, often treated with synthetic tanning agents such as chromium salts, is highly valued in the footwear, upholstery, and automotive industries for its durability, water resistance, and consistent coloration. Aldehyde-tanned leather, primarily tanned using glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine compounds, is favored in medical applications and high-end automotive interiors due to its softness, hypoallergenic properties, and enhanced biodegradability. The leather industry selects synthetic tanning for mass-produced, rugged products while aldehyde tanning addresses niche markets requiring eco-friendly and skin-friendly materials.
Health and Safety Considerations
Synthetic-tanned leather uses chemical agents such as chromium salts, which can pose health risks through skin irritation and respiratory issues if not handled properly, necessitating adequate ventilation and protective equipment in manufacturing. Aldehyde-tanned leather often employs glutaraldehyde or oxazolidine compounds, which are considered less toxic and emit fewer volatile organic compounds, improving worker safety and reducing environmental impact. Both tanning methods require strict adherence to safety protocols to mitigate exposure risks, but aldehyde tanning generally offers a safer profile for health and environmental considerations.
Cost Efficiency and Production Scalability
Synthetic-tanned leather offers greater cost efficiency due to lower raw material expenses and faster processing times compared to aldehyde-tanned leather, which requires more complex chemical treatments. Production scalability is more achievable with synthetic tanning methods because they rely on readily available synthetic chemicals that enable consistent large-scale manufacturing. Your choice of tanning method impacts overall budget and capacity, with synthetic tanning providing more economical and scalable solutions for mass leather production.
Future Trends in Leather Tanning Technologies
Future trends in leather tanning technologies emphasize eco-friendly and sustainable methods, with synthetic tanning agents designed to reduce environmental impact and chemical waste. Aldehyde-tanned leather, known for its softness and biodegradability, is gaining traction as industries prioritize non-toxic alternatives to chromium-based processes. Innovations in synthetic tannins derived from plant-based materials and advanced aldehyde formulations aim to enhance durability, reduce water usage, and support circular economy principles in leather production.
Synthetic-tanned vs aldehyde-tanned Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com