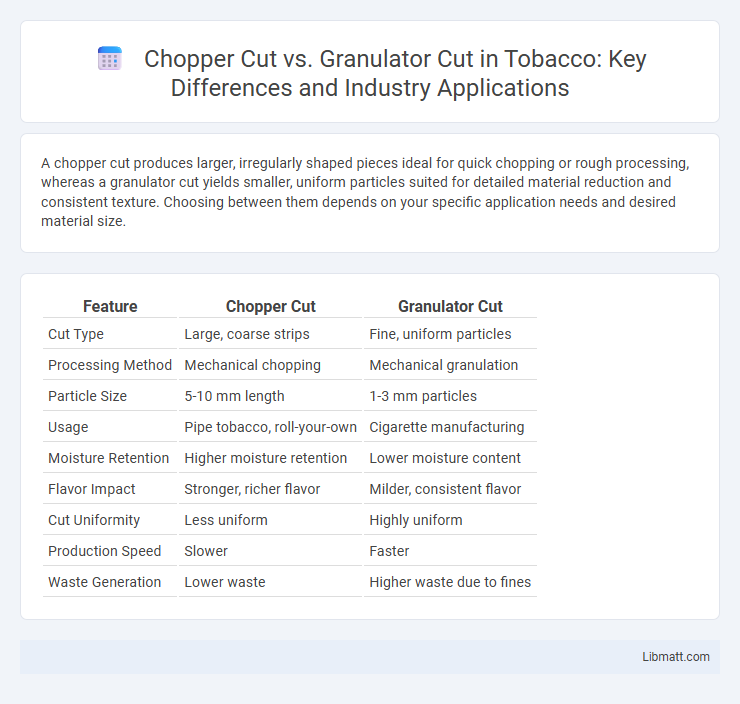
A chopper cut produces larger, irregularly shaped pieces ideal for quick chopping or rough processing, whereas a granulator cut yields smaller, uniform particles suited for detailed material reduction and consistent texture. Choosing between them depends on your specific application needs and desired material size.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chopper Cut | Granulator Cut |
|---|---|---|
| Cut Type | Large, coarse strips | Fine, uniform particles |
| Processing Method | Mechanical chopping | Mechanical granulation |
| Particle Size | 5-10 mm length | 1-3 mm particles |
| Usage | Pipe tobacco, roll-your-own | Cigarette manufacturing |
| Moisture Retention | Higher moisture retention | Lower moisture content |
| Flavor Impact | Stronger, richer flavor | Milder, consistent flavor |
| Cut Uniformity | Less uniform | Highly uniform |
| Production Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Waste Generation | Lower waste | Higher waste due to fines |
Introduction to Plastic Cutting Techniques
Plastic cutting techniques such as chopper cut and granulator cut differ primarily in particle size and application. Chopper cutting produces larger, irregularly shaped flakes ideal for recycling bulky plastic items, while granulator cutting yields finer, more uniform particles suitable for precise molding and extrusion processes. Selecting the appropriate method depends on the desired material consistency and end-use requirements in plastic processing industries.
Overview of Chopper Cut and Granulator Cut
Chopper cut and granulator cut represent two distinct methods for size reduction in material processing, with chopper cuts delivering coarser, irregularly shaped pieces by rapid blade action, while granulator cuts produce finer, uniform particles through a high-speed rotor and screen system. Chopper cuts are commonly used for shredding larger items like scrap metal or plastic waste, facilitating easier handling and initial size reduction. Granulator cuts excel in applications requiring precise particle size for recycling or manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent output for improved material quality and processing efficiency.
How Chopper Cut Systems Function
Chopper cut systems function by using rotating knives to slice materials into smaller, uniform pieces, improving handling and processing efficiency. These systems are particularly effective for bulky or fibrous waste, allowing precise control over particle size for downstream applications. Your choice between chopper cut and granulator cut depends on the specific material characteristics and desired end product size.
How Granulator Cut Systems Operate
Granulator cut systems operate by feeding materials into a chamber where rotating knives shear the input into smaller, uniform particles through repeated slicing actions. These machines create consistent granules by utilizing sharp, closely spaced blades that work in combination with a stationary screen to control particle size precisely. Your choice of granulator cut system ensures efficient size reduction with minimal dust and reduced noise, ideal for handling plastics, rubber, or other bulk materials.
Material Suitability: Chopper vs Granulator
Chopper cutters excel in processing bulky, fibrous, or film-like materials such as plastics, rubber, and textiles due to their robust blade design and slower cutting action, which prevents clogging and overheating. Granulators are better suited for rigid, homogenous materials like hard plastics and metal composites, providing consistent particle size reduction through high-speed rotor blades and precision screens. Material suitability depends on factors like toughness, elasticity, and thickness, with chopper cutters preferred for large, irregular pieces and granulators ideal for uniform, dense feedstocks.
Output Size and Consistency Comparison
Chopper cuts typically produce larger, less uniform output sizes ranging from 1 to 3 inches, making them suitable for applications requiring coarse material. Granulator cuts offer finer, more consistent particle sizes, often below 1 inch, ensuring uniformity ideal for processing, recycling, or blending. The granulator's precision cutting mechanism results in higher consistency and optimized particle distribution compared to the variable output of chopper cuts.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Chopper cuts generally consume less energy than granulator cuts due to their simpler mechanical design and faster processing speed, resulting in higher throughput with lower power requirements. Granulator cuts, while more energy-intensive, provide finer and more uniform particle sizes, enhancing material consistency and downstream processing efficiency. Energy consumption varies by application, but optimizing cut type based on material characteristics and desired output can significantly improve overall operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Chopper cut machines generally have lower maintenance costs due to simpler blade designs and fewer moving parts, resulting in reduced downtime and repair expenses. Granulator cuts often involve higher operational costs because their more complex shredding mechanisms require frequent blade sharpening and part replacements to maintain efficiency. Choosing the right equipment for your needs helps optimize operational budgets by balancing maintenance frequency with productivity demands.
Safety Considerations in Cutting Processes
Chopper cuts generally pose lower safety risks due to simpler mechanical designs and reduced blade sharpness, minimizing operator injury potential. Granulator cuts involve high-speed rotating blades that can increase hazards such as blade entanglement and flying debris, necessitating robust safety guards and emergency shutoff systems. Proper training and maintenance are critical to ensure safe operation in both cutting processes.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Application
Chopper cut and granulator cut techniques serve different industrial purposes, with chopper cut ideal for producing longer, fibrous materials and granulator cut suited for fine, uniform particle sizes. Selecting the right cutting method depends on your application's material type and desired output size, as chopper cuts excel in biomass and shredding tasks while granulators optimize plastic recycling and size reduction. Understanding these distinctions ensures precise processing and enhances operational efficiency for your production requirements.
chopper cut vs granulator cut Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com