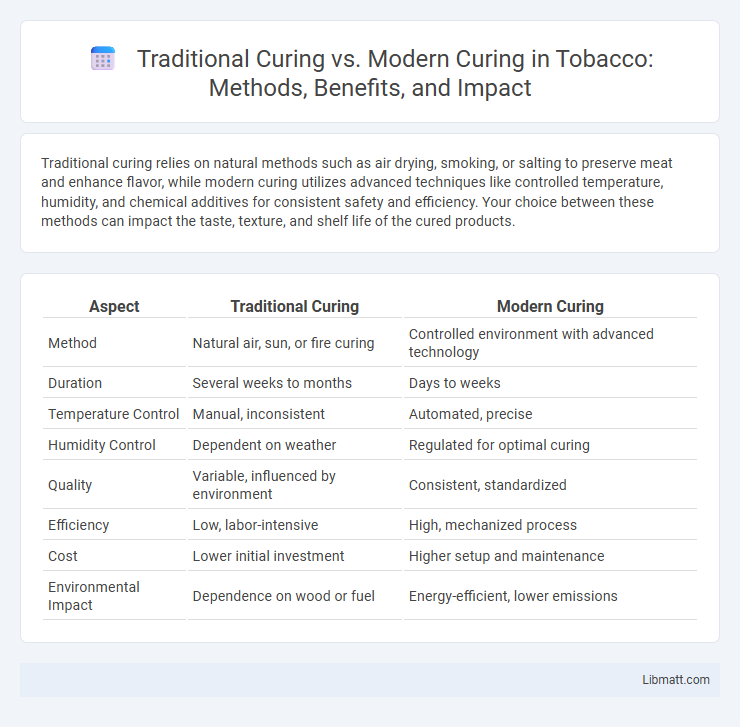
Traditional curing relies on natural methods such as air drying, smoking, or salting to preserve meat and enhance flavor, while modern curing utilizes advanced techniques like controlled temperature, humidity, and chemical additives for consistent safety and efficiency. Your choice between these methods can impact the taste, texture, and shelf life of the cured products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Curing | Modern Curing |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Natural air, sun, or fire curing | Controlled environment with advanced technology |
| Duration | Several weeks to months | Days to weeks |
| Temperature Control | Manual, inconsistent | Automated, precise |
| Humidity Control | Dependent on weather | Regulated for optimal curing |
| Quality | Variable, influenced by environment | Consistent, standardized |
| Efficiency | Low, labor-intensive | High, mechanized process |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher setup and maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Dependence on wood or fuel | Energy-efficient, lower emissions |
Introduction to Meat Curing
Meat curing is a preservation method that uses salt, nitrates, and sometimes sugar to inhibit bacterial growth and extend shelf life. Traditional curing relies on natural ingredients and slow processes such as dry salting or smoking, which impart distinct flavors and textures. Modern curing techniques incorporate controlled environments, synthetic curing agents, and precise timing to ensure food safety and consistent quality.
History of Traditional Curing Methods
Traditional curing methods date back thousands of years, utilizing natural elements like salt, smoke, and air to preserve meat and fish before refrigeration existed. These techniques, developed in various cultures worldwide, rely on dehydration, fermentation, and chemical reactions to inhibit bacterial growth and enhance flavor. Your understanding of these historical practices highlights the foundation upon which modern curing technologies build, combining time-tested methods with advanced scientific controls for consistent quality.
Principles Behind Traditional Curing
Traditional curing relies on natural methods such as salting, drying, and smoking to preserve food by reducing moisture and inhibiting bacterial growth. These techniques utilize environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and airflow to create inhospitable conditions for spoilage organisms. Understanding these principles helps you appreciate the time-tested processes that ensure flavor development and food safety without modern additives.
Modern Curing Techniques Explained
Modern curing techniques utilize advanced technologies like ultrasonic curing, vacuum curing, and microwave curing to accelerate polymerization processes, improve product quality, and reduce energy consumption compared to traditional methods. These techniques offer precise control over temperature, time, and pressure, ensuring consistent and efficient curing for diverse materials such as concrete, composites, and coatings. By adopting modern curing methods, your manufacturing processes can achieve higher durability, reduced defects, and faster production cycles.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Modern Curing
Traditional curing relies on natural methods like sun drying and air curing, while modern curing uses controlled environments with precise temperature and humidity regulation. Modern curing enhances efficiency and consistency, significantly reducing curing times compared to traditional methods. Your choice between the two affects product quality, safety, and scalability in various industries such as tobacco, meat, and concrete.
Benefits of Traditional Curing
Traditional curing preserves the natural flavors and textures of meats through methods like air drying, smoking, and salting, which also inhibit bacterial growth and extend shelf life without synthetic additives. These time-tested techniques often enhance nutritional value by retaining essential nutrients and fostering beneficial microbial activity. Your choice of traditional curing supports artisanal craftsmanship and can result in richer, more complex taste profiles than some modern industrial processes.
Advantages of Modern Curing
Modern curing techniques offer precise control over temperature and humidity, leading to consistent product quality and reduced curing time. Advanced methods enhance efficiency by optimizing energy usage and minimizing waste, which improves overall sustainability. Integration of automation and monitoring systems ensures uniformity and reduces human error compared to traditional curing processes.
Health and Safety Considerations
Traditional curing methods often involve natural agents like salt, smoke, and sun exposure, which can pose risks such as bacterial contamination and inconsistent preservation, leading to potential foodborne illnesses. Modern curing techniques employ controlled environments and chemical additives like nitrates and nitrites, enhancing pathogen inhibition and ensuring standardized safety protocols. Advanced monitoring and sanitation practices in modern curing significantly reduce health hazards compared to traditional methods.
Flavor and Texture Comparison
Traditional curing methods often enhance flavor complexity and develop a chewy, artisanal texture through slow fermentation and natural aging processes. Modern curing techniques, utilizing controlled environments and additives, provide consistent results with a balanced flavor profile and a tender texture tailored to consumer preferences. Your choice between these methods impacts the final product's sensory experience, balancing authenticity with efficiency.
Future Trends in Meat Curing
Future trends in meat curing emphasize sustainability and health-conscious methods, leveraging plant-based curing agents and reduced sodium formulations to meet consumer demand. Advances in biotechnology, such as enzyme innovation and microbial cultures, are improving flavor development and shelf-life without relying on synthetic additives. Smart curing technologies, including digital monitoring and controlled atmosphere curing, optimize product consistency and safety while minimizing environmental impact.
traditional curing vs modern curing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com