Pesticide-free produce offers a safer option by reducing your exposure to harmful chemicals, promoting better health and environmental sustainability. Conventional farming methods often rely on synthetic pesticides to enhance crop yield but may increase the risk of chemical residues on your food.
Table of Comparison
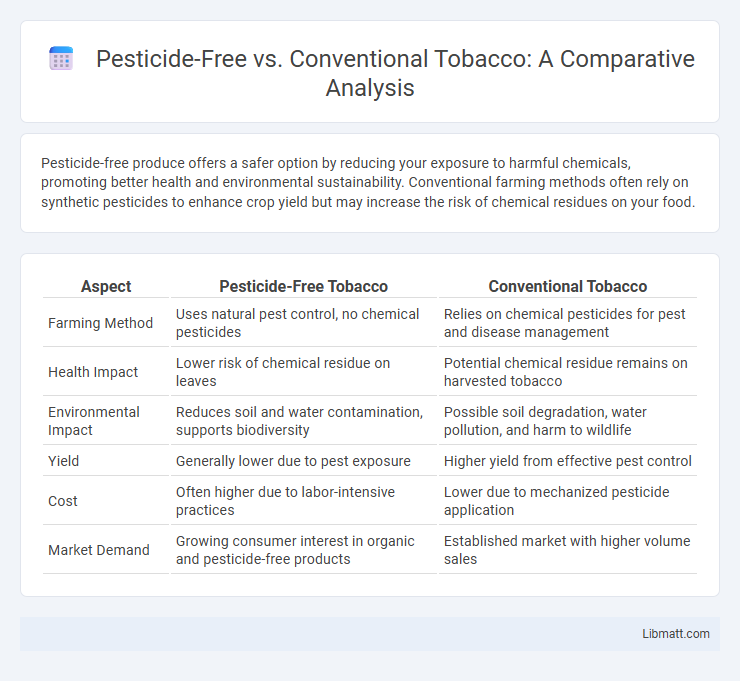
| Aspect | Pesticide-Free Tobacco | Conventional Tobacco |
|---|---|---|
| Farming Method | Uses natural pest control, no chemical pesticides | Relies on chemical pesticides for pest and disease management |
| Health Impact | Lower risk of chemical residue on leaves | Potential chemical residue remains on harvested tobacco |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces soil and water contamination, supports biodiversity | Possible soil degradation, water pollution, and harm to wildlife |
| Yield | Generally lower due to pest exposure | Higher yield from effective pest control |
| Cost | Often higher due to labor-intensive practices | Lower due to mechanized pesticide application |
| Market Demand | Growing consumer interest in organic and pesticide-free products | Established market with higher volume sales |
Understanding Pesticide-Free and Conventional Farming
Pesticide-free farming avoids synthetic chemicals, relying on natural pest control and crop rotation to maintain soil health and biodiversity, which can enhance ecosystem sustainability. Conventional farming uses synthetic pesticides and fertilizers to maximize yield and control pests, often leading to concerns about chemical residues and environmental impact. Understanding these methods helps you make informed choices about food safety, environmental conservation, and agricultural practices.
Key Differences Between Pesticide-Free and Conventional Methods
Pesticide-free farming relies on natural pest control methods, organic fertilizers, and crop rotation to maintain soil health and reduce chemical residues, whereas conventional farming commonly uses synthetic pesticides and fertilizers to maximize yield and control pests. The absence of chemical pesticides in pesticide-free methods supports biodiversity, reduces environmental pollution, and lowers health risks associated with chemical exposure. Conventional farming often achieves higher short-term productivity but may contribute to soil degradation, pesticide resistance, and potential harm to beneficial organisms in the long term.
Impact on Crop Yield and Productivity
Pesticide-free farming often results in lower crop yields compared to conventional methods due to increased pest damage and slower plant growth rates. Conventional agriculture relies on chemical pesticides to protect crops, enhancing productivity and minimizing losses from insects and diseases. Your decision between these methods will affect both the quantity and consistency of harvests, balancing sustainability with immediate food production needs.
Health Implications for Consumers
Pesticide-free produce reduces your exposure to harmful chemicals linked to long-term health risks such as cancer, hormone disruption, and neurological issues. Conventional foods may contain pesticide residues that, even in small amounts, pose potential cumulative health concerns over time. Choosing pesticide-free options supports safer dietary intake and promotes overall well-being.
Effects on Soil and Environmental Health
Pesticide-free farming enhances soil biodiversity by promoting beneficial microorganisms and improving nutrient cycling, leading to healthier soil structure and fertility. Conventional farming often relies on synthetic pesticides that can disrupt soil microbial communities, reduce earthworm populations, and contribute to chemical runoff, harming surrounding ecosystems. Your choice of pesticide-free methods supports long-term environmental sustainability and reduces pollution risks in agricultural landscapes.
Pesticide Residue: What’s on Your Food?
Pesticide-free foods contain significantly lower levels of pesticide residue compared to conventional produce, reducing your exposure to potentially harmful chemicals. Conventional farming often relies on synthetic pesticides to protect crops, leaving trace residues on fruits and vegetables that can impact health. Choosing pesticide-free options supports cleaner eating and minimizes the intake of chemical contaminants on your food.
Economic Considerations for Farmers
Pesticide-free farming often incurs higher labor costs due to manual weed control and pest monitoring, which can reduce short-term profitability compared to conventional methods relying on chemical pesticides. Conventional farming benefits from increased crop yields and reduced pest damage, enhancing economic efficiency, but faces risks of pesticide resistance and regulatory costs. Farmers must balance initial investment and potential market premiums for organic produce against ongoing expenses and yield variability when choosing between pesticide-free and conventional approaches.
Consumer Demand and Market Trends
Pesticide-free products are experiencing a significant surge in consumer demand due to increasing health and environmental awareness, fueling faster market growth compared to conventional alternatives. Market trends reveal a rising preference for organic and sustainably sourced goods, driven by stricter regulations and widespread media coverage on pesticide impacts. Your choices influence this shift, as retailers and producers adapt to meet the growing demand for pesticide-free options in retail and food industries.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Pesticide-free products adhere to stringent regulatory standards such as organic certifications issued by bodies like the USDA Organic or the EU Organic logo, ensuring minimal chemical residues. Conventional farming follows government regulations set by agencies like the EPA, which establish maximum residue limits and approved pesticide usage to safeguard public health. Your choice impacts exposure to chemical residues and aligns with varying certification guarantees and safety protocols.
The Future of Sustainable Agriculture
Pesticide-free farming promotes environmental health by reducing chemical runoff, enhancing biodiversity, and preserving soil integrity, which are crucial for the future of sustainable agriculture. Conventional methods often rely on synthetic chemicals that can degrade ecosystems and contribute to long-term soil depletion. Your choice to support pesticide-free practices drives innovation toward resilient food systems and sustainable farming solutions.
Pesticide-free vs conventional Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com