Primary processing involves the initial handling and organization of raw sensory data in the brain, enabling your perception of the environment. Secondary processing refines this information by integrating past experiences and knowledge, allowing for more complex interpretation and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
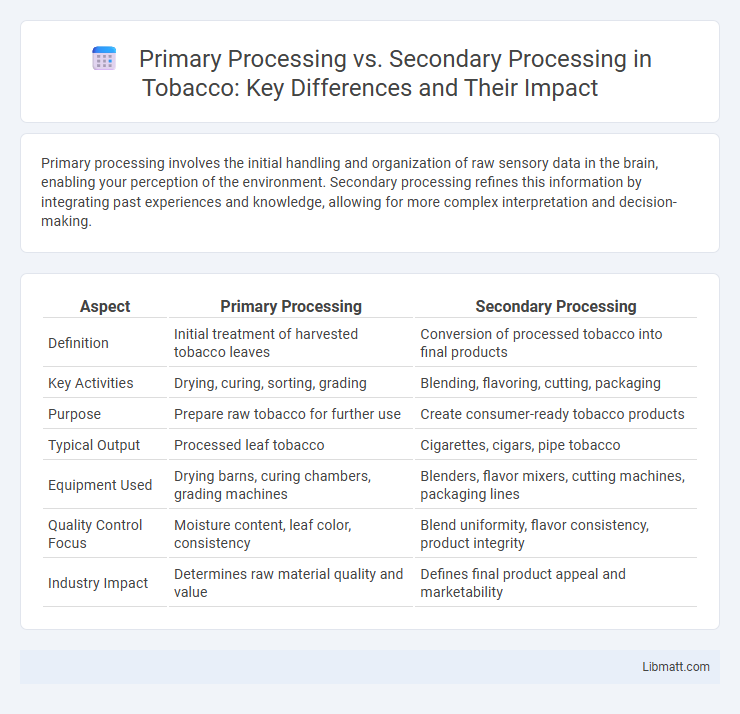
| Aspect | Primary Processing | Secondary Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial treatment of harvested tobacco leaves | Conversion of processed tobacco into final products |
| Key Activities | Drying, curing, sorting, grading | Blending, flavoring, cutting, packaging |
| Purpose | Prepare raw tobacco for further use | Create consumer-ready tobacco products |
| Typical Output | Processed leaf tobacco | Cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco |
| Equipment Used | Drying barns, curing chambers, grading machines | Blenders, flavor mixers, cutting machines, packaging lines |
| Quality Control Focus | Moisture content, leaf color, consistency | Blend uniformity, flavor consistency, product integrity |
| Industry Impact | Determines raw material quality and value | Defines final product appeal and marketability |
Introduction to Processing: Primary vs Secondary
Primary processing involves the initial transformation of raw materials into basic, usable forms, such as milling grains into flour or extracting crude oil from petroleum. Secondary processing takes these primary products and refines, enhances, or assembles them into finished goods like baked bread or plastic containers. Understanding the distinction between primary and secondary processing helps you optimize manufacturing workflows and improve product value.
Defining Primary Processing
Primary processing involves the initial stage of data manipulation where raw sensory inputs or information are converted into a basic, organized form for further analysis. This stage emphasizes automatic, unconscious mechanisms that structure perceptions based on innate neural functions. It contrasts with secondary processing, which engages higher-order cognitive functions such as reasoning and conscious evaluation.
Defining Secondary Processing
Secondary processing involves transforming raw materials into finished goods through techniques such as machining, forging, and casting to enhance product value and functionality. Unlike primary processing, which extracts or separates raw elements from natural sources, secondary processing modifies these materials to meet specific design and performance criteria. This stage is crucial in manufacturing sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where precision and material properties dictate final product quality.
Key Differences Between Primary and Secondary Processing
Primary processing involves the initial transformation and organization of raw sensory data into basic, meaningful patterns within the brain's sensory regions. Secondary processing refers to the higher-order analysis, interpretation, and integration of these primary inputs, enabling functions such as language, reasoning, and memory consolidation within associative cortical areas. The key difference lies in primary processing handling raw input and secondary processing managing complex cognitive functions based on that input.
Examples of Primary Processing Methods
Primary processing methods involve basic physical or mechanical treatments to prepare raw materials for further refinement or use. Examples include washing, sorting, crushing, drying, and milling, which help remove impurities and reduce size without altering the chemical composition. Understanding your specific product needs allows you to select the most effective primary processing technique to ensure quality and efficiency in production.
Examples of Secondary Processing Techniques
Secondary processing techniques include casting, molding, machining, and joining methods such as welding and brazing. These processes refine primary processed materials like metals, plastics, and composites into precise components or complex assemblies. Surface treatments such as coating, heat treatment, and grinding enhance material properties and functionality in secondary processing stages.
Importance and Applications of Primary Processing
Primary processing is crucial as it involves the initial treatment of raw materials to make them suitable for further use or consumption, ensuring quality and safety standards are met. It plays a vital role in industries such as agriculture, food production, and manufacturing by transforming raw inputs into usable products like cleaned grains, sorted minerals, or filtered liquids. Your understanding of primary processing can optimize supply chain efficiency and enhance product value, setting the foundation for all subsequent secondary processing steps.
Importance and Applications of Secondary Processing
Secondary processing is crucial for transforming raw materials obtained from primary processing into finished or semi-finished products with enhanced properties, increasing their market value and usability. It includes refining, purifying, and fabricating processes that tailor products to specific industrial applications such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food production. Understanding how secondary processing refines your materials can optimize product quality, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency in the supply chain.
Challenges in Primary and Secondary Processing
Challenges in primary processing include the removal of impurities, moisture content control, and maintaining raw material quality, which directly impact downstream efficiency and product consistency. Secondary processing faces difficulties such as uniform heat treatment, precise shape and size control, and ensuring product stability during packaging and storage. Both stages require stringent quality control measures to minimize defects and optimize overall production yield.
Future Trends in Processing Technologies
Future trends in processing technologies emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence with both primary processing, like sorting and cleaning raw materials, and secondary processing, which involves transforming those materials into finished products. Advancements in automation and real-time data analytics optimize efficiency and reduce waste across the entire value chain. Emerging techniques such as bioprocessing and advanced thermal treatments are reshaping secondary processing by enhancing product quality and sustainability.
primary processing vs secondary processing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com