Stem processing involves extracting fibers or nutrients from the plant's stem, often used in industries like paper production or textile manufacturing; leaf processing focuses on harvesting and treating leaves for purposes such as herbal teas, medicines, or culinary uses. Your choice between stem and leaf processing depends on the desired end product and specific plant characteristics.
Table of Comparison
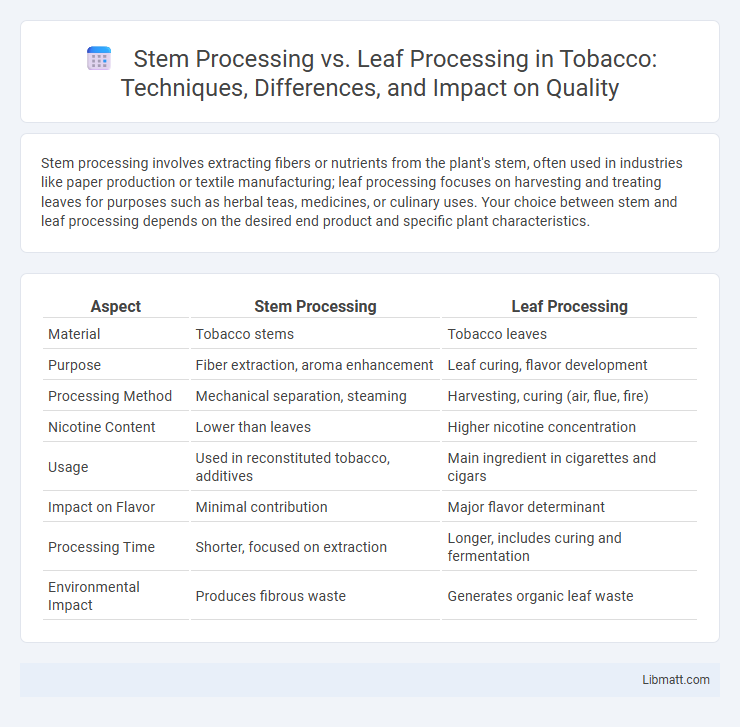
| Aspect | Stem Processing | Leaf Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Tobacco stems | Tobacco leaves |
| Purpose | Fiber extraction, aroma enhancement | Leaf curing, flavor development |
| Processing Method | Mechanical separation, steaming | Harvesting, curing (air, flue, fire) |
| Nicotine Content | Lower than leaves | Higher nicotine concentration |
| Usage | Used in reconstituted tobacco, additives | Main ingredient in cigarettes and cigars |
| Impact on Flavor | Minimal contribution | Major flavor determinant |
| Processing Time | Shorter, focused on extraction | Longer, includes curing and fermentation |
| Environmental Impact | Produces fibrous waste | Generates organic leaf waste |
Introduction to Stem and Leaf Processing
Stem processing involves transforming the main structural parts of plants into raw materials for various industries, emphasizing mechanical or chemical treatment of stems to extract fibers, biofuels, or paper pulp. Leaf processing, on the other hand, focuses on the utilization of leaves for medicinal extracts, teas, or animal fodder through drying, grinding, or chemical extraction techniques. Understanding the distinct methods and end-uses of stem and leaf processing helps optimize your approach to agricultural or industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Stems and Leaves
Stems provide structural support and transport water, nutrients, and sugars between roots and leaves, while leaves primarily conduct photosynthesis to produce food. Stems contain vascular tissues arranged in bundles, enabling efficient transport and growth through nodes and internodes, whereas leaves have a broad surface area with chloroplast-rich mesophyll cells optimized for light absorption. Unlike leaves, stems often store food and may have buds for new growth, demonstrating distinct roles in plant development and survival.
Importance of Proper Material Selection
Proper material selection is crucial in stem processing versus leaf processing to ensure optimal product quality and yield in industries like textile and herbal extraction. Stems, often denser and tougher, require materials with higher durability and tensile strength, whereas leaves demand softer, more flexible materials to preserve delicate structures and active compounds. Selecting appropriate materials enhances processing efficiency, reduces waste, and maintains the integrity of the final product.
Common Methods for Stem Processing
Common methods for stem processing include retting, decortication, and mechanical breaking. Retting involves microbial or chemical treatments to separate fibers from the stem by rotting away the softer tissues. Decortication uses machines to crush and scrape the stems, extracting fibers for applications in textiles and rope manufacturing.
Common Methods for Leaf Processing
Common methods for leaf processing include drying, grinding, and extraction techniques such as solvent extraction and steam distillation to obtain bioactive compounds. These processes preserve essential oils, nutrients, and phytochemicals crucial for product quality and efficacy. Your choice of leaf processing method significantly impacts the yield and potency of herbal and medicinal extracts.
Equipment Used in Stem vs Leaf Processing
Equipment used in stem processing typically includes industrial chippers, grinders, and pulpers designed to break down tough, fibrous material into manageable components for further use in paper production or biomass energy. Leaf processing equipment often involves specialized dryers, cutters, and shredders optimized for delicate, moisture-rich foliage to preserve essential oils and maintain leaf integrity for applications in herbal products or composting. Your choice between stem and leaf processing machinery depends on material characteristics and the desired end product quality.
Quality Control in Stem and Leaf Processing
Quality control in stem processing involves monitoring fiber strength, moisture content, and chemical treatments to ensure consistent raw material quality for textile production. In leaf processing, quality control focuses on pigment extraction efficiency, leaf freshness, and contamination levels to maintain product purity in herbal or agricultural applications. Your choice between stem and leaf processing methods depends on stringent quality assessment tailored to the end-use requirements.
Effects on Nutritional and Chemical Composition
Stem processing often results in higher fiber content but may reduce essential nutrients like vitamins and antioxidants compared to leaf processing. Leaf processing tends to preserve more chlorophyll, polyphenols, and bioactive compounds, enhancing the nutritional and chemical quality of the final product. Understanding these differences can help you optimize the nutritional value based on the desired application.
Industrial Applications of Stem and Leaf Processing
Stem processing in industrial applications primarily involves extracting fibers for textiles, paper, and bio-composites, offering strength and durability essential for construction and automotive industries. Leaf processing is utilized for producing specialty products like tea, medicinal extracts, and biofuels, capitalizing on the biochemical compounds unique to leaves. Understanding the distinct industrial roles of stem and leaf processing helps optimize your resource management and product development strategies.
Sustainability Considerations and Future Trends
Stem processing typically involves more energy-intensive mechanical or chemical treatments, raising concerns about higher carbon footprints and resource consumption compared to leaf processing, which often uses less invasive methods. Leaf processing leverages renewable biomaterials with lower waste generation, promoting circular economy principles in sustainable manufacturing. Future trends indicate growing adoption of green technologies and biorefinery integration to optimize both stem and leaf processing for enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
Stem processing vs Leaf processing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com