Less than truckload (LTL) shipping consolidates multiple smaller freight shipments from different customers into one truck, making it cost-effective for shipping smaller loads without needing a full truck. Full truckload (FTL) shipping reserves an entire truck for a single shipment, providing faster transit times and reduced handling, which is ideal for large shipments or items requiring direct transportation.
Table of Comparison
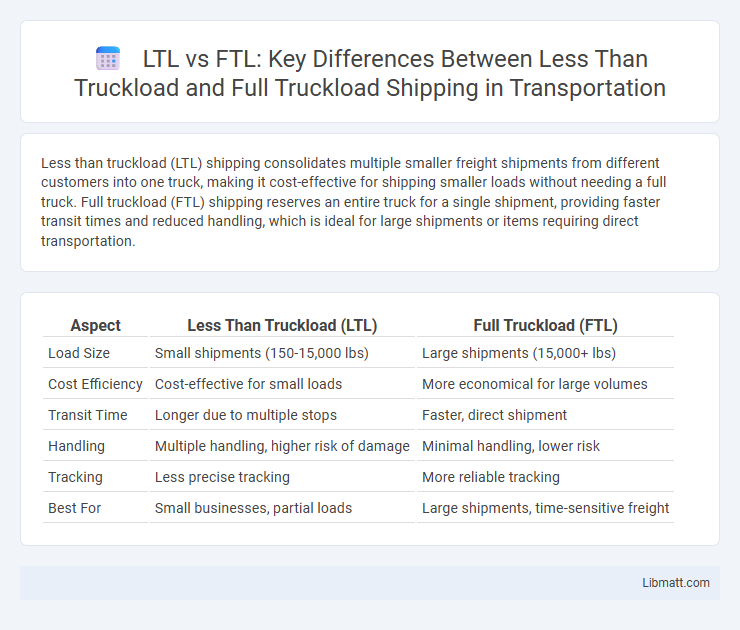
| Aspect | Less Than Truckload (LTL) | Full Truckload (FTL) |
|---|---|---|
| Load Size | Small shipments (150-15,000 lbs) | Large shipments (15,000+ lbs) |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for small loads | More economical for large volumes |
| Transit Time | Longer due to multiple stops | Faster, direct shipment |
| Handling | Multiple handling, higher risk of damage | Minimal handling, lower risk |
| Tracking | Less precise tracking | More reliable tracking |
| Best For | Small businesses, partial loads | Large shipments, time-sensitive freight |
Introduction to LTL and FTL Shipping
Less than Truckload (LTL) shipping involves consolidating multiple smaller shipments from various customers into one truck, optimizing cost efficiency for loads between 150 and 15,000 pounds. Full Truckload (FTL) shipping dedicates an entire trailer to a single customer's cargo, ideal for larger shipments exceeding 15,000 pounds or requiring direct, expedited transport. Understanding these shipping methods allows you to choose the best option for your freight needs based on shipment size, budget, and delivery speed requirements.
Key Differences Between LTL and FTL
Less than Truckload (LTL) shipments involve transporting smaller freight volumes from multiple customers within a single trailer, optimizing costs and space for shipments typically ranging from 150 to 15,000 pounds. Full Truckload (FTL) shipping dedicates an entire trailer to one customer's goods, providing faster transit times and reduced handling for large shipments exceeding 15,000 pounds. Key differences include shipment size, cost structure--LTL uses a shared pricing model based on weight and distance, while FTL charges a flat rate per truck--and transit speed, with FTL generally offering quicker, direct routes.
Cost Comparison: LTL vs FTL
Less than Truckload (LTL) shipping typically offers lower costs for smaller shipments by sharing trailer space with other shippers, reducing your expense compared to booking an entire trailer. Full Truckload (FTL) shipping is usually more cost-effective for larger shipments that can fill a truck, avoiding multiple handling fees and potentially faster transit times. Choosing between LTL and FTL depends largely on your shipment size, budget, and delivery speed requirements.
Freight Size and Weight Considerations
Less than truckload (LTL) shipping is ideal for smaller freight shipments typically weighing between 150 and 15,000 pounds, allowing multiple shippers to share space and reduce costs. Full truckload (FTL) is designed for larger shipments, usually exceeding 15,000 pounds or occupying an entire truck trailer, offering faster transit times without frequent stops. Understanding your freight size and weight helps determine whether LTL or FTL optimizes shipping efficiency and cost-effectiveness for your business needs.
Transit Time and Delivery Speed
Less than truckload (LTL) shipments typically experience longer transit times compared to full truckload (FTL) due to multiple stops and load transfers, which can slow down delivery speed. FTL offers faster delivery since your cargo remains on one truck from origin to destination, minimizing handling and delays. Choosing FTL ensures more reliable transit times and quicker delivery for time-sensitive shipments.
Suitability by Industry and Shipment Type
Less than truckload (LTL) shipping is ideal for industries with smaller, frequent shipments such as retail, manufacturing, and e-commerce, where multiple customers share trailer space to optimize costs. Full truckload (FTL) suits sectors like automotive, heavy machinery, and agriculture that require transporting large, bulky, or high-volume goods directly from origin to destination, minimizing handling and transit time. Your choice between LTL and FTL depends largely on the shipment size, frequency, and urgency, with LTL offering cost efficiency for smaller loads and FTL providing faster, dedicated transport for sizable freight.
Pros and Cons of LTL Shipping
Less than Truckload (LTL) shipping offers cost efficiency by allowing multiple shippers to share trailer space, reducing expenses for smaller shipments compared to Full Truckload (FTL) shipping. LTL can lead to longer transit times and increased handling risk, as shipments are transferred between multiple terminals. Your choice depends on shipment size, budget, and delivery speed requirements, with LTL ideal for smaller, less time-sensitive loads.
Pros and Cons of FTL Shipping
Full truckload (FTL) shipping offers faster transit times and reduced risk of damage since your goods occupy the entire trailer, minimizing handling during transport. However, FTL can be more expensive than less than truckload (LTL) shipping, especially if your shipment doesn't fully utilize the trailer space, leading to higher costs per unit. Choosing FTL ensures direct routes and better security, making it ideal for large, urgent shipments that prioritize speed and safety.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between LTL and FTL
When choosing between less than truckload (LTL) and full truckload (FTL) shipping, consider shipment size, delivery speed, and cost-efficiency. LTL is ideal for smaller shipments where you share truck space and reduce expenses, while FTL suits larger, time-sensitive loads requiring a dedicated trailer. Your decision should also factor in product fragility and the importance of minimizing handling to ensure optimal freight safety.
How to Optimize Your Freight Strategy
Optimizing your freight strategy involves choosing between Less Than Truckload (LTL) and Full Truckload (FTL) shipping based on shipment size, cost efficiency, and delivery speed. LTL is ideal for smaller shipments, reducing costs by sharing space with other shippers, while FTL suits larger loads that require direct transportation without stops, ensuring faster transit times and lower damage risk. Analyzing your freight volume, delivery deadlines, and budget will help you select the most effective option, improving supply chain efficiency and reducing overall logistics expenses.
less than truckload (LTL) vs full truckload (FTL) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com