Pipelining offers a cost-effective and efficient method for transporting liquids and gases over long distances, reducing traffic congestion and environmental impact compared to trucking. Your choice depends on factors like cargo type, distance, and infrastructure availability, with trucking providing more flexibility for shorter routes and diverse cargo.
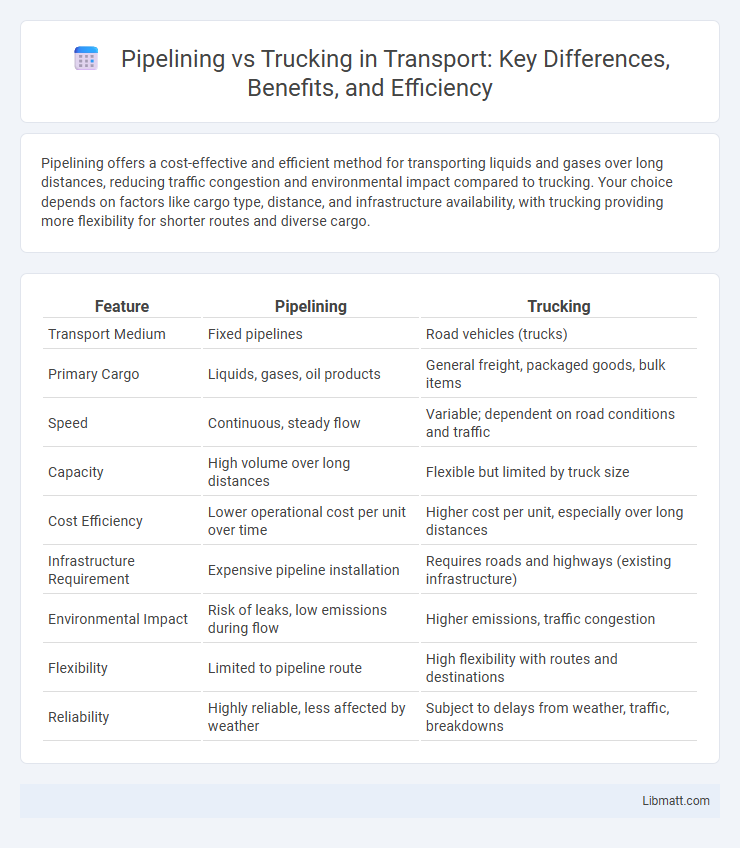
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pipelining | Trucking |
|---|---|---|
| Transport Medium | Fixed pipelines | Road vehicles (trucks) |
| Primary Cargo | Liquids, gases, oil products | General freight, packaged goods, bulk items |
| Speed | Continuous, steady flow | Variable; dependent on road conditions and traffic |
| Capacity | High volume over long distances | Flexible but limited by truck size |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational cost per unit over time | Higher cost per unit, especially over long distances |
| Infrastructure Requirement | Expensive pipeline installation | Requires roads and highways (existing infrastructure) |
| Environmental Impact | Risk of leaks, low emissions during flow | Higher emissions, traffic congestion |
| Flexibility | Limited to pipeline route | High flexibility with routes and destinations |
| Reliability | Highly reliable, less affected by weather | Subject to delays from weather, traffic, breakdowns |
Introduction to Pipelining and Trucking
Pipelining involves transporting liquids or gases through pipelines, offering efficient, continuous flow and reduced environmental impact compared to trucking. Trucking uses trucks to move goods over roads, providing flexible, point-to-point delivery suitable for diverse cargo and varying routes. Both methods play crucial roles in supply chain logistics, each optimized for specific types of freight and operational needs.
Overview of Logistics Transportation Methods
Pipelining and trucking are two critical logistics transportation methods with distinct operational advantages. Pipelining is ideal for transporting liquids and gases over long distances efficiently, minimizing spillage and weather impact, while trucking offers flexible, door-to-door delivery suitable for diverse cargo types and shorter routes. Your choice between these methods depends on cargo nature, distance, and time sensitivity to optimize supply chain performance.
How Pipelining Works
Pipelining transports liquids and gases through a network of connected pipes using pump stations that maintain constant pressure to ensure steady flow. This method reduces the reliance on road transportation, minimizing fuel consumption and emissions compared to trucking. Your product moves efficiently and safely over long distances without delays typical of traffic or loading times.
The Trucking Process Explained
The trucking process involves loading goods onto trucks, planning routes, and managing schedules to ensure timely delivery across various distances and terrains. Trucking offers flexibility in pickup and drop-off locations, making it essential for last-mile delivery and regions lacking pipeline infrastructure. Your choice between trucking and pipelining depends on the type of cargo, volume, delivery speed, and geographic constraints.
Key Differences Between Pipelining and Trucking
Pipelining and trucking represent two distinct methods for transporting goods, with pipelining primarily used for moving liquids and gases through continuous underground networks, while trucking involves the use of vehicles to transport various products over roads. Pipelining offers higher efficiency and safety for large volumes over long distances but requires significant initial infrastructure investment, whereas trucking provides greater flexibility in routes, schedules, and cargo types suitable for shorter distances or less consistent shipments. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your logistics strategy by matching the transportation mode to the specific needs of your supply chain.
Cost Analysis: Pipelining vs Trucking
Pipelining generally offers lower operational costs compared to trucking due to reduced labor, fuel, and maintenance expenses over long distances. Initial capital expenditure for pipeline infrastructure is high, but economies of scale make it more cost-effective for transporting large volumes continuously. Trucking incurs variable costs, including driver wages, fuel prices, and toll fees, which increase significantly with distance and payload complexity.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Pipelining significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to trucking due to its lower fuel consumption and reliance on steady, pressurized flow rather than intermittent diesel-powered transport. Trucking contributes more to air pollution and road congestion, resulting in higher carbon dioxide and particulate matter emissions per barrel of oil or gas moved. Environmentally, pipelines offer a more sustainable option by minimizing habitat disruption and spill risks associated with frequent truck trips.
Efficiency and Reliability Factors
Pipelining offers superior efficiency by enabling continuous, automated transport of liquids or gases with minimal energy consumption and reduced environmental impact compared to trucking. Trucking provides more flexibility and reliability in reaching diverse locations and handling variable volumes, especially where pipeline infrastructure is unavailable or inoperable. Your choice between pipelining and trucking should consider the trade-off between the high-capacity, low-maintenance pipeline systems and the adaptable, location-flexible trucking methods.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Pipelining is predominantly utilized in the oil and gas industry for the efficient, continuous transport of large volumes of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products over long distances, minimizing operational costs and environmental risks. Trucking serves as a flexible solution for short-haul transport, last-mile delivery, and distribution in sectors like retail, agriculture, and construction, where access to remote or less-developed infrastructure is necessary. The choice between pipelining and trucking depends on factors such as volume, distance, delivery speed, and terrain, with pipelines favored for bulk, consistent flows and trucking chosen for versatility and accessibility.
Future Trends in Pipelining and Trucking
Future trends in pipelining revolve around increased automation, smart sensor integration, and the adoption of AI-driven monitoring systems to optimize flow efficiency and leak detection. Trucking is rapidly advancing toward electrification, autonomous vehicle technology, and enhanced logistics software to improve route planning and reduce emissions. Your transportation strategy should consider these innovations, balancing the long-term cost benefits of pipelining with the flexibility and evolving capabilities of trucking.
pipelining vs trucking Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com