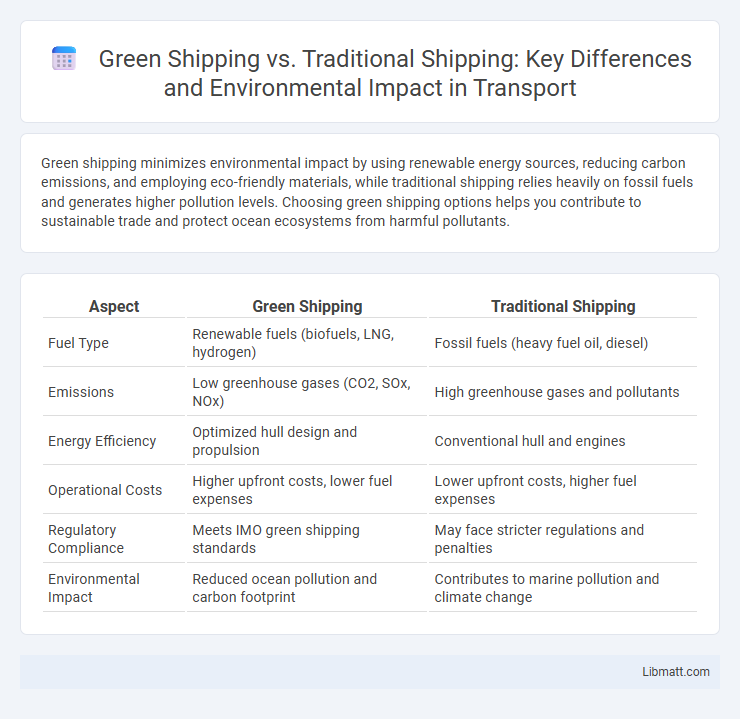
Green shipping minimizes environmental impact by using renewable energy sources, reducing carbon emissions, and employing eco-friendly materials, while traditional shipping relies heavily on fossil fuels and generates higher pollution levels. Choosing green shipping options helps you contribute to sustainable trade and protect ocean ecosystems from harmful pollutants.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Green Shipping | Traditional Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Renewable fuels (biofuels, LNG, hydrogen) | Fossil fuels (heavy fuel oil, diesel) |
| Emissions | Low greenhouse gases (CO2, SOx, NOx) | High greenhouse gases and pollutants |
| Energy Efficiency | Optimized hull design and propulsion | Conventional hull and engines |
| Operational Costs | Higher upfront costs, lower fuel expenses | Lower upfront costs, higher fuel expenses |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets IMO green shipping standards | May face stricter regulations and penalties |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced ocean pollution and carbon footprint | Contributes to marine pollution and climate change |
Introduction to Green Shipping vs Traditional Shipping
Green shipping utilizes environmentally friendly technologies and fuels such as LNG, biofuels, and electric propulsion to reduce carbon emissions and marine pollution, contrasting sharply with traditional shipping that predominantly relies on heavy fuel oil and diesel engines. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) targets a 50% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, driving the industry's shift towards green shipping practices like energy-efficient vessel design and slow steaming. Traditional shipping methods generate significant air pollutants and ocean contaminants, whereas green shipping prioritizes sustainability through innovation and regulatory compliance.
Environmental Impact: Green vs Traditional Shipping
Green shipping significantly reduces carbon emissions and air pollutants by using cleaner fuels, energy-efficient technologies, and renewable energy sources compared to traditional shipping, which relies heavily on fossil fuels and emits high levels of greenhouse gases. Your choice of green shipping can minimize ocean pollution, decrease the carbon footprint, and protect marine biodiversity, fostering sustainable global trade. Traditional shipping, though cost-effective, contributes to ocean acidification, oil spills, and harmful particulate matter that threaten marine ecosystems and public health.
Fuel Types and Emissions Comparison
Green shipping utilizes alternative fuels such as LNG, biofuels, and hydrogen, significantly reducing carbon dioxide and sulfur oxide emissions compared to traditional shipping, which predominantly relies on heavy fuel oil and marine diesel. Emissions from traditional shipping account for nearly 3% of global greenhouse gases, whereas green shipping technologies aim to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 through cleaner fuel implementation and energy-efficient vessel designs. Advances in battery propulsion and wind-assisted shipping further diminish reliance on fossil fuels, promoting sustainable maritime transport with lower environmental impact.
Operational Costs and Economic Benefits
Green shipping reduces operational costs by utilizing energy-efficient technologies and alternative fuels like LNG and hydrogen, lowering fuel expenses and emissions-related penalties. Traditional shipping often incurs higher costs due to reliance on heavy fuel oil and compliance with stricter environmental regulations. Economic benefits of green shipping include tax incentives, reduced carbon credits costs, and enhanced brand reputation, driving long-term profitability and sustainability.
Regulatory Compliance in Shipping Methods
Green shipping methods emphasize adherence to stringent international regulations such as the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) MARPOL Annex VI, which limits sulfur oxide emissions, whereas traditional shipping often relies on less environmentally friendly fuels that may struggle to meet these standards. Compliance with the IMO 2020 sulfur cap and the Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) is more seamlessly integrated into green shipping technologies, promoting reduced carbon footprints and enhanced fuel efficiency. The evolving regulatory landscape increasingly favors sustainable shipping practices, compelling traditional operators to invest in greener alternatives or risk non-compliance penalties and restricted port access.
Technological Innovations in Green Shipping
Technological innovations in green shipping include the development of advanced propulsion systems such as hydrogen fuel cells, electric batteries, and wind-assisted technologies that significantly reduce carbon emissions. Autonomous vessels equipped with AI optimize routes and fuel consumption, enhancing efficiency in green shipping operations. These innovations contribute to a sustainable transition by minimizing the environmental impact compared to traditional diesel-powered ships.
Challenges and Limitations of Green Shipping
Green shipping faces significant challenges such as high upfront costs for eco-friendly vessel technology and limited infrastructure for alternative fuels like hydrogen and ammonia. Regulatory uncertainties and slower refueling times further constrain widespread adoption. Traditional shipping benefits from established global networks and fuel availability but struggles with higher carbon emissions and environmental impact.
Market Adoption and Industry Trends
Green shipping adoption has surged as major ports and shipping companies integrate environmentally friendly technologies like LNG-powered vessels and battery-electric propulsion systems. Industry trends show a growing commitment to regulatory compliance with IMO 2030 and 2050 emissions targets, driving investments in sustainable fuels such as green ammonia and hydrogen. Market data reveals increasing demand for carbon-neutral shipping options, propelled by consumer pressure and corporate ESG initiatives shaping global maritime logistics.
Consumer Awareness and Demand Shifts
Consumer awareness of environmental issues has significantly increased, driving demand shifts toward green shipping solutions that reduce carbon emissions and ocean pollution. Market data indicates that environmentally conscious consumers prefer companies adopting sustainable practices, influencing shipping industry standards and practices. This shift compels traditional shipping operators to invest in cleaner technologies and alternative fuels to remain competitive and meet evolving consumer expectations.
Future Outlook: Towards Sustainable Shipping
Green shipping innovations are rapidly transforming the maritime industry by reducing carbon emissions through the adoption of alternative fuels like hydrogen, ammonia, and electrification technologies. Traditional shipping, reliant on heavy fuel oil, faces increasing regulatory pressures and carbon pricing mechanisms that drive companies to invest in sustainable vessel designs and energy-efficient operations. Your choice of green shipping options supports the future outlook of a cleaner, more resilient global supply chain that aligns with international climate goals.
green shipping vs traditional shipping Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com