Repositioning involves moving assets or inventory within a company to optimize operations, while repositioning cargo specifically refers to transporting goods from one location to another to meet logistical demands. Understanding how repositioning cargo affects supply chain efficiency can enhance your overall transportation strategy.
Table of Comparison
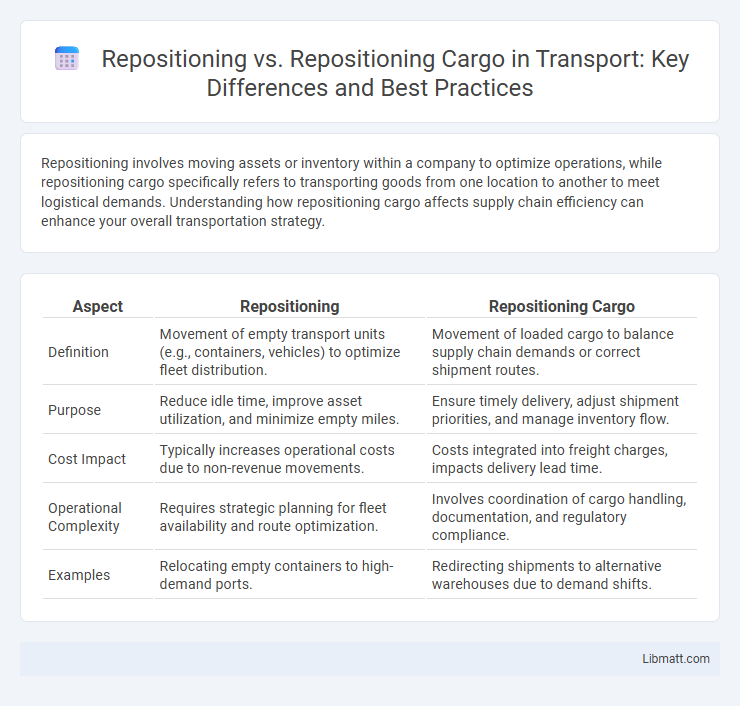
| Aspect | Repositioning | Repositioning Cargo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Movement of empty transport units (e.g., containers, vehicles) to optimize fleet distribution. | Movement of loaded cargo to balance supply chain demands or correct shipment routes. |
| Purpose | Reduce idle time, improve asset utilization, and minimize empty miles. | Ensure timely delivery, adjust shipment priorities, and manage inventory flow. |
| Cost Impact | Typically increases operational costs due to non-revenue movements. | Costs integrated into freight charges, impacts delivery lead time. |
| Operational Complexity | Requires strategic planning for fleet availability and route optimization. | Involves coordination of cargo handling, documentation, and regulatory compliance. |
| Examples | Relocating empty containers to high-demand ports. | Redirecting shipments to alternative warehouses due to demand shifts. |
Introduction to Repositioning and Repositioning Cargo
Repositioning involves shifting assets or resources from one location to another to optimize operational efficiency, often seen in logistics and transportation sectors. Repositioning cargo specifically refers to the strategic movement of goods between warehouses, ports, or vehicles to balance supply and demand while minimizing transportation costs. Understanding these concepts helps you streamline distribution processes and enhance supply chain management.
Defining Repositioning in Logistics
Repositioning in logistics refers to relocating empty or loaded transport assets such as containers, trucks, or vessels to balance supply and demand across different locations. Repositioning cargo specifically involves moving goods to adjust inventory distribution, optimize supply chain efficiency, and reduce shipping costs. Effective repositioning strategies improve asset utilization, minimize idle time, and enhance overall logistics network responsiveness.
What is Repositioning Cargo?
Repositioning cargo refers to the process of moving goods from one location to another to optimize shipping routes, reduce costs, or balance inventory levels across warehouses. This logistical strategy is essential for ensuring that goods are available where demand is highest, minimizing empty container moves and enhancing supply chain efficiency. Repositioning cargo plays a critical role in global trade, particularly in container shipping and freight management.
Key Differences Between Repositioning and Repositioning Cargo
Repositioning involves moving assets such as equipment or containers to optimize operational efficiency, while repositioning cargo specifically refers to shifting goods within or between transport modes for improved logistics flow. The key difference lies in the asset type: repositioning cargo focuses on the products being shipped, whereas repositioning may include empty containers or vehicles necessary for supply chain management. Understanding these distinctions helps streamline resource allocation and reduce transportation costs.
Strategic Importance of Repositioning in Supply Chains
Repositioning plays a critical role in supply chains by optimizing asset utilization, reducing idle time, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. Repositioning cargo specifically addresses the challenge of balancing inventory across locations to meet fluctuating demand and minimize transportation costs. Your supply chain resilience improves significantly when strategic repositioning ensures timely delivery and resource allocation.
Benefits and Challenges of Repositioning Cargo
Repositioning cargo optimizes supply chain efficiency by moving empty or underutilized containers to high-demand locations, reducing transportation costs and improving asset utilization. Challenges include increased complexity in logistics planning, potential delays, and higher fuel consumption. Your ability to balance these benefits and challenges directly impacts operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in global shipping.
Operational Processes Involved in Repositioning
Repositioning involves moving assets like ships or equipment within a company's network to optimize efficiency and meet demand, while repositioning cargo specifically refers to shifting goods between locations to streamline logistics. Operational processes in repositioning include route planning, scheduling, coordination with port authorities, and asset tracking to minimize downtime and costs. You can improve supply chain responsiveness by effectively managing these tasks and ensuring seamless communication across all stages.
Cost Implications: Repositioning vs. Repositioning Cargo
Repositioning a vessel often incurs higher costs due to fuel consumption, crew expenses, and potential downtime without cargo revenue, whereas repositioning cargo alone minimizes these expenses by utilizing existing vessel routes and capacity. Cargo repositioning leverages backhaul opportunities and reduces empty leg voyages, lowering overall operational costs and improving supply chain efficiency. Shipping companies prioritize cargo repositioning strategies to optimize utilization and minimize the substantial financial burden associated with moving idle vessels.
Best Practices for Optimizing Repositioning Strategies
Optimizing repositioning strategies requires analyzing cargo flow patterns and demand forecasts to minimize empty runs and reduce operational costs. Implementing real-time tracking systems and leveraging AI for route optimization improve asset utilization and turnaround times. You can enhance efficiency by coordinating closely with supply chain partners to align repositioning schedules with actual cargo needs.
Future Trends in Logistics Repositioning
Future trends in logistics indicate a growing shift toward intelligent repositioning strategies that leverage real-time data analytics and AI to optimize cargo movement and reduce empty runs. Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and advanced fleet management systems enhances transparency and efficiency in repositioning cargo across global supply chains. Your logistics operations benefit from predictive modeling that anticipates demand fluctuations, enabling proactive repositioning to meet future market needs.
repositioning vs repositioning cargo Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com