Cold soaking preserves the delicate flavors and nutrients in your ingredients by allowing them to infuse gradually at room temperature, while heat soaking accelerates extraction through gentle warming, enhancing aroma and richness. Choosing between cold soaking and heat soaking depends on the desired intensity and profile of your final dish or beverage.
Table of Comparison
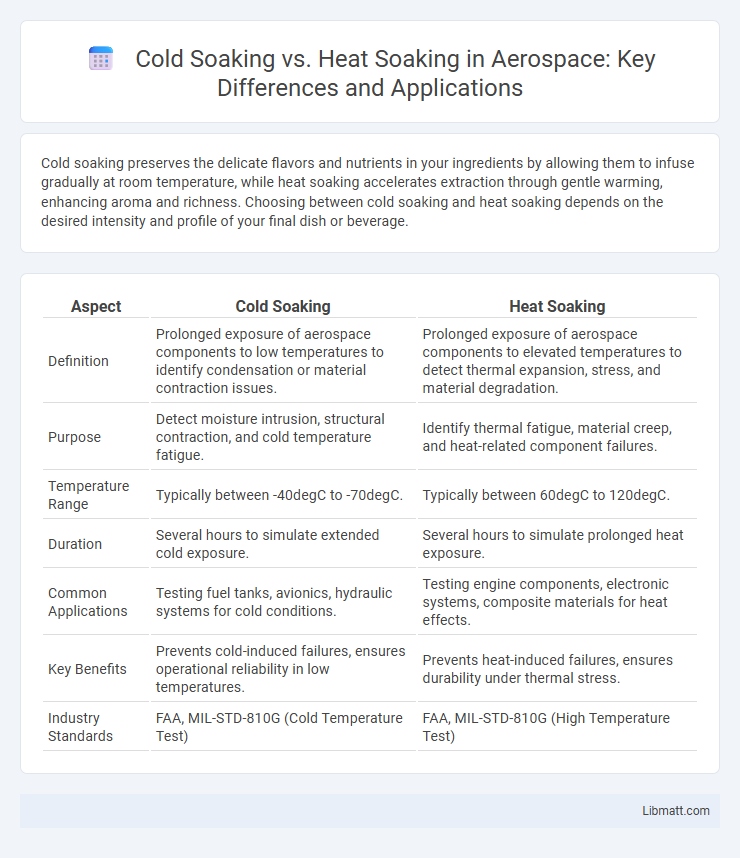
| Aspect | Cold Soaking | Heat Soaking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prolonged exposure of aerospace components to low temperatures to identify condensation or material contraction issues. | Prolonged exposure of aerospace components to elevated temperatures to detect thermal expansion, stress, and material degradation. |
| Purpose | Detect moisture intrusion, structural contraction, and cold temperature fatigue. | Identify thermal fatigue, material creep, and heat-related component failures. |
| Temperature Range | Typically between -40degC to -70degC. | Typically between 60degC to 120degC. |
| Duration | Several hours to simulate extended cold exposure. | Several hours to simulate prolonged heat exposure. |
| Common Applications | Testing fuel tanks, avionics, hydraulic systems for cold conditions. | Testing engine components, electronic systems, composite materials for heat effects. |
| Key Benefits | Prevents cold-induced failures, ensures operational reliability in low temperatures. | Prevents heat-induced failures, ensures durability under thermal stress. |
| Industry Standards | FAA, MIL-STD-810G (Cold Temperature Test) | FAA, MIL-STD-810G (High Temperature Test) |
Introduction to Cold Soaking and Heat Soaking
Cold soaking and heat soaking are fermentation techniques used to extract color, flavor, and tannins from grape skins in winemaking. Cold soaking involves macerating crushed grapes at low temperatures (10-15degC) before fermentation, enhancing color intensity and preserving fresh fruit aromas. Heat soaking applies controlled warmth (30-40degC) to crushed grapes after destemming to increase phenolic extraction and soften tannins, influencing the wine's body and structure.
Defining Cold Soaking: Process and Applications
Cold soaking is a process used to remove residual moisture from metal castings by exposing them to low temperatures for an extended period, which helps reduce the risk of hydrogen embrittlement and improve material integrity. This technique is commonly applied in steel and aluminum industries to alleviate internal stresses and prevent cracking in high-strength alloys. Your choice between cold soaking and heat soaking depends on the specific metallurgical requirements and the desired outcome for component durability and performance.
Understanding Heat Soaking: Methods and Uses
Heat soaking involves heating metal components, typically castings, to a specific temperature below their melting point to relieve internal stresses and eliminate impurities like hydrogen. This process is crucial in industries such as automotive and aerospace manufacturing to improve material durability and prevent defects like cracking. Understanding heat soaking methods allows you to select appropriate treatment parameters, enhancing the performance and longevity of your metal parts.
Key Differences Between Cold Soaking and Heat Soaking
Cold soaking uses cold water to break down tannins in wine slowly, enhancing subtle flavors without altering temperature-sensitive compounds. Heat soaking involves warming the wine to accelerate tannin softening and flavor development, but risks losing volatile aromas if not carefully controlled. Your choice between methods depends on whether you prefer a gentle, natural extraction or a faster, more intense flavor enhancement.
Benefits of Cold Soaking
Cold soaking preserves delicate flavors and aromas in hops by steeping them in cold water, enhancing the beer's freshness and brightness without extracting bitter compounds. This method reduces the risk of harsh tannins and unwanted grassy notes often associated with heat processing. Cold soaking also improves hop utilization efficiency, leading to a cleaner, crisper finish in craft beers and IPAs.
Advantages of Heat Soaking
Heat soaking effectively detects and eliminates potentially faulty tempered glass by exposing it to elevated temperatures, reducing the risk of spontaneous breakage in your glass installations. This method accelerates the identification of nickel sulfide inclusions that cause delayed glass failure, ensuring enhanced safety and durability. By preventing unpredictable breakage, heat soaking offers greater reliability and long-term performance compared to cold soaking.
Limitations and Drawbacks of Both Techniques
Cold soaking may lead to uneven temperature distribution, increasing the risk of incomplete contamination removal in glass or ceramics, while heat soaking requires significant energy consumption and extended processing times that may not be feasible for all facilities. Both methods can be limited by the material's susceptibility to thermal stress or structural damage, potentially compromising product integrity. Your choice between cold and heat soaking should consider these limitations alongside the specific requirements of the material and processing environment.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Cold Soaking
Cold soaking is best for preserving delicate flavors and nutrients in foods like fruits, vegetables, and grains without using heat. You should choose cold soaking when preparing raw or lightly softened foods for recipes such as salads, overnight oats, or hydration of dried fruits and legumes. This method is ideal for ensuring your ingredients retain their natural texture and nutritional profile.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Heat Soaking
Heat soaking is ideal for detecting latent defects in cast iron or heavy-duty steel components prone to temper embrittlement, making it essential in automotive and construction industries. This process accelerates the oxidation of impurities, revealing cracks or weaknesses that cold soaking may miss, ensuring structural integrity in safety-critical applications. Utilize heat soaking when component reliability under thermal stress and long-term durability are priorities in manufacturing and quality control protocols.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Soaking Technique
Cold soaking preserves delicate flavors and nutrients by maintaining low temperatures during extraction, ideal for teas and herbal infusions. Heat soaking enhances extraction efficiency and intensifies flavors by applying heat, best suited for robust ingredients like coffee and certain spices. Choosing the right soaking technique depends on the ingredient type, desired flavor profile, and nutritional goals.
Cold soaking vs Heat soaking Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com