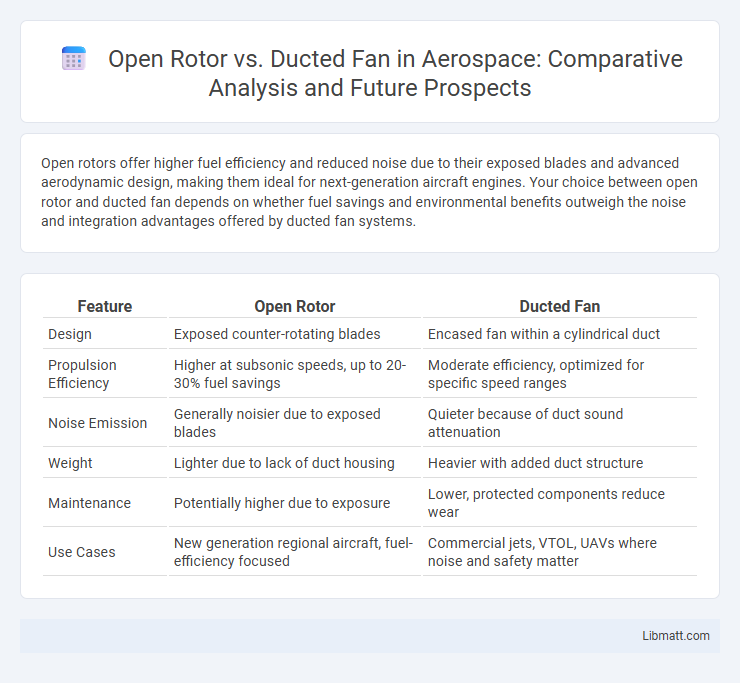
Open rotors offer higher fuel efficiency and reduced noise due to their exposed blades and advanced aerodynamic design, making them ideal for next-generation aircraft engines. Your choice between open rotor and ducted fan depends on whether fuel savings and environmental benefits outweigh the noise and integration advantages offered by ducted fan systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open Rotor | Ducted Fan |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Exposed counter-rotating blades | Encased fan within a cylindrical duct |
| Propulsion Efficiency | Higher at subsonic speeds, up to 20-30% fuel savings | Moderate efficiency, optimized for specific speed ranges |
| Noise Emission | Generally noisier due to exposed blades | Quieter because of duct sound attenuation |
| Weight | Lighter due to lack of duct housing | Heavier with added duct structure |
| Maintenance | Potentially higher due to exposure | Lower, protected components reduce wear |
| Use Cases | New generation regional aircraft, fuel-efficiency focused | Commercial jets, VTOL, UAVs where noise and safety matter |
Introduction to Open Rotor and Ducted Fan Technologies
Open rotor and ducted fan technologies represent two distinct approaches to aircraft propulsion, with open rotors featuring exposed blades that offer high aerodynamic efficiency and reduced fuel consumption, while ducted fans encase the blades within a cylindrical shroud to enhance noise reduction and safety. Open rotor systems achieve thrust by utilizing large, counter-rotating propellers that operate at lower speeds, making them suitable for fuel-efficient regional and short-haul aircraft. Ducted fans combine the benefits of traditional turbofan engines with improved static thrust and quieter operation, making them ideal for urban air mobility and advanced drone applications.
Historical Development and Core Principles
Open rotors originated in the mid-20th century as an effort to improve fuel efficiency by reducing drag through exposed blades, whereas ducted fans developed earlier as a safer, noise-reducing alternative with enclosed rotors. Open rotor designs harness aerodynamic principles by allowing airflow around large, variable-pitch blades for maximum thrust at lower fuel consumption, contrasting with ducted fans that optimize thrust via enclosed fans with fixed or variable pitch blades to reduce tip vortices and noise. Both technologies reflect evolving priorities in propulsion efficiency, noise reduction, and design complexity throughout aerospace history.
Aerodynamic Efficiency Comparisons
Open rotors exhibit higher aerodynamic efficiency than ducted fans due to reduced drag and lower tip losses, resulting in improved fuel consumption for aircraft. The absence of a duct allows more direct airflow interaction, enhancing propulsion efficiency particularly at high speeds. Ducted fans, however, provide better noise attenuation and protection, but this often comes at the cost of increased aerodynamic drag and slightly lower overall efficiency compared to open rotor designs.
Fuel Consumption and Environmental Impact
Open rotor engines typically offer lower fuel consumption compared to ducted fans due to their higher propulsive efficiency, which reduces CO2 emissions and overall environmental impact. However, open rotors generate more noise pollution, challenging noise regulations and sometimes necessitating operational restrictions. If your priority is minimizing fuel costs and carbon footprint, open rotors present a promising option despite their acoustic drawbacks.
Noise Generation and Mitigation Strategies
Open rotor engines generate higher noise levels due to unshielded rotating blades interacting directly with the airflow, causing increased aerodynamic noise compared to ducted fans. Ducted fans benefit from the surrounding nacelle, which acts as a noise barrier and accommodates acoustic liners that significantly reduce noise emissions. Understanding these distinctions helps you assess noise mitigation strategies, where open rotors rely on blade design optimization and phased blade spacing, while ducted fans combine structural enclosure with advanced liner technologies for quieter operation.
Design Complexity and Maintenance Needs
Open rotor engines feature exposed blades requiring intricate aerodynamic design to optimize efficiency while managing noise and vibration, leading to higher design complexity compared to ducted fans. Maintenance demands intensify due to increased exposure to environmental elements and blade wear, necessitating frequent inspections and specialized repairs. Ducted fans offer simpler maintenance regimes with protective nacelles reducing blade damage and noise control requirements, contributing to overall lower operational costs.
Safety Considerations and Operational Risks
Open rotors present increased safety risks due to exposed blades, which require stringent clearance zones and specialized containment measures to protect ground personnel and nearby structures. Ducted fans offer enhanced safety by enclosing blades within shrouds, reducing the potential for debris ejection and minimizing bird strike damage. Both systems demand rigorous maintenance protocols, but open rotors involve higher operational risk management due to blade tip speeds and vulnerability to foreign object damage.
Application Suitability: Commercial vs. Military Use
Open rotor engines excel in commercial aviation due to their superior fuel efficiency and lower emissions, making them ideal for long-haul passenger flights where operational cost and environmental impact are critical. Ducted fans, favored in military applications, provide enhanced thrust, noise reduction, and protection against foreign object damage, which are essential for high-performance, tactical aircraft and stealth missions. Commercial airlines prioritize open rotor designs for economic sustainability, while military forces rely on ducted fan technology for versatility and combat readiness.
Future Trends and Technological Innovations
Open rotor engines are advancing with innovative blade designs and noise reduction technology, targeting significant fuel efficiency improvements for future commercial aircraft. Ducted fans continue evolving through enhanced composite materials and electric propulsion integration, offering quieter operation and increased thrust-to-weight ratios. Your choice between these technologies will influence sustainability and performance as aerospace shifts towards greener, more efficient propulsion systems.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Propulsion System
Open rotor engines offer higher fuel efficiency and lower noise levels at cruise conditions, making them ideal for long-haul flights focused on sustainability. Ducted fans provide superior thrust at takeoff and better protection in adverse weather, benefiting short-haul and regional aircraft with frequent stops. Your choice depends on mission profiles prioritizing either fuel savings and noise reduction with open rotors or operational reliability and thrust consistency with ducted fans.
Open rotor vs Ducted fan Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com