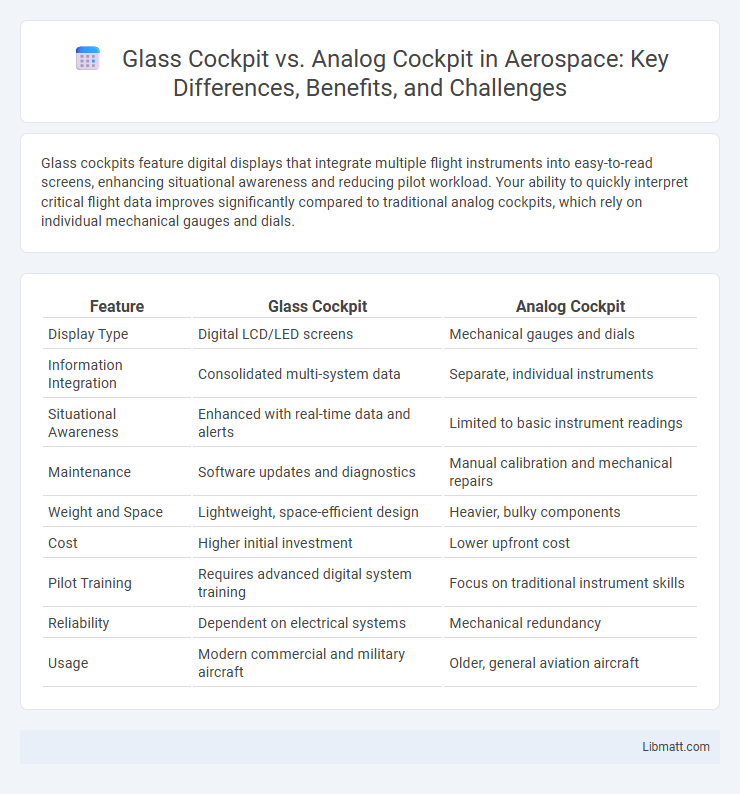
Glass cockpits feature digital displays that integrate multiple flight instruments into easy-to-read screens, enhancing situational awareness and reducing pilot workload. Your ability to quickly interpret critical flight data improves significantly compared to traditional analog cockpits, which rely on individual mechanical gauges and dials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Cockpit | Analog Cockpit |
|---|---|---|
| Display Type | Digital LCD/LED screens | Mechanical gauges and dials |
| Information Integration | Consolidated multi-system data | Separate, individual instruments |
| Situational Awareness | Enhanced with real-time data and alerts | Limited to basic instrument readings |
| Maintenance | Software updates and diagnostics | Manual calibration and mechanical repairs |
| Weight and Space | Lightweight, space-efficient design | Heavier, bulky components |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Pilot Training | Requires advanced digital system training | Focus on traditional instrument skills |
| Reliability | Dependent on electrical systems | Mechanical redundancy |
| Usage | Modern commercial and military aircraft | Older, general aviation aircraft |
Introduction to Cockpit Design Evolution
Glass cockpits revolutionized aviation by replacing traditional analog gauges with multifunctional digital displays, enhancing situational awareness and reducing pilot workload. Analog cockpits rely on mechanical instruments with individual dials and gauges, which can clutter the dashboard and require more interpretation. The evolution from analog to glass cockpit design marks a significant leap in integrating real-time data with intuitive interfaces for improved flight safety and efficiency.
What is a Glass Cockpit?
A Glass Cockpit is an advanced aircraft flight deck featuring digital electronic displays that integrate flight information, navigation data, and system status on large LCD screens. These digital interfaces replace traditional analog gauges, providing pilots with enhanced situational awareness through customizable layouts and real-time data. The streamlined presentation in Glass Cockpits improves decision-making efficiency and reduces pilot workload during flight operations.
What is an Analog Cockpit?
An Analog Cockpit features traditional mechanical gauges and dials that display flight information such as altitude, airspeed, and attitude through physical instruments. This system relies on individual analog indicators, each dedicated to a specific function, offering pilots tactile feedback and straightforward readings. While less integrated than digital systems, analog cockpits are valued for their simplicity and reliability in basic flight operations.
Key Differences Between Glass and Analog Cockpits
Glass cockpits utilize digital displays and advanced avionics systems to present flight data clearly and efficiently, while analog cockpits rely on traditional mechanical gauges and dials. Key differences include improved situational awareness, easier navigation, and enhanced integration of flight information in glass cockpits versus the manual interpretation and limited data consolidation in analog setups. Your choice affects the overall flight experience, safety, and operational efficiency.
Advantages of Glass Cockpits
Glass cockpits offer enhanced situational awareness by consolidating critical flight data into high-resolution digital displays, reducing pilot workload and improving decision-making speed. They provide real-time integration of navigation, weather, and aircraft system information, enabling more precise flight management compared to traditional analog gauges. The adaptability of glass cockpits allows for customizable interfaces and easier updates, which contribute to increased safety and operational efficiency.
Benefits of Analog Cockpits
Analog cockpits provide pilots with direct, intuitive readings through physical gauges, enhancing situational awareness during equipment failures or system malfunctions. Their mechanical nature ensures reliability under extreme conditions like electromagnetic interference or power loss, critical for maintaining flight safety. Familiarity with analog instruments also supports pilot training and transitions, offering a tangible interface that reduces cognitive overload during high-stress situations.
Pilot Training: Glass vs. Analog
Pilot training for glass cockpits emphasizes mastering digital flight displays, touchscreen controls, and integrated avionics systems, requiring familiarity with advanced software and real-time data interpretation. Analog cockpit training focuses on manual instrument reading, mechanical gauges, and traditional flight instruments, demanding strong fundamental skills in cross-checking and interpreting physical dials. Your proficiency in either cockpit type depends on thorough training tailored to the specific avionics technology to ensure safety and operational effectiveness.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Glass cockpits enhance safety by providing pilots with real-time data integration, intuitive displays, and automated alerts that reduce human error during critical flight phases. Analog cockpits rely on mechanical gauges that, while highly reliable and less prone to electronic failure, demand greater pilot workload and can delay response times in emergencies. Your choice between glass and analog cockpit should weigh the advanced situational awareness of glass systems against the proven durability of analog instruments to match specific operational safety and reliability requirements.
Cost Implications and Sustainability
Glass cockpits generally incur higher upfront costs due to advanced digital displays and integrated avionics compared to traditional analog cockpits, which utilize mechanical gauges and simpler electronics. However, glass cockpits contribute to sustainability by reducing pilot workload and enabling more efficient flight management, leading to lower fuel consumption and emissions. Your choice between the two should balance initial investment with long-term operational savings and environmental impact.
Future Trends in Cockpit Technology
Future trends in cockpit technology emphasize the growing adoption of glass cockpits, featuring customizable digital displays that enhance situational awareness and reduce pilot workload. Advances in augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) integration within glass cockpits promise to provide real-time data visualization and predictive analytics, improving flight safety and efficiency. Your cockpit experience is set to transform with these innovations, moving away from traditional analog instruments toward fully interactive and adaptive flight interfaces.
Glass Cockpit vs Analog Cockpit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com