Vortex generators improve airflow by creating small vortices that delay flow separation, enhancing lift and reducing drag on wings during various flight conditions. Winglets reduce wingtip vortices and induced drag by extending the wingtip vertically, increasing fuel efficiency and overall aerodynamic performance for your aircraft.
Table of Comparison
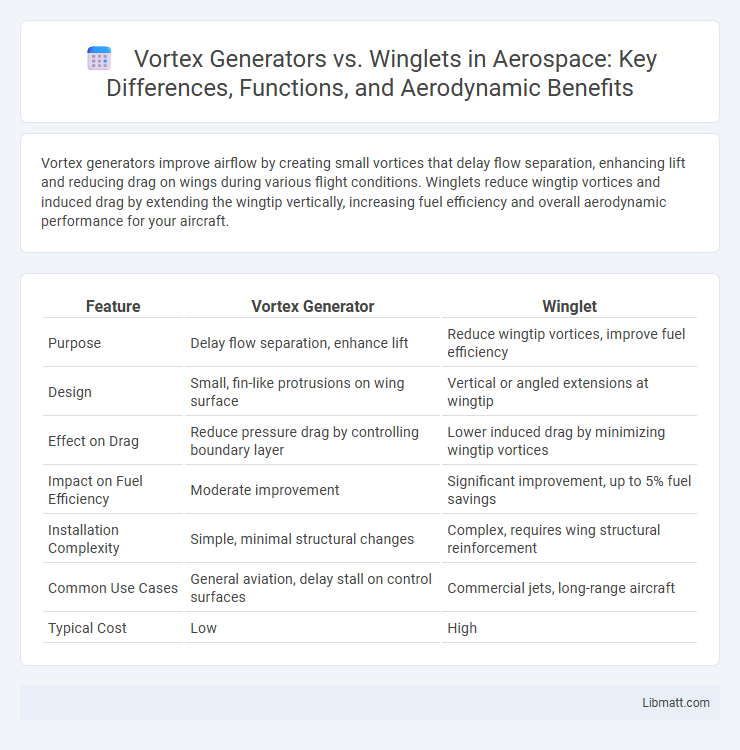
| Feature | Vortex Generator | Winglet |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Delay flow separation, enhance lift | Reduce wingtip vortices, improve fuel efficiency |
| Design | Small, fin-like protrusions on wing surface | Vertical or angled extensions at wingtip |
| Effect on Drag | Reduce pressure drag by controlling boundary layer | Lower induced drag by minimizing wingtip vortices |
| Impact on Fuel Efficiency | Moderate improvement | Significant improvement, up to 5% fuel savings |
| Installation Complexity | Simple, minimal structural changes | Complex, requires wing structural reinforcement |
| Common Use Cases | General aviation, delay stall on control surfaces | Commercial jets, long-range aircraft |
| Typical Cost | Low | High |
Introduction to Vortex Generators and Winglets
Vortex generators are small aerodynamic devices installed on aircraft wings to delay flow separation and improve lift by creating controlled vortices. Winglets, on the other hand, are vertical or angled extensions at the wingtips designed to reduce wingtip vortices and decrease drag, enhancing fuel efficiency. Understanding the differences between vortex generators and winglets can help optimize your aircraft's aerodynamic performance.
Fundamental Differences Between Vortex Generators and Winglets
Vortex generators are small aerodynamic devices installed on aircraft wings or surfaces to delay flow separation by creating controlled vortices, improving lift and control at low speeds. Winglets are vertical or angled extensions at the wingtips designed to reduce wingtip vortices, decreasing induced drag and enhancing fuel efficiency during cruise. While vortex generators primarily manage boundary layer behavior for better stability, winglets focus on minimizing drag to boost overall aerodynamic performance.
How Vortex Generators Work: Principles and Benefits
Vortex generators work by creating small, controlled vortices that energize the boundary layer of airflow over a wing or surface, delaying flow separation and reducing drag. These aerodynamic devices improve lift and stability by enhancing airflow attachment, which boosts fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance. Your aircraft can benefit from vortex generators through improved control at low speeds and increased operational safety.
The Functionality of Winglets: Aerodynamic Advantages
Winglets reduce induced drag by redirecting wingtip vortices, improving lift-to-drag ratio and fuel efficiency in aircraft. By smoothing airflow around the wingtip, winglets enhance stability and reduce turbulence, leading to better aerodynamic performance. These aerodynamic advantages contribute to increased range and lower operational costs for airlines.
Comparative Analysis: Vortex Generator vs Winglet
Vortex generators and winglets both enhance aerodynamic efficiency but target different airflow challenges; vortex generators control boundary layer separation by creating small vortices that increase surface airflow attachment, improving lift and control at low speeds. Winglets reduce wingtip vortices, thereby decreasing induced drag and improving fuel efficiency and range for aircraft. Comparing their application, vortex generators are more common on control surfaces and low-speed aircraft, while winglets are integral to high-speed commercial and long-range aircraft designs for maximizing cruise efficiency.
Applications in Aviation: Where Each Is Used
Vortex generators are commonly used on aircraft wings and control surfaces to improve airflow, delay flow separation, and enhance lift at low speeds, benefiting commercial airliners, fighter jets, and general aviation. Winglets are primarily installed at the wingtips of commercial and business jets to reduce induced drag, improve fuel efficiency, and increase range by minimizing wingtip vortices. Your choice between vortex generators and winglets depends on specific aerodynamic goals and aircraft types, with vortex generators focusing on improved control and stall characteristics while winglets target overall fuel savings and performance.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency and Aircraft Performance
Vortex generators and winglets both enhance aircraft fuel efficiency and performance, but they do so through different aerodynamic mechanisms. Vortex generators improve airflow by delaying boundary layer separation, which reduces drag and enhances lift, leading to better fuel economy during various flight phases. Winglets reduce wingtip vortices and induced drag, significantly lowering fuel consumption during cruise and increasing overall aircraft range and stability.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Vortex generators typically require simpler installation with minimal structural modifications, making them cost-effective for retrofit applications. Winglets demand precise aerodynamic integration and structural reinforcement, leading to higher installation complexity and maintenance needs. Both components necessitate regular inspections, but winglets often involve greater upkeep due to their size and exposure to operational stresses.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Vortex Generators vs Winglets
Vortex generators typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to winglets while providing effective drag reduction and improved airflow control on aircraft surfaces. Winglets, although more expensive to install, deliver significant fuel savings and enhanced aerodynamic efficiency over long-term operation, often justifying their higher initial investment through reduced operational costs. The cost-benefit analysis favors vortex generators for short-term or smaller aircraft applications, whereas winglets provide greater returns for commercial aviation with extended flight durations.
Future Trends in Aircraft Aerodynamics
Future trends in aircraft aerodynamics emphasize the integration of vortex generators and winglets to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce drag. Advanced vortex generators enhance boundary layer control by delaying flow separation, while winglets improve lift-to-drag ratios by minimizing wingtip vortices. Emerging technologies focus on adaptive winglets with morphing capabilities and micro-scale vortex generators that dynamically adjust to flight conditions for improved aerodynamic performance.
vortex generator vs winglet Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com