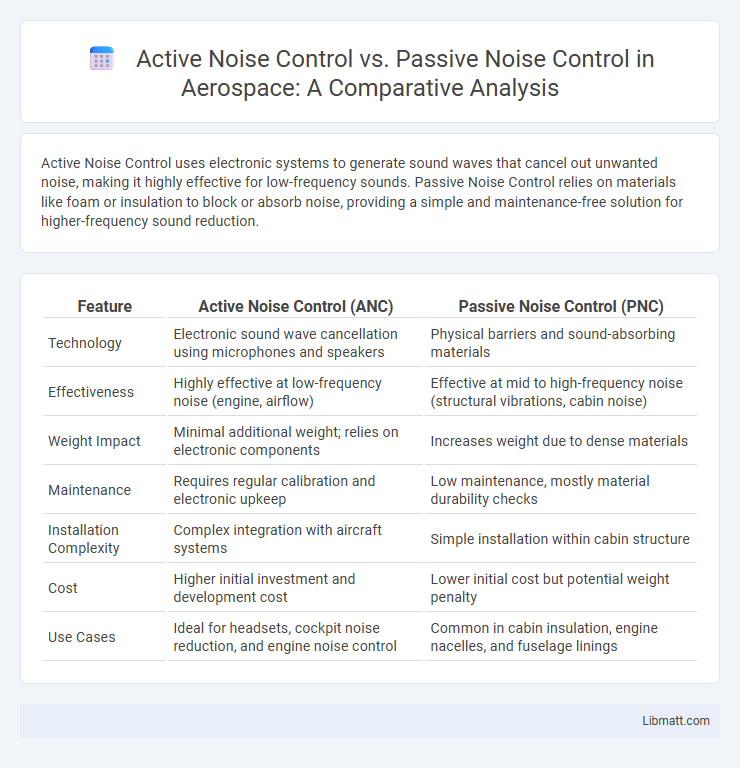
Active Noise Control uses electronic systems to generate sound waves that cancel out unwanted noise, making it highly effective for low-frequency sounds. Passive Noise Control relies on materials like foam or insulation to block or absorb noise, providing a simple and maintenance-free solution for higher-frequency sound reduction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Active Noise Control (ANC) | Passive Noise Control (PNC) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Electronic sound wave cancellation using microphones and speakers | Physical barriers and sound-absorbing materials |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective at low-frequency noise (engine, airflow) | Effective at mid to high-frequency noise (structural vibrations, cabin noise) |
| Weight Impact | Minimal additional weight; relies on electronic components | Increases weight due to dense materials |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and electronic upkeep | Low maintenance, mostly material durability checks |
| Installation Complexity | Complex integration with aircraft systems | Simple installation within cabin structure |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and development cost | Lower initial cost but potential weight penalty |
| Use Cases | Ideal for headsets, cockpit noise reduction, and engine noise control | Common in cabin insulation, engine nacelles, and fuselage linings |
Introduction to Noise Control Techniques
Active Noise Control (ANC) uses electronic systems with microphones and speakers to generate counteracting sound waves that reduce unwanted noise, making it highly effective for low-frequency sounds. Passive Noise Control involves physical barriers like insulation, acoustic panels, or earplugs that block or absorb sound waves, excelling in high-frequency noise reduction without requiring power sources. Your choice between ANC and passive methods depends on the noise type, environment, and desired level of noise attenuation for optimal hearing comfort.
What is Active Noise Control?
Active Noise Control (ANC) is a technology that reduces unwanted sound by emitting sound waves with opposite phase to the noise, effectively canceling it out through destructive interference. It relies on microphones to detect ambient noise, digital signal processors to analyze the sound, and speakers to generate anti-noise signals in real time. ANC is commonly used in headphones, automotive cabins, and industrial environments to enhance sound quality and reduce acoustic disturbances.
What is Passive Noise Control?
Passive Noise Control (PNC) involves the use of physical barriers or materials to block or absorb sound waves, effectively reducing noise through insulation, vibration damping, or soundproofing. Common examples include acoustic panels, foam, heavy curtains, and double-glazed windows that prevent sound transmission by reflecting or absorbing noise frequencies. PNC is highly effective at mitigating high-frequency sounds without the need for electronic components, making it a simple and maintenance-free noise reduction solution.
Core Principles of Active vs Passive Noise Control
Active noise control uses electro-acoustic systems that generate anti-phase sound waves to cancel out unwanted noise, effectively reducing low-frequency sounds. Passive noise control relies on physical barriers or materials like foam, fiberglass, or heavy curtains to absorb or block sound waves, primarily targeting mid to high-frequency noise. Both methods differ fundamentally, with active control focusing on sound wave interference and passive control emphasizing sound absorption and attenuation.
Effectiveness in Different Environments
Active Noise Control (ANC) excels in reducing low-frequency noise in controlled environments such as aircraft cabins and office spaces, using sound waves to cancel unwanted noise. Passive Noise Control (PNC) performs better at blocking high-frequency sounds in dynamic settings like construction sites or urban streets, relying on physical barriers and insulation materials. Effectiveness varies as ANC adapts to changing noise patterns, while PNC provides consistent attenuation regardless of environmental changes.
Advantages of Active Noise Control
Active Noise Control (ANC) effectively reduces low-frequency noise by generating inverse sound waves that cancel incoming unwanted sounds, making it ideal for environments like aircraft cabins and open office spaces. Unlike Passive Noise Control, which relies on physical barriers and materials to block sound, ANC offers lightweight, adaptable, and energy-efficient solutions without increasing bulk or weight. This adaptability enables enhanced user comfort and clearer audio experiences in headphones and automotive applications where passive methods fall short.
Benefits of Passive Noise Control
Passive Noise Control offers benefits such as requiring no power source, making it highly reliable and maintenance-free. It effectively reduces a broad spectrum of noise frequencies using materials like foam, fiberglass, and mass-loaded vinyl. This method excels in environments where consistent noise blocking is needed without electronic intervention.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Approach
Active Noise Control (ANC) faces limitations such as reduced effectiveness at higher frequencies, increased complexity, and higher power consumption due to its reliance on electronic components and sensors. Passive Noise Control (PNC) often struggles with bulky materials and limited attenuation of low-frequency sounds, posing challenges in achieving lightweight and space-efficient solutions. Understanding these trade-offs helps you select the best noise reduction method based on your specific environmental and practical needs.
Applications: When to Choose Active or Passive
Active Noise Control suits environments with consistent, low-frequency noise like HVAC systems or airplane cabins, providing adaptive sound cancellation using electronic sensors and speakers. Passive Noise Control is ideal for high-frequency noise or settings with one-time or unpredictable sounds, relying on insulation, barriers, or materials to block or absorb sound waves. Your choice depends on the noise frequency and variability, with Active offering dynamic cancellation and Passive delivering static, maintenance-free noise reduction.
Future Trends in Noise Control Technology
Active Noise Control (ANC) technology rapidly advances with innovations in adaptive algorithms, machine learning, and miniaturized sensors enhancing real-time noise cancellation across various environments. Passive Noise Control relies on improved materials such as meta-materials and acoustic foams engineered to block or absorb sound more effectively in construction and personal protective equipment. The future of noise control integrates hybrid systems combining ANC and advanced passive materials, enabling smarter, energy-efficient, and highly customizable noise mitigation solutions for industrial, automotive, and consumer applications.
Active Noise Control vs Passive Noise Control Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com