Anti-icing prevents ice from forming on surfaces by applying chemicals or treatments before freezing conditions occur, helping maintain safety and functionality. De-icing removes existing ice using methods like heating or chemical agents, ensuring surfaces are clear and safe after ice has already accumulated.
Table of Comparison
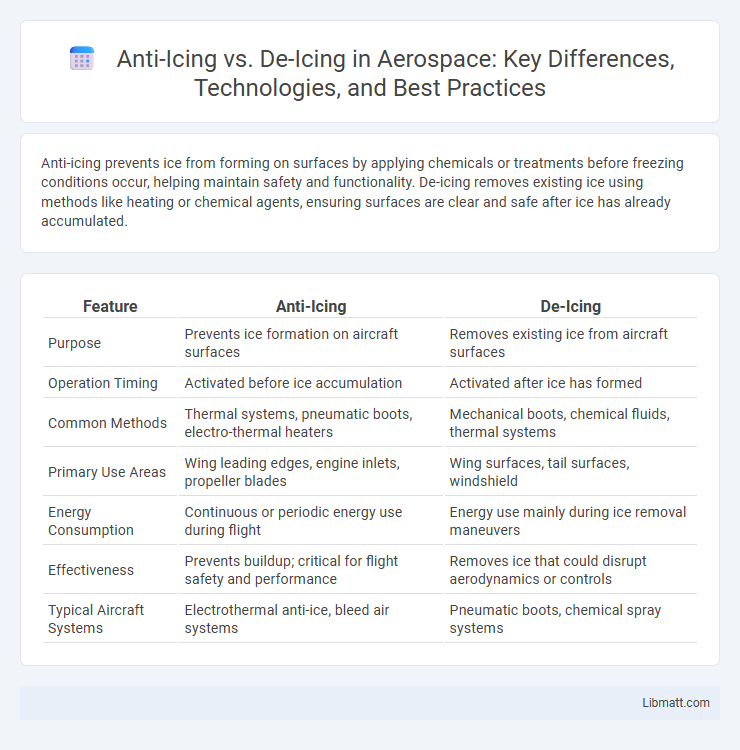
| Feature | Anti-Icing | De-Icing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents ice formation on aircraft surfaces | Removes existing ice from aircraft surfaces |
| Operation Timing | Activated before ice accumulation | Activated after ice has formed |
| Common Methods | Thermal systems, pneumatic boots, electro-thermal heaters | Mechanical boots, chemical fluids, thermal systems |
| Primary Use Areas | Wing leading edges, engine inlets, propeller blades | Wing surfaces, tail surfaces, windshield |
| Energy Consumption | Continuous or periodic energy use during flight | Energy use mainly during ice removal maneuvers |
| Effectiveness | Prevents buildup; critical for flight safety and performance | Removes ice that could disrupt aerodynamics or controls |
| Typical Aircraft Systems | Electrothermal anti-ice, bleed air systems | Pneumatic boots, chemical spray systems |
Introduction to Anti-Icing and De-Icing
Anti-icing involves applying chemicals or coatings to prevent ice formation on surfaces, commonly used in aviation and road safety to enhance operational efficiency and reduce hazards. De-icing refers to the removal of existing ice using methods such as heated fluids, mechanical scraping, or chemical agents, essential for restoring functionality and safety. Understanding the distinction between anti-icing and de-icing is critical for selecting appropriate strategies in weather-sensitive industries.
Understanding the Science Behind Ice Formation
Ice formation occurs when water molecules freeze on surfaces, creating hazardous conditions that affect safety and performance. Anti-icing prevents ice by applying chemical agents or heating elements before ice forms, maintaining surface integrity and visibility. De-icing removes already formed ice through mechanical, chemical, or thermal methods, ensuring your equipment or vehicles remain operational in freezing conditions.
What is Anti-Icing? Definitions and Methods
Anti-icing refers to the proactive process of preventing ice formation on surfaces such as aircraft wings, roads, and power lines by applying specialized fluids or coatings before conditions reach freezing. Common methods include the use of glycol-based anti-icing fluids in aviation, heated pavement systems on roads, and hydrophobic coatings that inhibit ice adhesion. This technique differs from de-icing, which involves removing ice after it has formed, emphasizing prevention to enhance safety and operational efficiency.
What is De-Icing? Techniques and Applications
De-icing involves the removal of ice and frost from surfaces after accumulation, typically using chemical agents like glycol-based fluids or mechanical methods such as scraping and heating systems. Techniques include spraying de-icing chemicals on aircraft wings before takeoff or using heated pavement systems on roads to melt ice, ensuring safety and operational efficiency. Your choice of de-icing method depends on the surface type, environmental conditions, and urgency for ice removal.
Key Differences Between Anti-Icing and De-Icing
Anti-icing prevents ice from forming on surfaces by applying chemicals or materials before ice buildup occurs, while de-icing removes ice that has already formed, typically using mechanical methods or chemical agents. Anti-icing enhances safety and efficiency by maintaining ice-free conditions, whereas de-icing requires more effort and resources to restore safe conditions after ice accumulation. Your choice between anti-icing and de-icing depends on timing, effectiveness, and the specific environment you need to manage.
Pros and Cons of Anti-Icing Solutions
Anti-icing solutions prevent ice formation on surfaces by applying chemicals before freezing conditions occur, reducing the risk of hazardous ice buildup and enhancing safety. These methods provide long-lasting protection and reduce the frequency of maintenance, but they often involve higher upfront costs and potential environmental concerns due to chemical runoff. Balancing efficiency with environmental impact, selecting the appropriate anti-icing agent is crucial for effective and sustainable ice management.
Pros and Cons of De-Icing Methods
De-icing methods effectively remove ice accumulation from surfaces like aircraft wings, runways, and roads, ensuring safety and functionality in icy conditions. Common techniques include chemical deicers, mechanical removal, and thermal systems, each offering quick ice clearance but varying in environmental impact, cost, and equipment wear. Your choice of de-icing method should balance efficiency, potential corrosion, environmental effects, and operational feasibility to maintain optimal safety and sustainability.
Industry Applications: Roadways, Aviation, and Beyond
Anti-icing systems prevent ice formation on surfaces such as roadways and aircraft wings by applying chemical agents or heating elements before freezing conditions occur, thereby enhancing safety and operational efficiency. De-icing methods involve removing existing ice using mechanical, chemical, or thermal techniques, critical for maintaining functional surfaces in aviation runways and transportation infrastructure. Beyond transportation, industries like power transmission and wind energy also rely on anti-icing and de-icing technologies to protect equipment and ensure continuous performance in cold environments.
Environmental Impacts of Anti-Icing vs De-Icing
Anti-icing techniques prevent ice formation by applying chemicals before freezing conditions, reducing the overall amount of de-icing agents released into the environment, which minimizes soil and water contamination. De-icing involves removing existing ice with chemical agents that can lead to higher concentrations of chlorides and other pollutants, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems and vegetation. Your choice of anti-icing methods can support sustainable environmental management by lowering chemical usage and mitigating long-term ecological damage.
Choosing the Right Ice Management Strategy
Selecting the appropriate ice management strategy requires understanding the fundamental difference between anti-icing and de-icing methods. Anti-icing prevents ice formation through proactive measures like applying liquid chemicals before freezing conditions, enhancing road safety and reducing labor costs. De-icing involves removing ice after it forms, typically using mechanical means or chemical agents, which can be less efficient and more resource-intensive.
anti-icing vs de-icing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com