Color fastness refers to the resistance of a fabric or material to fading or running when exposed to washing, rubbing, or perspiration, while light fastness measures how well a color withstands exposure to sunlight or artificial light without fading. Your choice of materials should consider both properties to ensure long-lasting vibrancy in different environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
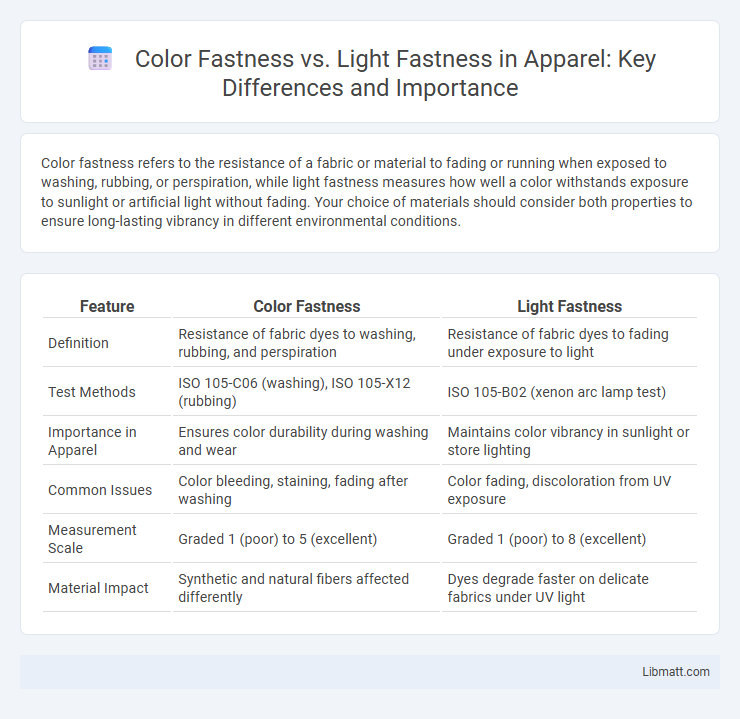
| Feature | Color Fastness | Light Fastness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Resistance of fabric dyes to washing, rubbing, and perspiration | Resistance of fabric dyes to fading under exposure to light |
| Test Methods | ISO 105-C06 (washing), ISO 105-X12 (rubbing) | ISO 105-B02 (xenon arc lamp test) |
| Importance in Apparel | Ensures color durability during washing and wear | Maintains color vibrancy in sunlight or store lighting |
| Common Issues | Color bleeding, staining, fading after washing | Color fading, discoloration from UV exposure |
| Measurement Scale | Graded 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent) | Graded 1 (poor) to 8 (excellent) |
| Material Impact | Synthetic and natural fibers affected differently | Dyes degrade faster on delicate fabrics under UV light |
Introduction to Color Fastness and Light Fastness
Color fastness refers to a material's ability to retain its color when exposed to various conditions such as washing, rubbing, or perspiration, ensuring durability and appearance over time. Light fastness specifically measures how well a color withstands exposure to light, preventing fading or discoloration caused by sunlight or artificial lighting. Your choice of textiles or dyes should consider both color fastness and light fastness to maintain vibrant and long-lasting colors in different environments.
Defining Color Fastness
Color fastness refers to a textile or dye's resistance to fading or running when exposed to various conditions such as washing, rubbing, or perspiration. It measures how well a material maintains its original color under mechanical and chemical stress, ensuring durability during everyday use. Unlike light fastness, which specifically assesses resistance to fading caused by exposure to light, color fastness encompasses a broader range of environmental factors affecting color stability.
Understanding Light Fastness
Light fastness refers to a material's ability to resist fading or discoloration when exposed to light, especially sunlight or ultraviolet rays. This property is crucial for fabrics, inks, and paints as it determines the longevity of colors under natural or artificial light conditions. Understanding light fastness helps you select materials that maintain vibrant colors over time, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal.
Key Differences Between Color Fastness and Light Fastness
Color fastness measures a material's resistance to fading or running when exposed to various conditions such as washing, rubbing, or perspiration, whereas light fastness specifically evaluates the durability of color when exposed to light, especially ultraviolet rays. Color fastness tests involve multiple factors including washing, crocking, and perspiration, while light fastness is assessed through controlled light exposure tests like the Blue Wool Scale. Understanding these key differences ensures appropriate selection of dyes and materials for products intended for specific environmental exposures.
Factors Affecting Color Fastness
Color fastness is primarily influenced by the type of dye or pigment, the fabric or material used, and the application method, determining how well the color resists washing, rubbing, and perspiration. Light fastness depends largely on the chemical stability of the dye when exposed to ultraviolet and visible light, as well as environmental factors like temperature and humidity during exposure. Both properties are affected by fabric treatments, presence of antioxidants or UV absorbers, and the duration and intensity of exposure to stressors.
Factors Influencing Light Fastness
Light fastness is influenced by factors such as the chemical structure of the dye, the presence of UV stabilizers, and the type of fiber or fabric used. Exposure to sunlight and environmental pollutants also plays a critical role in the degradation rate of color under light. Understanding these factors helps you select materials and treatments that enhance the durability of colors in outdoor or well-lit conditions.
Testing Methods for Color Fastness
Testing methods for color fastness primarily involve standardized procedures such as ISO 105 and AATCC test methods, which evaluate a fabric's resistance to fading or running during washing, rubbing, and exposure to light. Light fastness is specifically measured through exposure to xenon arc lamps or UV light sources for set durations, assessing color retention against a gray scale. Your choice of testing ensures accurate prediction of durability and performance of textiles under various environmental conditions.
Measuring Light Fastness: Standard Procedures
Measuring light fastness involves standardized tests such as the Blue Wool Scale and Xenon Arc testing to evaluate a material's resistance to fading under light exposure. These procedures expose textile samples to controlled light sources simulating natural sunlight, assessing color durability based on changes in color strength or hue. Accurate measurement of light fastness ensures the longevity and quality of fabrics in various lighting conditions, distinguishing it from color fastness tests that focus on resistance to washing, rubbing, or perspiration.
Importance in Textile and Dye Selection
Color fastness and light fastness are critical factors in textile and dye selection because they determine the durability and appearance retention of fabrics over time. High color fastness ensures resistance to washing, rubbing, and perspiration, maintaining vibrant hues during use. Light fastness measures a dye's ability to withstand fading when exposed to sunlight, crucial for textiles used in outdoor environments or areas with intense lighting.
Enhancing Fastness Properties in Fabrics
Enhancing fastness properties in fabrics involves improving both color fastness and light fastness to ensure durability and resistance to fading. Techniques such as applying UV-resistant coatings, using high-quality dyes with strong chemical bonding, and incorporating anti-oxidants can significantly boost light fastness, preventing color degradation under sunlight exposure. Optimizing dye-fiber interactions through reactive or vat dyeing processes increases color fastness, maintaining vibrant hues despite washing, rubbing, and perspiration.
color fastness vs light fastness Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com