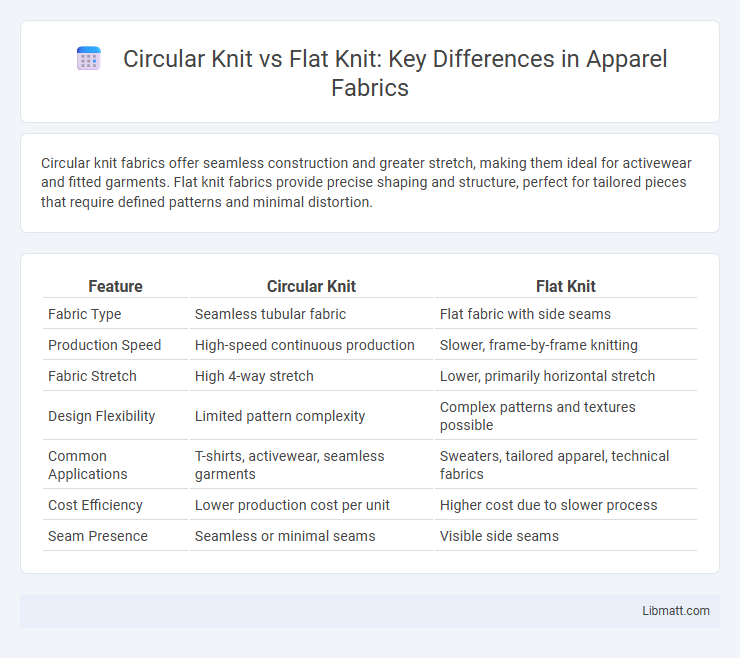
Circular knit fabrics offer seamless construction and greater stretch, making them ideal for activewear and fitted garments. Flat knit fabrics provide precise shaping and structure, perfect for tailored pieces that require defined patterns and minimal distortion.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Circular Knit | Flat Knit |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric Type | Seamless tubular fabric | Flat fabric with side seams |
| Production Speed | High-speed continuous production | Slower, frame-by-frame knitting |
| Fabric Stretch | High 4-way stretch | Lower, primarily horizontal stretch |
| Design Flexibility | Limited pattern complexity | Complex patterns and textures possible |
| Common Applications | T-shirts, activewear, seamless garments | Sweaters, tailored apparel, technical fabrics |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower production cost per unit | Higher cost due to slower process |
| Seam Presence | Seamless or minimal seams | Visible side seams |
Introduction to Circular Knit and Flat Knit
Circular knit fabric is created by a continuous circular knitting machine producing a seamless tube ideal for garments like t-shirts and socks, offering stretch and comfort. Flat knit fabric is made on flat knitting machines that produce panels with distinct edges, enabling more intricate patterns and shapes, commonly used in sweaters and tailored clothing. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right knit for your apparel needs, balancing fit, design complexity, and production efficiency.
Key Differences Between Circular and Flat Knitting
Circular knitting produces seamless, tubular fabric ideal for garments like t-shirts and socks, while flat knitting creates flat pieces that require stitching to form shapes. Your choice depends on project needs; circular knitting offers faster production and elasticity, whereas flat knitting allows for more complex patterns and shaping. Understanding these key differences helps optimize fabric construction for durability, comfort, and design precision.
Manufacturing Processes: Circular vs Flat Knit
Circular knit manufacturing uses a continuous, tubular process where yarns form seamless tubes of fabric ideal for seamless garments and stretchy applications. Flat knit manufacturing involves linear needles that produce flat pieces of fabric, allowing for more complex patterns and shapes with minimal waste in tailored designs. Circular knitting machines typically operate faster for mass production, while flat knitting machines excel in customization and intricate stitch patterns.
Fabric Structure and Appearance
Circular knit fabric has a seamless, tubular structure created by knitting in a continuous round, resulting in a smooth, uniform appearance ideal for stretch and flexibility. Flat knit fabric is produced by knitting rows back and forth on a flat needle bed, creating a fabric with edges that can be cut and sewn, offering more intricate patterns and a structured look. Your choice between circular and flat knit depends on the desired fabric texture, stretch, and garment construction needs.
Common Applications of Circular Knit Fabrics
Circular knit fabrics are widely used in activewear, casual apparel, and hosiery due to their stretchability and seamless construction. Their ability to provide comfort and fit makes them ideal for t-shirts, leggings, and underwear. The seamless nature also reduces production time and material waste, enhancing efficiency in mass-market clothing manufacturing.
Typical Uses of Flat Knit Fabrics
Flat knit fabrics are commonly used for tailored garments such as sweaters, cardigans, and scarves, where precise shaping and patterning are essential. Their construction allows for greater control over stitch tension and intricate designs, making them ideal for custom fits and high-quality fashion pieces. You will find flat knit fabrics favored in applications requiring durability and detailed texture, especially in luxury apparel and accessories.
Advantages of Circular Knitting
Circular knitting offers seamless tubular fabric production, enhancing comfort and reducing garment assembly time. This technique allows for faster manufacturing speeds and greater fabric elasticity compared to flat knitting. Your investment in circular knitting can lead to cost-effective, high-quality apparel with minimal waste.
Benefits of Flat Knitting
Flat knitting offers precise control over fabric shape and tension, enabling complex patterns and customized garment fitting. This method reduces material waste by producing panels that can be seamlessly assembled, enhancing sustainability and cost-efficiency. Flat knitting machines also allow for faster prototyping and easier design adjustments, making them ideal for high-quality, tailored apparel production.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Knit Type
Choosing between circular knit and flat knit involves considering factors such as stretchability, garment shape, and production speed. Circular knits offer seamless construction ideal for stretchy, tubular garments, while flat knits provide versatility in design with defined edges suitable for structured shapes. Your decision should align with the desired fit, fabric behavior, and manufacturing requirements to optimize comfort and style.
Future Trends in Knitting Technology
Advancements in circular knit technology are driving future trends with greater efficiency, seamless garment construction, and enhanced fabric elasticity, making it ideal for activewear and smart textiles. Flat knit machines are evolving with increased automation and precision control, enabling complex patterns, customization, and integration of technical fibers for performance and sustainability. Innovations in hybrid knitting techniques are emerging, combining circular and flat knit benefits to optimize production speed, fabric versatility, and material conservation.
Circular knit vs flat knit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com